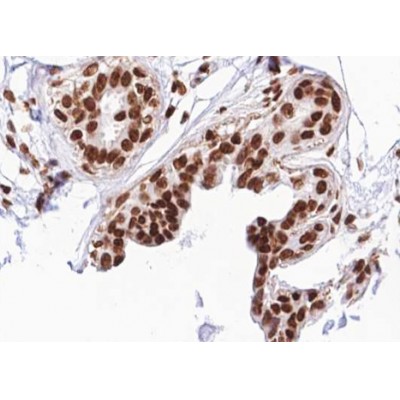
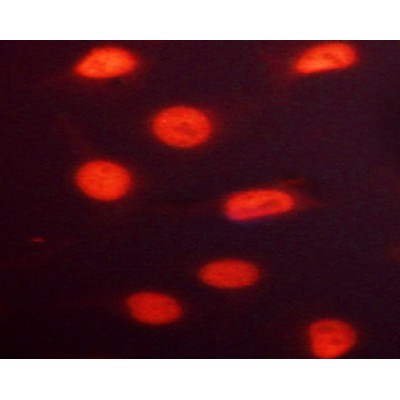
Phospho-RACGAP1 (Ser387) Antibody - #AF3482
| Product: | Phospho-RACGAP1 (Ser387) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF3482 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-RACGAP1 (Ser387) |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 72kDa; 71kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9H0H5 |
| RRID: | AB_2834920 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF3482, RRID:AB_2834920.
Fold/Unfold
CYK4; GAP; Gap1; GTPase activating protein; HsCYK-4; ID GAP; KIAA1478; Male germ cell RacGap; MgcRacGAP; Protein CYK4 homolg; Protein CYK4 homolog; Rac GTPase activating protein 1; Rac GTPase-activating protein 1; RACGAP 1; Racgap1; RGAP1_HUMAN;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human RACGAP1 around the phosphorylation site of Ser387.
Highly expressed in testis, thymus and placenta. Expressed at lower levels in spleen and peripheral blood lymphocytes. In testis, expression is restricted to germ cells with the highest levels of expression found in spermatocytes. Expression is regulated in a cell cycle-dependent manner and peaks during G2/M phase.
- Q9H0H5 RGAP1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDTMMLNVRNLFEQLVRRVEILSEGNEVQFIQLAKDFEDFRKKWQRTDHELGKYKDLLMKAETERSALDVKLKHARNQVDVEIKRRQRAEADCEKLERQIQLIREMLMCDTSGSIQLSEEQKSALAFLNRGQPSSSNAGNKRLSTIDESGSILSDISFDKTDESLDWDSSLVKTFKLKKREKRRSTSRQFVDGPPGPVKKTRSIGSAVDQGNESIVAKTTVTVPNDGGPIEAVSTIETVPYWTRSRRKTGTLQPWNSDSTLNSRQLEPRTETDSVGTPQSNGGMRLHDFVSKTVIKPESCVPCGKRIKFGKLSLKCRDCRVVSHPECRDRCPLPCIPTLIGTPVKIGEGMLADFVSQTSPMIPSIVVHCVNEIEQRGLTETGLYRISGCDRTVKELKEKFLRVKTVPLLSKVDDIHAICSLLKDFLRNLKEPLLTFRLNRAFMEAAEITDEDNSIAAMYQAVGELPQANRDTLAFLMIHLQRVAQSPHTKMDVANLAKVFGPTIVAHAVPNPDPVTMLQDIKRQPKVVERLLSLPLEYWSQFMMVEQENIDPLHVIENSNAFSTPQTPDIKVSLLGPVTTPEHQLLKTPSSSSLSQRVRSTLTKNTPRFGSKSKSATNLGRQGNFFASPMLK
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Component of the centralspindlin complex that serves as a microtubule-dependent and Rho-mediated signaling required for the myosin contractile ring formation during the cell cycle cytokinesis. Required for proper attachment of the midbody to the cell membrane during cytokinesis. Plays key roles in controlling cell growth and differentiation of hematopoietic cells through mechanisms other than regulating Rac GTPase activity. Also involved in the regulation of growth-related processes in adipocytes and myoblasts. May be involved in regulating spermatogenesis and in the RACGAP1 pathway in neuronal proliferation. Shows strong GAP (GTPase activation) activity towards CDC42 and RAC1 and less towards RHOA. Essential for the early stages of embryogenesis. May play a role in regulating cortical activity through RHOA during cytokinesis. May participate in the regulation of sulfate transport in male germ cells.
Phosphorylated at multiple sites in the midbody during cytokinesis. Phosphorylation by AURKB on Ser-387 at the midbody is, at least in part, responsible for exerting its latent GAP activity towards RhoA. Phosphorylation on multiple serine residues by PLK1 enhances its association with ECT2 and is critical for cleavage furrow formation.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Spindle. Cytoplasmic vesicle>Secretory vesicle>Acrosome. Cleavage furrow. Midbody>Midbody ring. Cell membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side.
Note: Colocalizes with RND2 in Golgi-derived proacrosomal vesicles and the acrosome (By similarity). During interphase, localized to the nucleus and cytoplasm along with microtubules, in anaphase, is redistributed to the central spindle and, in telophase and cytokinesis, to the midbody ring, also called Flemming body. Colocalizes with RHOA at the myosin contractile ring during cytokinesis. Colocalizes with ECT2 to the mitotic spindles during anaphase/metaphase, the cleavage furrow during telophase and at the midbody at the end of cytokinesis. Colocalizes with Cdc42 to spindle microtubules from prometaphase to telophase.
Highly expressed in testis, thymus and placenta. Expressed at lower levels in spleen and peripheral blood lymphocytes. In testis, expression is restricted to germ cells with the highest levels of expression found in spermatocytes. Expression is regulated in a cell cycle-dependent manner and peaks during G2/M phase.
The coiled coil region is indispensible for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis.
The phorbol-ester/DAG-type zinc finger domain mediates interaction with membranes enriched in phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate and is required during mitotic cytokinesis for normal attachment of the midbody to the cell membrane.
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.