ADCY5/6 Antibody - #DF3508
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF3508, RRID:AB_2835870.
Fold/Unfold
AC 5; AC5; ADCY 5; Adcy5; ADCY5_HUMAN; Adenylate cyclase type 5; Adenylate cyclase type V; Adenylyl cyclase 5; ATP pyrophosphate lyase 5; ATP pyrophosphate-lyase 5; AC6; ACVI; ADCY 6; Adcy6; ADCY6_HUMAN; ADCYB; Adenylate cyclase 6; Adenylate cyclase type 6; Adenylate cyclase type VI; Adenylyl cyclase 6; ATP pyrophosphate lyase 6; ATP pyrophosphate-lyase 6; Ca(2+) inhibitable adenylyl cyclase; Ca(2+)-inhibitable adenylyl cyclase; DKFZp779F075; EC 4.6.1.1; KIAA0422;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human ADCY5/6, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Detected in pancreas islets (at protein level). Detected in pancreas islets.
O43306 ADCY6_HUMAN:Detected in peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:17916776). Detected in thyroid (PubMed:10978539).
- O95622 ADCY5_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSGSKSVSPPGYAAQKTAAPAPRGGPEHRSAWGEADSRANGYPHAPGGSARGSTKKPGGAVTPQQQQRLASRWRSDDDDDPPLSGDDPLAGGFGFSFRSKSAWQERGGDDCGRGSRRQRRGAASGGSTRAPPAGGGGGSAAAAASAGGTEVRPRSVEVGLEERRGKGRAADELEAGAVEGGEGSGDGGSSADSGSGAGPGAVLSLGACCLALLQIFRSKKFPSDKLERLYQRYFFRLNQSSLTMLMAVLVLVCLVMLAFHAARPPLQLPYLAVLAAAVGVILIMAVLCNRAAFHQDHMGLACYALIAVVLAVQVVGLLLPQPRSASEGIWWTVFFIYTIYTLLPVRMRAAVLSGVLLSALHLAIALRTNAQDQFLLKQLVSNVLIFSCTNIVGVCTHYPAEVSQRQAFQETRECIQARLHSQRENQQQERLLLSVLPRHVAMEMKADINAKQEDMMFHKIYIQKHDNVSILFADIEGFTSLASQCTAQELVMTLNELFARFDKLAAENHCLRIKILGDCYYCVSGLPEARADHAHCCVEMGMDMIEAISLVREVTGVNVNMRVGIHSGRVHCGVLGLRKWQFDVWSNDVTLANHMEAGGKAGRIHITKATLNYLNGDYEVEPGCGGERNAYLKEHSIETFLILRCTQKRKEEKAMIAKMNRQRTNSIGHNPPHWGAERPFYNHLGGNQVSKEMKRMGFEDPKDKNAQESANPEDEVDEFLGRAIDARSIDRLRSEHVRKFLLTFREPDLEKKYSKQVDDRFGAYVACASLVFLFICFVQITIVPHSIFMLSFYLTCSLLLTLVVFVSVIYSCVKLFPSPLQTLSRKIVRSKMNSTLVGVFTITLVFLAAFVNMFTCNSRDLLGCLAQEHNISASQVNACHVAESAVNYSLGDEQGFCGSPWPNCNFPEYFTYSVLLSLLACSVFLQISCIGKLVLMLAIELIYVLIVEVPGVTLFDNADLLVTANAIDFFNNGTSQCPEHATKVALKVVTPIIISVFVLALYLHAQQVESTARLDFLWKLQATEEKEEMEELQAYNRRLLHNILPKDVAAHFLARERRNDELYYQSCECVAVMFASIANFSEFYVELEANNEGVECLRLLNEIIADFDEIISEDRFRQLEKIKTIGSTYMAASGLNDSTYDKVGKTHIKALADFAMKLMDQMKYINEHSFNNFQMKIGLNIGPVVAGVIGARKPQYDIWGNTVNVASRMDSTGVPDRIQVTTDMYQVLAANTYQLECRGVVKVKGKGEMMTYFLNGGPPLS
- O43306 ADCY6_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSWFSGLLVPKVDERKTAWGERNGQKRSRRRGTRAGGFCTPRYMSCLRDAEPPSPTPAGPPRCPWQDDAFIRRGGPGKGKELGLRAVALGFEDTEVTTTAGGTAEVAPDAVPRSGRSCWRRLVQVFQSKQFRSAKLERLYQRYFFQMNQSSLTLLMAVLVLLTAVLLAFHAAPARPQPAYVALLACAAALFVGLMVVCNRHSFRQDSMWVVSYVVLGILAAVQVGGALAADPRSPSAGLWCPVFFVYIAYTLLPIRMRAAVLSGLGLSTLHLILAWQLNRGDAFLWKQLGANVLLFLCTNVIGICTHYPAEVSQRQAFQETRGYIQARLHLQHENRQQERLLLSVLPQHVAMEMKEDINTKKEDMMFHKIYIQKHDNVSILFADIEGFTSLASQCTAQELVMTLNELFARFDKLAAENHCLRIKILGDCYYCVSGLPEARADHAHCCVEMGVDMIEAISLVREVTGVNVNMRVGIHSGRVHCGVLGLRKWQFDVWSNDVTLANHMEAGGRAGRIHITRATLQYLNGDYEVEPGRGGERNAYLKEQHIETFLILGASQKRKEEKAMLAKLQRTRANSMEGLMPRWVPDRAFSRTKDSKAFRQMGIDDSSKDNRGTQDALNPEDEVDEFLSRAIDARSIDQLRKDHVRRFLLTFQREDLEKKYSRKVDPRFGAYVACALLVFCFICFIQLLIFPHSTLMLGIYASIFLLLLITVLICAVYSCGSLFPKALQRLSRSIVRSRAHSTAVGIFSVLLVFTSAIANMFTCNHTPIRSCAARMLNLTPADITACHLQQLNYSLGLDAPLCEGTMPTCSFPEYFIGNMLLSLLASSVFLHISSIGKLAMIFVLGLIYLVLLLLGPPATIFDNYDLLLGVHGLASSNETFDGLDCPAAGRVALKYMTPVILLVFALALYLHAQQVESTARLDFLWKLQATGEKEEMEELQAYNRRLLHNILPKDVAAHFLARERRNDELYYQSCECVAVMFASIANFSEFYVELEANNEGVECLRLLNEIIADFDEIISEERFRQLEKIKTIGSTYMAASGLNASTYDQVGRSHITALADYAMRLMEQMKHINEHSFNNFQMKIGLNMGPVVAGVIGARKPQYDIWGNTVNVSSRMDSTGVPDRIQVTTDLYQVLAAKGYQLECRGVVKVKGKGEMTTYFLNGGPSS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Catalyzes the formation of the signaling molecule cAMP in response to G-protein signaling. Mediates signaling downstream of ADRB1. Regulates the increase of free cytosolic Ca(2+) in response to increased blood glucose levels and contributes to the regulation of Ca(2+)-dependent insulin secretion.
Phosphorylated by RAF1.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection>Cilium.
Detected in pancreas islets (at protein level). Detected in pancreas islets.
The protein contains two modules with six transmembrane helices each; both are required for catalytic activity. Isolated N-terminal or C-terminal guanylate cyclase domains have no catalytic activity, but when they are brought together, enzyme activity is restored. The active site is at the interface of the two domains. Both contribute substrate-binding residues, but the catalytic metal ions are bound exclusively via the N-terminal guanylate cyclase domain.
Belongs to the adenylyl cyclase class-4/guanylyl cyclase family.
