NR1D1 Antibody - #DF12430
| Product: | NR1D1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF12430 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to NR1D1 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 55-68 kDa; 67kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P20393 |
| RRID: | AB_2845235 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF12430, RRID:AB_2845235.
Fold/Unfold
EAR-1; EAR1; ERBA-related 1; hRev; Nr1d1; NR1D1_HUMAN; Nuclear receptor Rev ErbA alpha; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group D member 1; Rev erbAalpha; Rev erbalpha; Rev-erbA-alpha; Rev-ErbAalpha; Reverba; THRA1; THRAL; Thyroid hormone receptor, alpha like; Thyroid hormone receptor, alpha-1- like; V-erbA-related protein 1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human NR1D1, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
Widely expressed. Expressed at high levels in the liver, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and brain. Also expressed in endothelial cells (ECs), vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and macrophages. Expression oscillates diurnally in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus as well as in peripheral tissues. Expression increases during the differentiation of pre-adipocytes into mature adipocytes. Expressed at high levels in some squamous carcinoma cell lines.
- P20393 NR1D1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MTTLDSNNNTGGVITYIGSSGSSPSRTSPESLYSDNSNGSFQSLTQGCPTYFPPSPTGSLTQDPARSFGSIPPSLSDDGSPSSSSSSSSSSSSFYNGSPPGSLQVAMEDSSRVSPSKSTSNITKLNGMVLLCKVCGDVASGFHYGVHACEGCKGFFRRSIQQNIQYKRCLKNENCSIVRINRNRCQQCRFKKCLSVGMSRDAVRFGRIPKREKQRMLAEMQSAMNLANNQLSSQCPLETSPTQHPTPGPMGPSPPPAPVPSPLVGFSQFPQQLTPPRSPSPEPTVEDVISQVARAHREIFTYAHDKLGSSPGNFNANHASGSPPATTPHRWENQGCPPAPNDNNTLAAQRHNEALNGLRQAPSSYPPTWPPGPAHHSCHQSNSNGHRLCPTHVYAAPEGKAPANSPRQGNSKNVLLACPMNMYPHGRSGRTVQEIWEDFSMSFTPAVREVVEFAKHIPGFRDLSQHDQVTLLKAGTFEVLMVRFASLFNVKDQTVMFLSRTTYSLQELGAMGMGDLLSAMFDFSEKLNSLALTEEELGLFTAVVLVSADRSGMENSASVEQLQETLLRALRALVLKNRPLETSRFTKLLLKLPDLRTLNNMHSEKLLSFRVDAQ
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Transcriptional repressor which coordinates circadian rhythm and metabolic pathways in a heme-dependent manner. Integral component of the complex transcription machinery that governs circadian rhythmicity and forms a critical negative limb of the circadian clock by directly repressing the expression of core clock components ARTNL/BMAL1, CLOCK and CRY1. Also regulates genes involved in metabolic functions, including lipid and bile acid metabolism, adipogenesis, gluconeogenesis and the macrophage inflammatory response. Acts as a receptor for heme which stimulates its interaction with the NCOR1/HDAC3 corepressor complex, enhancing transcriptional repression. Recognizes two classes of DNA response elements within the promoter of its target genes and can bind to DNA as either monomers or homodimers, depending on the nature of the response element. Binds as a monomer to a response element composed of the consensus half-site motif 5'-[A/G]GGTCA-3' preceded by an A/T-rich 5' sequence (RevRE), or as a homodimer to a direct repeat of the core motif spaced by two nucleotides (RevDR-2). Acts as a potent competitive repressor of ROR alpha (RORA) function and regulates the levels of its ligand heme by repressing the expression of PPARGC1A, a potent inducer of heme synthesis. Regulates lipid metabolism by repressing the expression of APOC3 and by influencing the activity of sterol response element binding proteins (SREBPs); represses INSIG2 which interferes with the proteolytic activation of SREBPs which in turn govern the rhythmic expression of enzymes with key functions in sterol and fatty acid synthesis. Regulates gluconeogenesis via repression of G6PC and PEPCK and adipocyte differentiation via repression of PPARG. Regulates glucagon release in pancreatic alpha-cells via the AMPK-NAMPT-SIRT1 pathway and the proliferation, glucose-induced insulin secretion and expression of key lipogenic genes in pancreatic-beta cells. Positively regulates bile acid synthesis by increasing hepatic expression of CYP7A1 via repression of NR0B2 and NFIL3 which are negative regulators of CYP7A1. Modulates skeletal muscle oxidative capacity