XIAP Antibody - #AF6368
| Product: | XIAP Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6368 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to XIAP |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit |
| Mol.Wt.: | 57kDa; 57kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P98170 |
| RRID: | AB_2835212 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6368, RRID:AB_2835212.
Fold/Unfold
AP 13; API3; Apoptosis Inhibitor 3; Baculoviral IAP repeat containing 4; Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing Protein 4; Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 4; BIRC 4; BIRC4; E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase XIAP; hIAP-3; hIAP3; HILP; IAP 3; IAP like protein; IAP-3; IAP-like protein; IAP3; ILP 1; ILP; ILP1; Inhibitor of apoptosis protein 3; Inhibitor of Apoptosis X Linked; Mammalian IAP Homologue A; MIHA; X linked IAP; X linked inhibitor of apoptosis; X linked inhibitor of apoptosis E3 ubiquitin protein ligase; X linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein; X-linked IAP; X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein; Xiap; XIAP_HUMAN; XLP2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human XIAP, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
- P98170 XIAP_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MTFNSFEGSKTCVPADINKEEEFVEEFNRLKTFANFPSGSPVSASTLARAGFLYTGEGDTVRCFSCHAAVDRWQYGDSAVGRHRKVSPNCRFINGFYLENSATQSTNSGIQNGQYKVENYLGSRDHFALDRPSETHADYLLRTGQVVDISDTIYPRNPAMYSEEARLKSFQNWPDYAHLTPRELASAGLYYTGIGDQVQCFCCGGKLKNWEPCDRAWSEHRRHFPNCFFVLGRNLNIRSESDAVSSDRNFPNSTNLPRNPSMADYEARIFTFGTWIYSVNKEQLARAGFYALGEGDKVKCFHCGGGLTDWKPSEDPWEQHAKWYPGCKYLLEQKGQEYINNIHLTHSLEECLVRTTEKTPSLTRRIDDTIFQNPMVQEAIRMGFSFKDIKKIMEEKIQISGSNYKSLEVLVADLVNAQKDSMQDESSQTSLQKEISTEEQLRRLQEEKLCKICMDRNIAIVFVPCGHLVTCKQCAEAVDKCPMCYTVITFKQKIFMS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Multi-functional protein which regulates not only caspases and apoptosis, but also modulates inflammatory signaling and immunity, copper homeostasis, mitogenic kinase signaling, cell proliferation, as well as cell invasion and metastasis. Acts as a direct caspase inhibitor. Directly bind to the active site pocket of CASP3 and CASP7 and obstructs substrate entry. Inactivates CASP9 by keeping it in a monomeric, inactive state. Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase regulating NF-kappa-B signaling and the target proteins for its E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity include: RIPK1, CASP3, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, MAP3K2/MEKK2, DIABLO/SMAC, AIFM1, CCS and BIRC5/survivin. Ubiquitinion of CCS leads to enhancement of its chaperone activity toward its physiologic target, SOD1, rather than proteasomal degradation. Ubiquitinion of MAP3K2/MEKK2 and AIFM1 does not lead to proteasomal degradation. Plays a role in copper homeostasis by ubiquitinationg COMMD1 and promoting its proteasomal degradation. Can also function as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase of the NEDD8 conjugation pathway, targeting effector caspases for neddylation and inactivation. Regulates the BMP signaling pathway and the SMAD and MAP3K7/TAK1 dependent pathways leading to NF-kappa-B and JNK activation. Acts as an important regulator of innate immune signaling via regulation of Nodlike receptors (NLRs). Protects cells from spontaneous formation of the ripoptosome, a large multi-protein complex that has the capability to kill cancer cells in a caspase-dependent and caspase-independent manner. Suppresses ripoptosome formation by ubiquitinating RIPK1 and CASP8. Acts as a positive regulator of Wnt signaling and ubiquitinates TLE1, TLE2, TLE3, TLE4 and AES. Ubiquitination of TLE3 results in inhibition of its interaction with TCF7L2/TCF4 thereby allowing efficient recruitment and binding of the transcriptional coactivator beta-catenin to TCF7L2/TCF4 that is required to initiate a Wnt-specific transcriptional program.
S-Nitrosylation down-regulates its E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity.
Autoubiquitinated and degraded by the proteasome in apoptotic cells.
Phosphorylation by PKB/AKT protects XIAP against ubiquitination and protects the protein against proteasomal degradation.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: TLE3 promotes its nuclear localization.
Ubiquitous, except peripheral blood leukocytes.
The first BIR domain is involved in interaction with TAB1/MAP3K7IP1 and is important for dimerization. The second BIR domain is sufficient to inhibit CASP3 and CASP7, while the third BIR is involved in CASP9 inhibition. The interactions with DIABLO/SMAC and PRSS25 are mediated by the second and third BIR domains.
Belongs to the IAP family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Necroptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Platinum drug resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: Phodopus sungorus
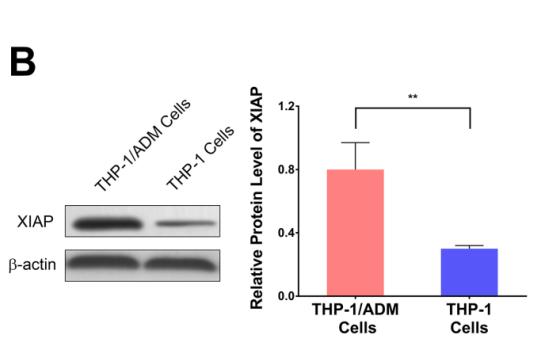
Application: WB Species: human Sample: THP-1/ADM cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.