Catalyzes the formation of the signaling molecule cAMP downstream of G protein-coupled receptors. Functions in signaling cascades downstream of beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart and in vascular smooth muscle cells. Functions in signaling cascades downstream of the vasopressin receptor in the kidney and has a role in renal water reabsorption. Functions in signaling cascades downstream of PTH1R and plays a role in regulating renal phosphate excretion. Functions in signaling cascades downstream of the VIP and SCT receptors in pancreas and contributes to the regulation of pancreatic amylase and fluid secretion (By similarity). Signaling mediates cAMP-dependent activation of protein kinase PKA. This promotes increased phosphorylation of various proteins, including AKT. Plays a role in regulating cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) uptake and storage, and is required for normal heart ventricular contractibility. May contribute to normal heart function (By similarity). Mediates vasodilatation after activation of beta-adrenergic receptors by isoproterenol. Contributes to bone cell responses to mechanical stimuli (By similarity).
Phosphorylation by RAF1 increases enzyme activity. Phosphorylation by PKA at Ser-662 inhibits the GNAS-mediated increase in catalytic activity. Phosphorylation by PKC at Ser-556, Ser-662 and Thr-919 inhibits catalytic activity.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection>Cilium. Cell projection>Stereocilium.
Detected in peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes (at protein level). Detected in thyroid.
The protein contains two modules with six transmembrane helices each; both are required for catalytic activity. Isolated N-terminal or C-terminal guanylate cyclase domains have no catalytic activity, but when they are brought together, enzyme activity is restored. The active site is at the interface of the two domains. Both contribute substrate-binding residues, but the catalytic metal ions are bound exclusively via the N-terminal guanylate cyclase domain.
Belongs to the adenylyl cyclase class-4/guanylyl cyclase family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Oocyte meiosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Gap junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Phospholipase D signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Parkinson's disease.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Cocaine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Amphetamine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Morphine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Alcoholism.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).
· Metabolism > Nucleotide metabolism > Purine metabolism.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Circulatory system > Vascular smooth muscle contraction. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Platelet activation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Environmental adaptation > Circadian entrainment.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Glutamatergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Cholinergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Serotonergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > GABAergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Dopaminergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Sensory system > Taste transduction.
· Organismal Systems > Sensory system > Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin secretion. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Ovarian steroidogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Melanogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone synthesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Renin secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Aldosterone synthesis and secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Excretory system > Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption.
· Organismal Systems > Excretory system > Vasopressin-regulated water reabsorption.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Salivary secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Gastric acid secretion.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Pancreatic secretion.
References
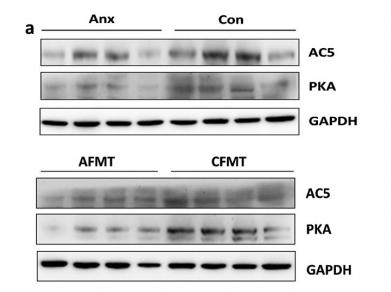
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: liver and brain
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.