Nrf2 Antibody - #AF7006
| Product: | Nrf2 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF7006 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Nrf2 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 100~120kD; 68kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q16236 |
| RRID: | AB_2835314 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF7006, RRID:AB_2835314.
Fold/Unfold
erythroid derived 2; HEBP1; like 2; NF E2 related factor 2; NF-E2-related factor 2; NF2L2_HUMAN; NFE2 related factor 2; NFE2-related factor 2; Nfe2l2; Nrf 2; NRF2; Nuclear factor (erythroid derived 2) like 2; Nuclear factor; nuclear factor erythroid 2 like 2; Nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2; Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Nuclear factor erythroid derived 2 like 2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Nrf2, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Widely expressed. Highest expression in adult muscle, kidney, lung, liver and in fetal muscle.
- Q16236 NF2L2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MMDLELPPPGLPSQQDMDLIDILWRQDIDLGVSREVFDFSQRRKEYELEKQKKLEKERQEQLQKEQEKAFFAQLQLDEETGEFLPIQPAQHIQSETSGSANYSQVAHIPKSDALYFDDCMQLLAQTFPFVDDNEVSSATFQSLVPDIPGHIESPVFIATNQAQSPETSVAQVAPVDLDGMQQDIEQVWEELLSIPELQCLNIENDKLVETTMVPSPEAKLTEVDNYHFYSSIPSMEKEVGNCSPHFLNAFEDSFSSILSTEDPNQLTVNSLNSDATVNTDFGDEFYSAFIAEPSISNSMPSPATLSHSLSELLNGPIDVSDLSLCKAFNQNHPESTAEFNDSDSGISLNTSPSVASPEHSVESSSYGDTLLGLSDSEVEELDSAPGSVKQNGPKTPVHSSGDMVQPLSPSQGQSTHVHDAQCENTPEKELPVSPGHRKTPFTKDKHSSRLEAHLTRDELRAKALHIPFPVEKIINLPVVDFNEMMSKEQFNEAQLALIRDIRRRGKNKVAAQNCRKRKLENIVELEQDLDHLKDEKEKLLKEKGENDKSLHLLKKQLSTLYLEVFSMLRDEDGKPYSPSEYSLQQTRDGNVFLVPKSKKPDVKKN
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Transcription factor that plays a key role in the response to oxidative stress: binds to antioxidant response (ARE) elements present in the promoter region of many cytoprotective genes, such as phase 2 detoxifying enzymes, and promotes their expression, thereby neutralizing reactive electrophiles. In normal conditions, ubiquitinated and degraded in the cytoplasm by the BCR(KEAP1) complex. In response to oxidative stress, electrophile metabolites inhibit activity of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, promoting nuclear accumulation of NFE2L2/NRF2, heterodimerization with one of the small Maf proteins and binding to ARE elements of cytoprotective target genes. The NFE2L2/NRF2 pathway is also activated in response to selective autophagy: autophagy promotes interaction between KEAP1 and SQSTM1/p62 and subsequent inactivation of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, leading to NFE2L2/NRF2 nuclear accumulation and expression of cytoprotective genes. May also be involved in the transcriptional activation of genes of the beta-globin cluster by mediating enhancer activity of hypersensitive site 2 of the beta-globin locus control region.
Ubiquitinated in the cytoplasm by the BCR(KEAP1) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex leading to its degradation. In response to oxidative stress, electrophile metabolites, such as sulforaphane, modify KEAP1, leading to inhibit activity of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, promoting NFE2L2/NRF2 nuclear accumulation and activity. In response to autophagy, the BCR(KEAP1) complex is inactivated (By similarity).
Phosphorylation of Ser-40 by PKC in response to oxidative stress dissociates NFE2L2 from its cytoplasmic inhibitor KEAP1, promoting its translocation into the nucleus.
Acetylation at Lys-596 and Lys-599 increases nuclear localization whereas deacetylation by SIRT1 enhances cytoplasmic presence.
Glycation impairs transcription factor activity by preventing heterodimerization with small Maf proteins. Deglycation by FN3K restores activity.
Cytoplasm>Cytosol. Nucleus.
Note: Cytosolic under unstressed conditions: ubiquitinated and degraded by the BCR(KEAP1) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex (PubMed:15601839, PubMed:21196497). Translocates into the nucleus upon induction by electrophilic agents that inactivate the BCR(KEAP1) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex (PubMed:21196497).
Widely expressed. Highest expression in adult muscle, kidney, lung, liver and in fetal muscle.
The ETGE motif, and to a lower extent the DLG motif, mediate interaction with KEAP1.
Belongs to the bZIP family. CNC subfamily.
Research Fields
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
References
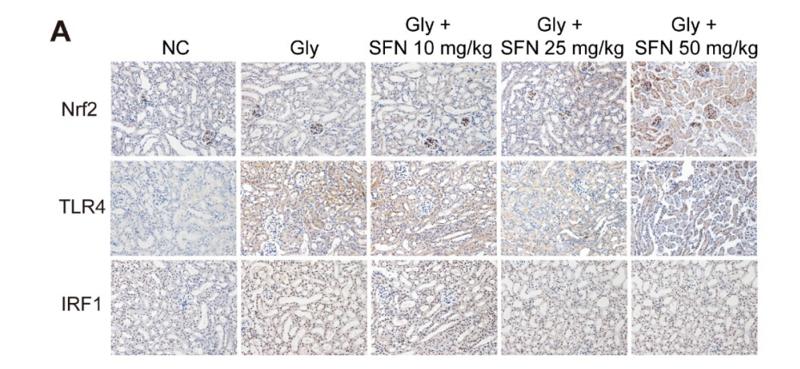
Application: IHC Species: mice Sample: tubular epithelial cells
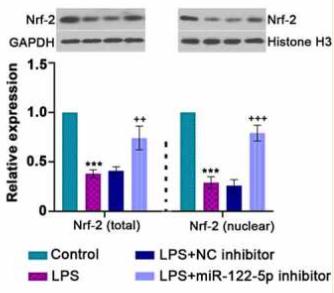
Application: WB Species: mice Sample: BMDMs
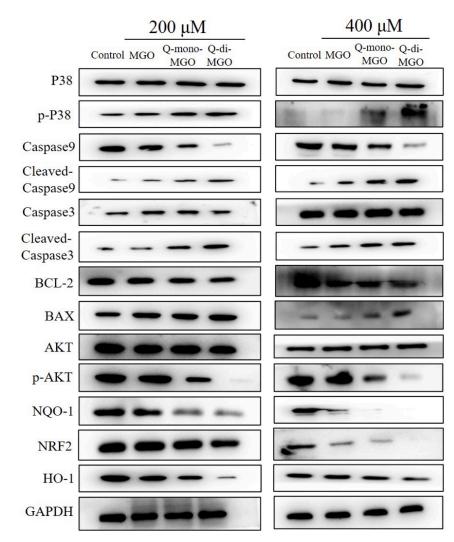
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: PC-12 cells
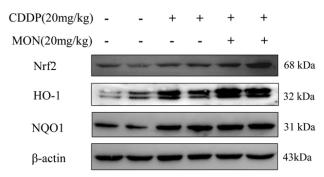
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: kidney tissue
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: liver
Application: IHC Species: mouse Sample: liver
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: RAW264.7 macrophages
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.