Estrogen Receptor-beta Antibody - #AF6469
| Product: | Estrogen Receptor-beta Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6469 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Estrogen Receptor-beta |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Horse, Sheep, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 59kDa; 59kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q92731 |
| RRID: | AB_2835288 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6469, RRID:AB_2835288.
Fold/Unfold
ER BETA; ER-beta; Erb; ESR B; ESR BETA; ESR2; ESR2_HUMAN; ESRB; ESTRB; estrogen nuclear receptor beta variant a; estrogen nuclear receptor beta variant b; estrogen receptor 2 (ER beta); Estrogen receptor 2; estrogen receptor beta 4; Estrogen receptor beta; NR3A2; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Estrogen Receptor-beta, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
Isoform 1 is expressed in testis and ovary, and at a lower level in heart, brain, placenta, liver, skeletal muscle, spleen, thymus, prostate, colon, bone marrow, mammary gland and uterus. Also found in uterine bone, breast, and ovarian tumor cell lines, but not in colon and liver tumors. Isoform 2 is expressed in spleen, thymus, testis and ovary and at a lower level in skeletal muscle, prostate, colon, small intestine, leukocytes, bone marrow, mammary gland and uterus. Isoform 4 is found in testis. Isoform 5 is expressed in testis, and at a lower level in spleen, thymus, ovary, mammary gland and uterus. Isoform 6 is expressed in testis, placenta, skeletal muscle, spleen and leukocytes, and at a lower level in heart, lung, liver, kidney, pancreas, thymus, prostate, colon, small intestine, bone marrow, mammary gland and uterus. Not expressed in brain.
- Q92731 ESR2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDIKNSPSSLNSPSSYNCSQSILPLEHGSIYIPSSYVDSHHEYPAMTFYSPAVMNYSIPSNVTNLEGGPGRQTTSPNVLWPTPGHLSPLVVHRQLSHLYAEPQKSPWCEARSLEHTLPVNRETLKRKVSGNRCASPVTGPGSKRDAHFCAVCSDYASGYHYGVWSCEGCKAFFKRSIQGHNDYICPATNQCTIDKNRRKSCQACRLRKCYEVGMVKCGSRRERCGYRLVRRQRSADEQLHCAGKAKRSGGHAPRVRELLLDALSPEQLVLTLLEAEPPHVLISRPSAPFTEASMMMSLTKLADKELVHMISWAKKIPGFVELSLFDQVRLLESCWMEVLMMGLMWRSIDHPGKLIFAPDLVLDRDEGKCVEGILEIFDMLLATTSRFRELKLQHKEYLCVKAMILLNSSMYPLVTATQDADSSRKLAHLLNAVTDALVWVIAKSGISSQQQSMRLANLLMLLSHVRHASNKGMEHLLNMKCKNVVPVYDLLLEMLNAHVLRGCKSSITGSECSPAEDSKSKEGSQNPQSQ
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Nuclear hormone receptor. Binds estrogens with an affinity similar to that of ESR1, and activates expression of reporter genes containing estrogen response elements (ERE) in an estrogen-dependent manner. Isoform beta-cx lacks ligand binding ability and has no or only very low ere binding activity resulting in the loss of ligand-dependent transactivation ability. DNA-binding by ESR1 and ESR2 is rapidly lost at 37 degrees Celsius in the absence of ligand while in the presence of 17 beta-estradiol and 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen loss in DNA-binding at elevated temperature is more gradual.
Phosphorylation at Ser-87 and Ser-105 recruits NCOA1.
Nucleus.
Isoform 1 is expressed in testis and ovary, and at a lower level in heart, brain, placenta, liver, skeletal muscle, spleen, thymus, prostate, colon, bone marrow, mammary gland and uterus. Also found in uterine bone, breast, and ovarian tumor cell lines, but not in colon and liver tumors. Isoform 2 is expressed in spleen, thymus, testis and ovary and at a lower level in skeletal muscle, prostate, colon, small intestine, leukocytes, bone marrow, mammary gland and uterus. Isoform 4 is found in testis. Isoform 5 is expressed in testis, and at a lower level in spleen, thymus, ovary, mammary gland and uterus. Isoform 6 is expressed in testis, placenta, skeletal muscle, spleen and leukocytes, and at a lower level in heart, lung, liver, kidney, pancreas, thymus, prostate, colon, small intestine, bone marrow, mammary gland and uterus. Not expressed in brain.
Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal ligand-binding domain.
Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR3 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Prolactin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
Application: WB Species: human Sample: Meg-01 cells
Application: IF/ICC Species: human Sample: Meg-01 cells
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mouse Sample: spinal cord
Application: IHC Species: Human Sample: decidua tissue
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
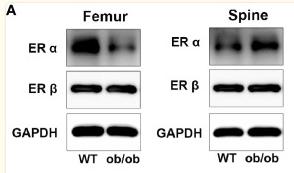
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: femoral and spine
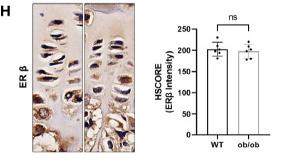
Application: IHC Species: Mice Sample: femoral and vertebral
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.