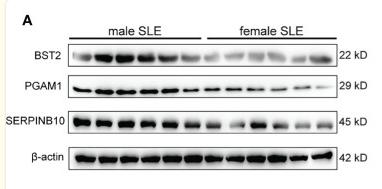
BST2 Antibody - #DF3846
| Product: | BST2 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF3846 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to BST2 |
| Application: | WB IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 22 KD; 20kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q10589 |
| RRID: | AB_2836203 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF3846, RRID:AB_2836203.
Fold/Unfold
Bone marrow stromal antigen 2; Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2; Bone marrow stromal cell antigen; BST 2; BST-2; BST2; BST2_HUMAN; CD 317; CD317; CD317 antigen; HM1.24 antigen; NPC A 7; Tetherin;
Immunogens
Predominantly expressed in liver, lung, heart and placenta. Lower levels in pancreas, kidney, skeletal muscle and brain. Overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells. Highly expressed during B-cell development, from pro-B precursors to plasma cells. Highly expressed on T-cells, monocytes, NK cells and dendritic cells (at protein level).
- Q10589 BST2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MASTSYDYCRVPMEDGDKRCKLLLGIGILVLLIIVILGVPLIIFTIKANSEACRDGLRAVMECRNVTHLLQQELTEAQKGFQDVEAQAATCNHTVMALMASLDAEKAQGQKKVEELEGEITTLNHKLQDASAEVERLRRENQVLSVRIADKKYYPSSQDSSSAAAPQLLIVLLGLSALLQ
PTMs - Q10589 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| T4 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y6 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y8 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K18 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| N65 | N-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| N92 | N-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| K112 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K112 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T121 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| T122 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| K126 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S131 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| S131 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K151 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
IFN-induced antiviral host restriction factor which efficiently blocks the release of diverse mammalian enveloped viruses by directly tethering nascent virions to the membranes of infected cells. Acts as a direct physical tether, holding virions to the cell membrane and linking virions to each other. The tethered virions can be internalized by endocytosis and subsequently degraded or they can remain on the cell surface. In either case, their spread as cell-free virions is restricted. Its target viruses belong to diverse families, including retroviridae: human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2), simian immunodeficiency viruses (SIVs), equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV), feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV), prototype foamy virus (PFV), Mason-Pfizer monkey virus (MPMV), human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1), Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) and murine leukemia virus (MLV), flavivirideae: hepatitis C virus (HCV), filoviridae: ebola virus (EBOV) and marburg virus (MARV), arenaviridae: lassa virus (LASV) and machupo virus (MACV), herpesviridae: kaposis sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), rhabdoviridae: vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), orthomyxoviridae: influenza A virus, and paramyxoviridae: nipah virus. Can inhibit cell surface proteolytic activity of MMP14 causing decreased activation of MMP15 which results in inhibition of cell growth and migration. Can stimulate signaling by LILRA4/ILT7 and consequently provide negative feedback to the production of IFN by plasmacytoid dendritic cells in response to viral infection. Plays a role in the organization of the subapical actin cytoskeleton in polarized epithelial cells. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are both effective viral restriction factors but have differing antiviral and signaling activities. Isoform 2 is resistant to HIV-1 Vpu-mediated degradation and restricts HIV-1 viral budding in the presence of Vpu. Isoform 1 acts as an activator of NF-kappa-B and this activity is inhibited by isoform 2.
Monoubiquitinated by KSHV E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase K5, leading to its targeting to late endosomes and degradation.
The GPI anchor is essential for its antiviral activity.
Golgi apparatus>trans-Golgi network. Cell membrane>Single-pass type II membrane protein. Cell membrane>Lipid-anchor. Late endosome. Membrane raft. Cytoplasm. Apical cell membrane.
Note: Shuttles between the cell membrane, where it is present predominantly in membrane/lipid rafts, and the trans-Golgi network. HIV-1 VPU and HIV-2 ENV can target it to the trans-Golgi network thus sequestering it away from virus assembly sites on the cell membrane. Targeted to late endosomes upon KSHV infection and subsequent ubiquitination. Forms a complex with MMP14 and localizes to the cytoplasm.
Predominantly expressed in liver, lung, heart and placenta. Lower levels in pancreas, kidney, skeletal muscle and brain. Overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells. Highly expressed during B-cell development, from pro-B precursors to plasma cells. Highly expressed on T-cells, monocytes, NK cells and dendritic cells (at protein level).
Parallel homodimer; disulfide-linked. May form homotetramers under reducing conditions. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 form homodimers and also heterodimers with each other. Dimerization is essential for its antiviral activity. Interacts (via cytoplasmic domain) with ARHGAP44 (By similarity). Interacts with MMP14 (via C-terminal cytoplasmic tail). Interacts with LILRA4/ILT7. Interacts (via transmembrane domain) with HIV-1 VPU (via transmembrane domain). Interacts with HIV-2 ENV and ebola GP protein.
The extracellular coiled coil domain forms an extended 170 A long semi-flexible rod-like structure important for virion retention at the cell surface and prevention of virus spreading.
Belongs to the tetherin family.
References
Application: WB Species: Human Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.