Phospho-Smad7 (Ser249) Antibody - #AF3827
| Product: | Phospho-Smad7 (Ser249) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF3827 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-Smad7 (Ser249) |
| Application: | IHC |
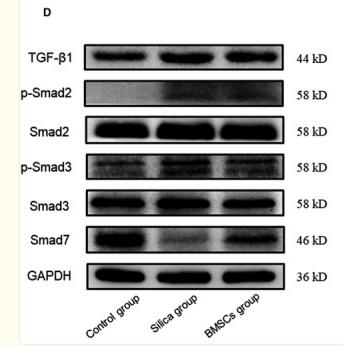
| Cited expt.: | |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 46kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | O15105 |
| RRID: | AB_2847141 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF3827, RRID:AB_2847141.
Fold/Unfold
CRCS3; FLJ16482; hSMAD 7; hSMAD7; MAD (mothers against decapentaplegic Drosophila) homolog 7; MAD; Mad homolog 7; MAD homolog 8; MAD mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7; MADH 7; MADH 8; MADH6; MADH7; MADH8; Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Drosophila Homolog of 6; Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Drosophila Homolog of 7; Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7; Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 8; Mothers against DPP homolog 7; Mothers against DPP homolog 8; SMA- AND MAD-RELATED PROTEIN 7; SMAD 7; SMAD; SMAD family member 7; SMAD, mothers against DPP homolog 7 (Drosophila); SMAD, mothers against DPP homolog 7; SMAD6; Smad7; SMAD7_HUMAN;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Smad7 around the phosphorylation site of Ser249.
- O15105 SMAD7_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MFRTKRSALVRRLWRSRAPGGEDEEEGAGGGGGGGELRGEGATDSRAHGAGGGGPGRAGCCLGKAVRGAKGHHHPHPPAAGAGAAGGAEADLKALTHSVLKKLKERQLELLLQAVESRGGTRTACLLLPGRLDCRLGPGAPAGAQPAQPPSSYSLPLLLCKVFRWPDLRHSSEVKRLCCCESYGKINPELVCCNPHHLSRLCELESPPPPYSRYPMDFLKPTADCPDAVPSSAETGGTNYLAPGGLSDSQLLLEPGDRSHWCVVAYWEEKTRVGRLYCVQEPSLDIFYDLPQGNGFCLGQLNSDNKSQLVQKVRSKIGCGIQLTREVDGVWVYNRSSYPIFIKSATLDNPDSRTLLVHKVFPGFSIKAFDYEKAYSLQRPNDHEFMQQPWTGFTVQISFVKGWGQCYTRQFISSCPCWLEVIFNSR
Research Backgrounds
Antagonist of signaling by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) type 1 receptor superfamily members; has been shown to inhibit TGF-beta (Transforming growth factor) and activin signaling by associating with their receptors thus preventing SMAD2 access. Functions as an adapter to recruit SMURF2 to the TGF-beta receptor complex. Also acts by recruiting the PPP1R15A-PP1 complex to TGFBR1, which promotes its dephosphorylation. Positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator.
Phosphorylation on Ser-249 does not affect its stability, nuclear localization or inhibitory function in TGFB signaling; however it affects its ability to regulate transcription (By similarity). Phosphorylated by PDPK1.
Ubiquitinated by WWP1 (By similarity). Polyubiquitinated by RNF111, which is enhanced by AXIN1 and promotes proteasomal degradation. In response to TGF-beta, ubiquitinated by SMURF1; which promotes its degradation.
Acetylation prevents ubiquitination and degradation mediated by SMURF1.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Note: Interaction with NEDD4L or RNF111 induces translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm (PubMed:16601693). TGF-beta stimulates its translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. PDPK1 inhibits its translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in response to TGF-beta (PubMed:17327236).
Ubiquitous with higher expression in the lung and vascular endothelium.
Belongs to the dwarfin/SMAD family.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TGF-beta signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: lung tissues
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: TCMK-1 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.