nNOS Antibody - #AF6249
| Product: | nNOS Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6249 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to nNOS |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 120~160kDa; 161kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P29475 |
| RRID: | AB_2835113 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6249, RRID:AB_2835113.
Fold/Unfold
2310005C01Rik; BNOS; Constitutive NOS; EC 1.14.13.39; IHPS 1; IHPS1; N-NOS; NC-NOS; neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase; Neuronal NOS; Nitric oxide synthase , neuronal, included; Nitric oxide synthase 1 (neuronal); Nitric oxide synthase 1; Nitric oxide synthase, brain; Nitric oxide synthase, penile neuronal, included; NNOS; NO; NOS 1; NOS; NOS type I; NOS-I; NOS1; NOS1_HUMAN; Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase NOS1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human nNOS, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Isoform 1 is ubiquitously expressed: detected in skeletal muscle and brain, also in testis, lung and kidney, and at low levels in heart, adrenal gland and retina. Not detected in the platelets. Isoform 3 is expressed only in testis. Isoform 4 is detected in testis, skeletal muscle, lung, and kidney, at low levels in the brain, but not in the heart and adrenal gland.
- P29475 NOS1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEDHMFGVQQIQPNVISVRLFKRKVGGLGFLVKERVSKPPVIISDLIRGGAAEQSGLIQAGDIILAVNGRPLVDLSYDSALEVLRGIASETHVVLILRGPEGFTTHLETTFTGDGTPKTIRVTQPLGPPTKAVDLSHQPPAGKEQPLAVDGASGPGNGPQHAYDDGQEAGSLPHANGLAPRPPGQDPAKKATRVSLQGRGENNELLKEIEPVLSLLTSGSRGVKGGAPAKAEMKDMGIQVDRDLDGKSHKPLPLGVENDRVFNDLWGKGNVPVVLNNPYSEKEQPPTSGKQSPTKNGSPSKCPRFLKVKNWETEVVLTDTLHLKSTLETGCTEYICMGSIMHPSQHARRPEDVRTKGQLFPLAKEFIDQYYSSIKRFGSKAHMERLEEVNKEIDTTSTYQLKDTELIYGAKHAWRNASRCVGRIQWSKLQVFDARDCTTAHGMFNYICNHVKYATNKGNLRSAITIFPQRTDGKHDFRVWNSQLIRYAGYKQPDGSTLGDPANVQFTEICIQQGWKPPRGRFDVLPLLLQANGNDPELFQIPPELVLEVPIRHPKFEWFKDLGLKWYGLPAVSNMLLEIGGLEFSACPFSGWYMGTEIGVRDYCDNSRYNILEEVAKKMNLDMRKTSSLWKDQALVEINIAVLYSFQSDKVTIVDHHSATESFIKHMENEYRCRGGCPADWVWIVPPMSGSITPVFHQEMLNYRLTPSFEYQPDPWNTHVWKGTNGTPTKRRAIGFKKLAEAVKFSAKLMGQAMAKRVKATILYATETGKSQAYAKTLCEIFKHAFDAKVMSMEEYDIVHLEHETLVLVVTSTFGNGDPPENGEKFGCALMEMRHPNSVQEERKSYKVRFNSVSSYSDSQKSSGDGPDLRDNFESAGPLANVRFSVFGLGSRAYPHFCAFGHAVDTLLEELGGERILKMREGDELCGQEEAFRTWAKKVFKAACDVFCVGDDVNIEKANNSLISNDRSWKRNKFRLTFVAEAPELTQGLSNVHKKRVSAARLLSRQNLQSPKSSRSTIFVRLHTNGSQELQYQPGDHLGVFPGNHEDLVNALIERLEDAPPVNQMVKVELLEERNTALGVISNWTDELRLPPCTIFQAFKYYLDITTPPTPLQLQQFASLATSEKEKQRLLVLSKGLQEYEEWKWGKNPTIVEVLEEFPSIQMPATLLLTQLSLLQPRYYSISSSPDMYPDEVHLTVAIVSYRTRDGEGPIHHGVCSSWLNRIQADELVPCFVRGAPSFHLPRNPQVPCILVGPGTGIAPFRSFWQQRQFDIQHKGMNPCPMVLVFGCRQSKIDHIYREETLQAKNKGVFRELYTAYSREPDKPKKYVQDILQEQLAESVYRALKEQGGHIYVCGDVTMAADVLKAIQRIMTQQGKLSAEDAGVFISRMRDDNRYHEDIFGVTLRTYEVTNRLRSESIAFIEESKKDTDEVFSS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is a messenger molecule with diverse functions throughout the body. In the brain and peripheral nervous system, NO displays many properties of a neurotransmitter. Probably has nitrosylase activity and mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of cytoplasmic target proteins such SRR.
