Phospho-Synapsin I (Ser605) Antibody - #AF2416
| Product: | Phospho-Synapsin I (Ser605) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF2416 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-Synapsin I (Ser605) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 75-90kDa; 74kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P17600 |
| RRID: | AB_2845430 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF2416, RRID:AB_2845430.
Fold/Unfold
Brain protein 4.1; SYN 1; SYN 1a; SYN 1b; SYN I; SYN1; SYN1_HUMAN; SYN1a; SYN1b; Synapsin 1; Synapsin I; Synapsin-1; Synapsin1; SynapsinI; SYNI;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Synapsin I around the phosphorylation site of Ser605.
- P17600 SYN1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MNYLRRRLSDSNFMANLPNGYMTDLQRPQPPPPPPGAHSPGATPGPGTATAERSSGVAPAASPAAPSPGSSGGGGFFSSLSNAVKQTTAAAAATFSEQVGGGSGGAGRGGAASRVLLVIDEPHTDWAKYFKGKKIHGEIDIKVEQAEFSDLNLVAHANGGFSVDMEVLRNGVKVVRSLKPDFVLIRQHAFSMARNGDYRSLVIGLQYAGIPSVNSLHSVYNFCDKPWVFAQMVRLHKKLGTEEFPLIDQTFYPNHKEMLSSTTYPVVVKMGHAHSGMGKVKVDNQHDFQDIASVVALTKTYATAEPFIDAKYDVRVQKIGQNYKAYMRTSVSGNWKTNTGSAMLEQIAMSDRYKLWVDTCSEIFGGLDICAVEALHGKDGRDHIIEVVGSSMPLIGDHQDEDKQLIVELVVNKMAQALPRQRQRDASPGRGSHGQTPSPGALPLGRQTSQQPAGPPAQQRPPPQGGPPQPGPGPQRQGPPLQQRPPPQGQQHLSGLGPPAGSPLPQRLPSPTSAPQQPASQAAPPTQGQGRQSRPVAGGPGAPPAARPPASPSPQRQAGPPQATRQTSVSGPAPPKASGAPPGGQQRQGPPQKPPGPAGPTRQASQAGPVPRTGPPTTQQPRPSGPGPAGRPKPQLAQKPSQDVPPPATAAAGGPPHPQLNKSQSLTNAFNLPEPAPPRPSLSQDEVKAETIRSLRKSFASLFSD
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Neuronal phosphoprotein that coats synaptic vesicles, binds to the cytoskeleton, and is believed to function in the regulation of neurotransmitter release. The complex formed with NOS1 and CAPON proteins is necessary for specific nitric-oxid functions at a presynaptic level.
Substrate of at least four different protein kinases. It is probable that phosphorylation plays a role in the regulation of synapsin-1 in the nerve terminal.
Phosphorylation at Ser-9 dissociates synapsins from synaptic vesicles.
Cell junction>Synapse. Golgi apparatus.
The A region binds phospholipids with a preference for negatively charged species.
Belongs to the synapsin family.
References
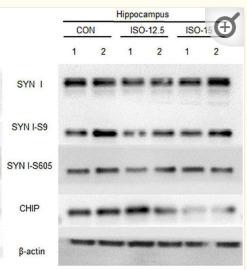
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: cortex brain tissue
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: N2a cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.