CDC25C Antibody - #AF6258
| Product: | CDC25C Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6258 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CDC25C |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Prediction: | Horse, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 60kDa; 53kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P30307 |
| RRID: | AB_2835119 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6258, RRID:AB_2835119.
Fold/Unfold
CDC 25; Cdc 25C; CDC25; CDC25C; Cell division cycle 25 homolog C; Cell division cycle 25C; Cell division cycle 25C protein; Dual specificity phosphatase Cdc25C; M phase inducer phosphatase 3; M-phase inducer phosphatase 3; Mitosis inducer CDC25; MPIP3; MPIP3_HUMAN; Phosphotyrosine phosphatase; PPP1R60; protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 60;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CDC25C, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P30307 MPIP3_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSTELFSSTREEGSSGSGPSFRSNQRKMLNLLLERDTSFTVCPDVPRTPVGKFLGDSANLSILSGGTPKRCLDLSNLSSGEITATQLTTSADLDETGHLDSSGLQEVHLAGMNHDQHLMKCSPAQLLCSTPNGLDRGHRKRDAMCSSSANKENDNGNLVDSEMKYLGSPITTVPKLDKNPNLGEDQAEEISDELMEFSLKDQEAKVSRSGLYRSPSMPENLNRPRLKQVEKFKDNTIPDKVKKKYFSGQGKLRKGLCLKKTVSLCDITITQMLEEDSNQGHLIGDFSKVCALPTVSGKHQDLKYVNPETVAALLSGKFQGLIEKFYVIDCRYPYEYLGGHIQGALNLYSQEELFNFFLKKPIVPLDTQKRIIIVFHCEFSSERGPRMCRCLREEDRSLNQYPALYYPELYILKGGYRDFFPEYMELCEPQSYCPMHHQDHKTELLRCRSQSKVQEGERQLREQIALLVKDMSP
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Functions as a dosage-dependent inducer in mitotic control. Tyrosine protein phosphatase required for progression of the cell cycle. When phosphorylated, highly effective in activating G2 cells into prophase. Directly dephosphorylates CDK1 and activates its kinase activity.
Phosphorylated by CHEK1 and MAPK14 at Ser-216. This phosphorylation creates a binding site for 14-3-3 protein and inhibits the phosphatase. Phosphorylated by PLK4. Phosphorylated by PLK1, leading to activate the phosphatase activity. Phosphorylation by PLK3 at Ser-191 promotes nuclear translocation. Ser-198 is a minor phosphorylation site. Was initially reported to be phosphorylated by PLK3 at Ser-216. However, such phosphorylation by PLK3 was not confirmed by other groups. Phosphorylation at Thr-48, Thr-67, Ser-122, Thr-130, Ser-168 and Ser-214 occurs at G2 and G2-M transition and is probably catalyzed by CDK1. Ser-168 phosphorylation levels are lower than those at the other 5 CDK1 sites. Phosphorylation by CDK1 leads to increased activity.
Nucleus.
Belongs to the MPI phosphatase family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Oocyte meiosis. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
References
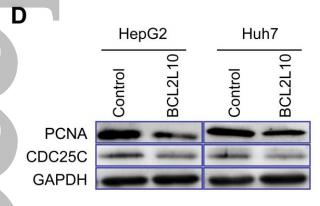
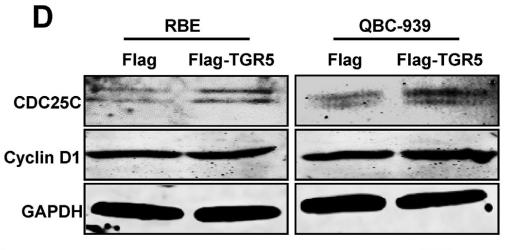
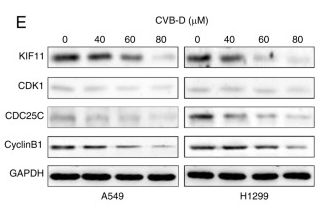
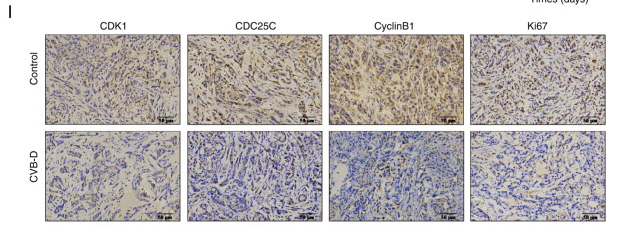
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: NSCLC cells
Application: IHC Species: Mouse Sample: A549 cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: CC cell
Application: WB Species: human Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.