Ubiquitinated; mediated by STUB1/CHIP in the presence of Hsp70 and Hsp40 (in vitro).
Cell membrane>Sarcolemma>Peripheral membrane protein. Cell projection>Dendritic spine.
Note: In skeletal muscle, it is localized beneath the sarcolemma of fast-twitch muscle fiber by associating with the dystrophin glycoprotein complex. In neurons, enriched in dendritic spines (By similarity).
Isoform 1 is ubiquitously expressed: detected in skeletal muscle and brain, also in testis, lung and kidney, and at low levels in heart, adrenal gland and retina. Not detected in the platelets. Isoform 3 is expressed only in testis. Isoform 4 is detected in testis, skeletal muscle, lung, and kidney, at low levels in the brain, but not in the heart and adrenal gland.
The PDZ domain in the N-terminal part of the neuronal isoform participates in protein-protein interaction, and is responsible for targeting nNos to synaptic membranes in muscles. Mediates interaction with VAC14 (By similarity).
Belongs to the NOS family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Phagosome. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Calcium signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Alzheimer's disease.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
· Metabolism > Amino acid metabolism > Arginine biosynthesis.
· Metabolism > Amino acid metabolism > Arginine and proline metabolism.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Metabolic pathways.
· Organismal Systems > Environmental adaptation > Circadian entrainment.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Long-term depression.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Salivary secretion.
References
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: gastric tissues
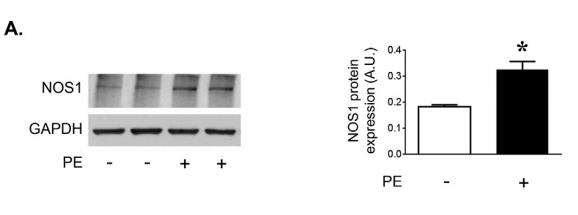
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: corpus cavernosum
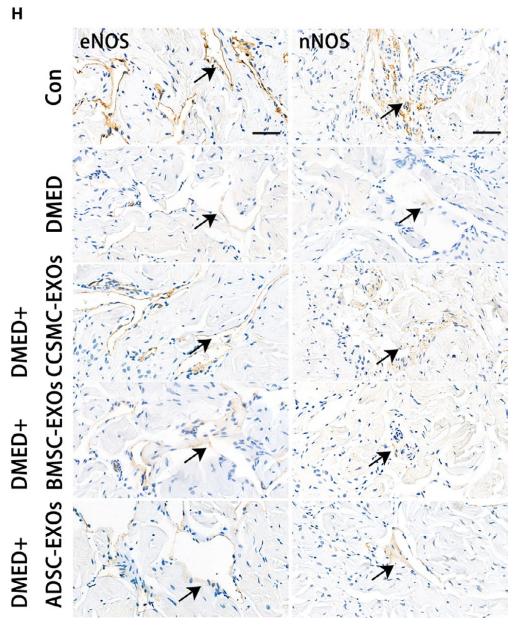
Application: IHC Species: Rat Sample: corpus cavernosum
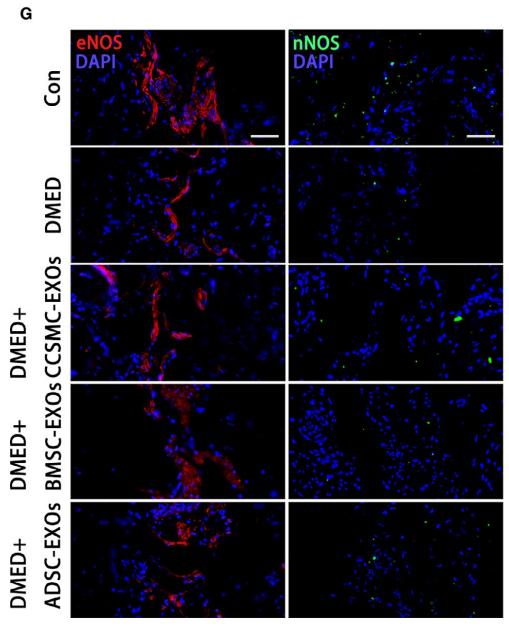
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample: corpus cavernosum
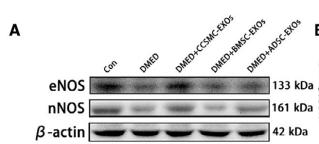
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: cardiomyocyte
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.