MYOCD Antibody - #AF0023
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Fold/Unfold
MYCD; MYCD_HUMAN; Myocardin; Myocd;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human MYOCD, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expressed in heart, aorta, and in smooth muscle cell-containing tissues: stomach, bladder, small intestine, colon, lung, placenta and uterus. Very faint expression in prostate and skeletal muscle.
- Q8IZQ8 MYCD_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MTLLGSEHSLLIRSKFRSVLQLRLQQRRTQEQLANQGIIPPLKRPAEFHEQRKHLDSDKAKNSLKRKARNRCNSADLVNMHILQASTAERSIPTAQMKLKRARLADDLNEKIALRPGPLELVEKNILPVDSAVKEAIKGNQVSFSKSTDAFAFEEDSSSDGLSPDQTRSEDPQNSAGSPPDAKASDTPSTGSLGTNQDLASGSENDRNDSASQPSHQSDAGKQGLGPPSTPIAVHAAVKSKSLGDSKNRHKKPKDPKPKVKKLKYHQYIPPDQKAEKSPPPMDSAYARLLQQQQLFLQLQILSQQQQQQQHRFSYLGMHQAQLKEPNEQMVRNPNSSSTPLSNTPLSPVKNSFSGQTGVSSFKPGPLPPNLDDLKVSELRQQLRIRGLPVSGTKTALMDRLRPFQDCSGNPVPNFGDITTVTFPVTPNTLPNYQSSSSTSALSNGFYHFGSTSSSPPISPASSDLSVAGSLPDTFNDASPSFGLHPSPVHVCTEESLMSSLNGGSVPSELDGLDSEKDKMLVEKQKVINELTWKLQQEQRQVEELRMQLQKQKRNNCSEKKPLPFLAASIKQEEAVSSCPFASQVPVKRQSSSSECHPPACEAAQLQPLGNAHCVESSDQTNVLSSTFLSPQCSPQHSPLGAVKSPQHISLPPSPNNPHFLPSSSGAQGEGHRVSSPISSQVCTAQMAGLHSSDKVGPKFSIPSPTFSKSSSAISEVTQPPSYEDAVKQQMTRSQQMDELLDVLIESGEMPADAREDHSCLQKVPKIPRSSRSPTAVLTKPSASFEQASSGSQIPFDPYATDSDEHLEVLLNSQSPLGKMSDVTLLKIGSEEPHFDGIMDGFSGKAAEDLFNAHEILPGPLSPMQTQFSPSSVDSNGLQLSFTESPWETMEWLDLTPPNSTPGFSALTTSSPSIFNIDFLDVTDLNLNSSMDLHLQQW
PTMs - Q8IZQ8 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| S74 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K138 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| S178 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S229 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T230 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S242 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K264 | Methylation | Uniprot | |
| S451 | Phosphorylation | P49841 (GSK3B) | Uniprot |
| S455 | Phosphorylation | P49841 (GSK3B) | Uniprot |
| S459 | Phosphorylation | P49841 (GSK3B) | Uniprot |
| S463 | Phosphorylation | P49841 (GSK3B) | Uniprot |
| K571 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K588 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| S626 | Phosphorylation | P49841 (GSK3B) | Uniprot |
| S630 | Phosphorylation | P49841 (GSK3B) | Uniprot |
| S634 | Phosphorylation | P49841 (GSK3B) | Uniprot |
| S638 | Phosphorylation | P49841 (GSK3B) | Uniprot |
| S704 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T732 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S734 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S815 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) | Uniprot |
| S862 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) | Uniprot |
| S869 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) | Uniprot |
| T896 | Phosphorylation | P28482 (MAPK1) | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Smooth muscle cells (SM) and cardiac muscle cells-specific transcriptional factor which uses the canonical single or multiple CArG boxes DNA sequence. Acts as a cofactor of serum response factor (SRF) with the potential to modulate SRF-target genes. Plays a crucial role in cardiogenesis and differentiation of the smooth muscle cell lineage (myogenesis) (By similarity).
Phosphorylation regulates negatively the intrinsic myocardin transcriptional activity.
Nucleus.
Expressed in heart, aorta, and in smooth muscle cell-containing tissues: stomach, bladder, small intestine, colon, lung, placenta and uterus. Very faint expression in prostate and skeletal muscle.
Homodimer. Interacts with SRF, its association does not depend on specific DNA sequences for ternary complex formation (By similarity). Interacts with MLLT7/FOXO4. Interacts (via C-terminal) with EP300 (via the CREB-binding domain). Interacts with HDAC4 and HDAC5 (By similarity). Interacts with MEF2C (By similarity).
The C-terminal region contains a general transcription activation domain. The N-terminal region, comprising a basic and a Gln-rich domain, confers transcriptional potency and specificity by mediating association with the MADS box of SRF. The basic domain may be required for nuclear localization. The SAP domain is important for transactivation and ternary complex formation (By similarity).
References
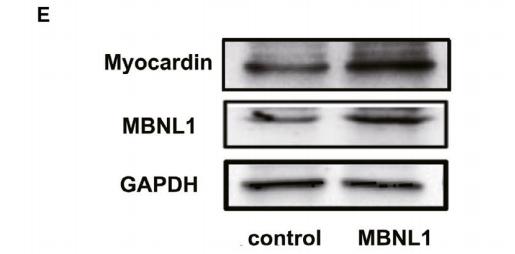
Application: WB Species: mice Sample: cardiomyocytes
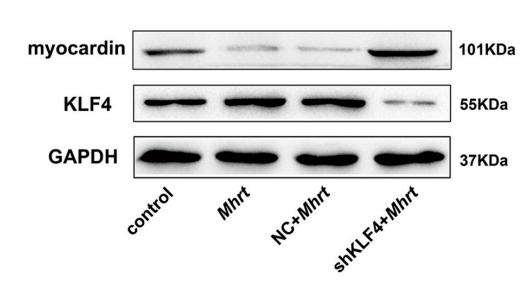
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: primary cardiomyocytes
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.