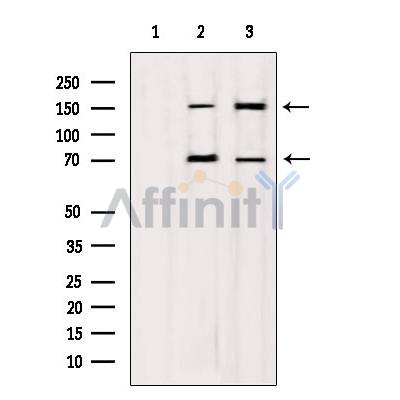
DIAPH1 Antibody - #DF12292
| Product: | DIAPH1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF12292 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to DIAPH1 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 140-150, 70 kDa; 141kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | O60610 |
| RRID: | AB_2845097 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF12292, RRID:AB_2845097.
Fold/Unfold
DIAPH1; deafness, autosomal dominant 1; DFNA1; DIA1; DIAP1; DIAP1_HUMAN; DIAPH1; Diaphanous homolog 1 (Drosophila); diaphanous homolog 1; Diaphanous related formin 1; Diaphanous-related formin-1; DRF1; FLJ25265; hDIA1; LFHL1; low frequency hearing loss 1; p140DIA; Protein diaphanous homolog 1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human DIAPH1, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
Expressed in brain, heart, placenta, lung, kidney, pancreas, liver, skeletal muscle and cochlea. Expressed in platelets (PubMed:26912466).
- O60610 DIAP1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEPPGGSLGPGRGTRDKKKGRSPDELPSAGGDGGKSKKFTLKRLMADELERFTSMRIKKEKEKPNSAHRNSSASYGDDPTAQSLQDVSDEQVLVLFEQMLLDMNLNEEKQQPLREKDIIIKREMVSQYLYTSKAGMSQKESSKSAMMYIQELRSGLRDMPLLSCLESLRVSLNNNPVSWVQTFGAEGLASLLDILKRLHDEKEETAGSYDSRNKHEIIRCLKAFMNNKFGIKTMLETEEGILLLVRAMDPAVPNMMIDAAKLLSALCILPQPEDMNERVLEAMTERAEMDEVERFQPLLDGLKSGTTIALKVGCLQLINALITPAEELDFRVHIRSELMRLGLHQVLQDLREIENEDMRVQLNVFDEQGEEDSYDLKGRLDDIRMEMDDFNEVFQILLNTVKDSKAEPHFLSILQHLLLVRNDYEARPQYYKLIEECISQIVLHKNGADPDFKCRHLQIEIEGLIDQMIDKTKVEKSEAKAAELEKKLDSELTARHELQVEMKKMESDFEQKLQDLQGEKDALHSEKQQIATEKQDLEAEVSQLTGEVAKLTKELEDAKKEMASLSAAAITVPPSVPSRAPVPPAPPLPGDSGTIIPPPPAPGDSTTPPPPPPPPPPPPPLPGGVCISSPPSLPGGTAISPPPPLSGDATIPPPPPLPEGVGIPSPSSLPGGTAIPPPPPLPGSARIPPPPPPLPGSAGIPPPPPPLPGEAGMPPPPPPLPGGPGIPPPPPFPGGPGIPPPPPGMGMPPPPPFGFGVPAAPVLPFGLTPKKLYKPEVQLRRPNWSKLVAEDLSQDCFWTKVKEDRFENNELFAKLTLTFSAQTKTSKAKKDQEGGEEKKSVQKKKVKELKVLDSKTAQNLSIFLGSFRMPYQEIKNVILEVNEAVLTESMIQNLIKQMPEPEQLKMLSELKDEYDDLAESEQFGVVMGTVPRLRPRLNAILFKLQFSEQVENIKPEIVSVTAACEELRKSESFSNLLEITLLVGNYMNAGSRNAGAFGFNISFLCKLRDTKSTDQKMTLLHFLAELCENDYPDVLKFPDELAHVEKASRVSAENLQKNLDQMKKQISDVERDVQNFPAATDEKDKFVEKMTSFVKDAQEQYNKLRMMHSNMETLYKELGEYFLFDPKKLSVEEFFMDLHNFRNMFLQAVKENQKRRETEEKMRRAKLAKEKAEKERLEKQQKREQLIDMNAEGDETGVMDSLLEALQSGAAFRRKRGPRQANRKAGCAVTSLLASELTKDDAMAAVPAKVSKNSETFPTILEEAKELVGRAS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Actin nucleation and elongation factor required for the assembly of F-actin structures, such as actin cables and stress fibers (By similarity). Binds to the barbed end of the actin filament and slows down actin polymerization and depolymerization (By similarity). Required for cytokinesis, and transcriptional activation of the serum response factor (By similarity). DFR proteins couple Rho and Src tyrosine kinase during signaling and the regulation of actin dynamics (By similarity). Functions as a scaffold protein for MAPRE1 and APC to stabilize microtubules and promote cell migration (By similarity). Has neurite outgrowth promoting activity. Acts in a Rho-dependent manner to recruit PFY1 to the membrane (By similarity). In hear cells, it may play a role in the regulation of actin polymerization in hair cells. The MEMO1-RHOA-DIAPH1 signaling pathway plays an important role in ERBB2-dependent stabilization of microtubules at the cell cortex. It controls the localization of APC and CLASP2 to the cell membrane, via the regulation of GSK3B activity. In turn, membrane-bound APC allows the localization of the MACF1 to the cell membrane, which is required for microtubule capture and stabilization. Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. Required in the control of cell shape. Plays a role in brain development. Also acts as an actin nucleation and elongation factor in the nucleus by promoting nuclear actin polymerization inside the nucleus to drive serum-dependent SRF-MRTFA activity (By similarity).
Phosphorylation at Thr-768 is stimulated by cAMP and regulates stability, complex formation and mitochondrial movement.
Cell membrane. Cell projection>Ruffle membrane. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Spindle. Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Membrane ruffles, especially at the tip of ruffles, of motile cells.
Expressed in brain, heart, placenta, lung, kidney, pancreas, liver, skeletal muscle and cochlea. Expressed in platelets.
The DAD domain regulates activation via by an autoinhibitory interaction with the GBD/FH3 domain (By similarity). This autoinhibition is released upon competitive binding of an activated GTPase (By similarity). The release of DAD allows the FH2 domain to then nucleate and elongate nonbranched actin filaments (By similarity).
Belongs to the formin homology family. Diaphanous subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Shigellosis.
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.