by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy; controls mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration by interfering with the STK11-PRKAA1/2-SIRT1-PPARGC1A signaling pathway. Represses the expression of SERPINE1/PAI1, an important modulator of cardiovascular disease and the expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in macrophages. Represses gene expression at a distance in macrophages by inhibiting the transcription of enhancer-derived RNAs (eRNAs). Plays a role in the circadian regulation of body temperature and negatively regulates thermogenic transcriptional programs in brown adipose tissue (BAT); imposes a circadian oscillation in BAT activity, increasing body temperature when awake and depressing thermogenesis during sleep. In concert with NR2E3, regulates transcriptional networks critical for photoreceptor development and function. In addition to its activity as a repressor, can also act as a transcriptional activator. In the ovarian granulosa cells acts as a transcriptional activator of STAR which plays a role in steroid biosynthesis. In collaboration with SP1, activates GJA1 transcription in a heme-independent manner. Represses the transcription of CYP2B10, CYP4A10 and CYP4A14 (By similarity). Represses the transcription of CES2 (By similarity). Represses and regulates the circadian expression of TSHB in a NCOR1-dependent manner (By similarity). Negatively regulates the protein stability of NR3C1 and influences the time-dependent subcellular distribution of NR3C1, thereby affecting its transcriptional regulatory activity (By similarity). Plays a critical role in the circadian control of neutrophilic inflammation in the lung; under resting, non-stress conditions, acts as a rhythmic repressor to limit inflammatory activity whereas in the presence of inflammatory triggers undergoes ubiquitin-mediated degradation thereby relieving inhibition of the inflammatory response (By similarity). Plays a key role in the circadian regulation of microglial activation and neuroinflammation; suppresses microglial activation through the NF-kappaB pathway in the central nervous system (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of the diurnal rhythms of lipid and protein metabolism in the skeletal muscle via transcriptional repression of genes controlling lipid and amino acid metabolism in the muscle (By similarity).
Ubiquitinated, leading to its proteasomal degradation. Ubiquitinated by SIAH2; leading to its proteasomal degradation. Ubiquitinated by the SCF(FBXW7) complex when phosphorylated by CDK1 leading to its proteasomal degradation (By similarity). Rapidly ubiquitinated in response to inflammatory triggers and sumoylation is a prerequisite to its ubiquitination (By similarity).
Sumoylated by UBE2I, desumoylated by SENP1, and sumoylation is a prerequisite to its ubiquitination.
Phosphorylated by CSNK1E; phosphorylation enhances its cytoplasmic localization.
Undergoes lysosome-mediated degradation in a time-dependent manner in the liver.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell projection>Dendrite. Cell projection>Dendritic spine.
Note: Localizes to the cytoplasm, dendrites and dendritic spine in the presence of OPHN1. Localizes predominantly to the nucleus at ZT8 whereas it is cytoplasmic at ZT20. Phosphorylation by CSNK1E enhances its cytoplasmic localization.
Widely expressed. Expressed at high levels in the liver, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and brain. Also expressed in endothelial cells (ECs), vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and macrophages. Expression oscillates diurnally in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus as well as in peripheral tissues. Expression increases during the differentiation of pre-adipocytes into mature adipocytes. Expressed at high levels in some squamous carcinoma cell lines.
Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal ligand-binding domain.
Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR1 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Organismal Systems > Environmental adaptation > Circadian rhythm. (View pathway)
References
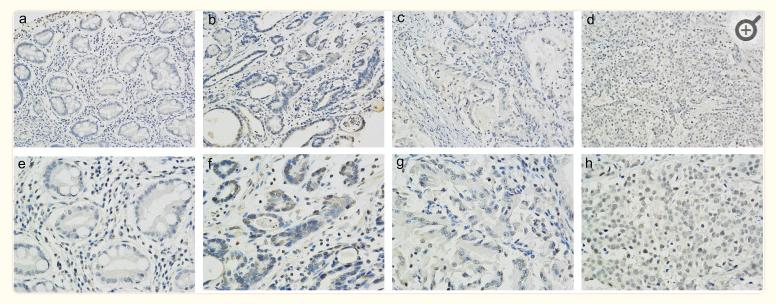
Application: IHC Species: Human Sample: gastric and GC tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.