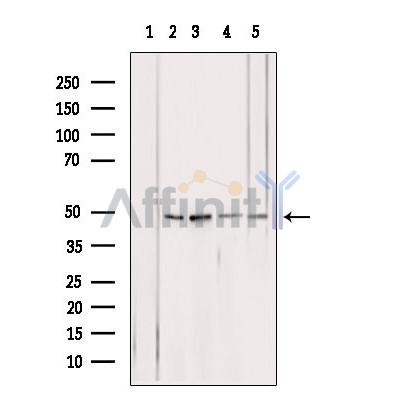
ATPB Antibody - #DF12111
| Product: | ATPB Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF12111 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to ATPB |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 45-57 kDa; 57kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P06576 |
| RRID: | AB_2844916 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF12111, RRID:AB_2844916.
Fold/Unfold
ATP 5B; ATP synthase H+ transporting mitochondrial F1 complex beta polypeptide; ATP synthase subunit beta mitochondrial; ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial; atp5b; ATPB; ATPB_HUMAN; ATPMB; ATPSB; Epididymis secretory protein Li 271; HEL-S-271; Mitochondrial ATP synthase beta subunit; Mitochondrial ATP Synthase Subunit Beta; Mitochondrial ATP synthetase beta subunit;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human ATPB, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P06576 ATPB_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MLGFVGRVAAAPASGALRRLTPSASLPPAQLLLRAAPTAVHPVRDYAAQTSPSPKAGAATGRIVAVIGAVVDVQFDEGLPPILNALEVQGRETRLVLEVAQHLGESTVRTIAMDGTEGLVRGQKVLDSGAPIKIPVGPETLGRIMNVIGEPIDERGPIKTKQFAPIHAEAPEFMEMSVEQEILVTGIKVVDLLAPYAKGGKIGLFGGAGVGKTVLIMELINNVAKAHGGYSVFAGVGERTREGNDLYHEMIESGVINLKDATSKVALVYGQMNEPPGARARVALTGLTVAEYFRDQEGQDVLLFIDNIFRFTQAGSEVSALLGRIPSAVGYQPTLATDMGTMQERITTTKKGSITSVQAIYVPADDLTDPAPATTFAHLDATTVLSRAIAELGIYPAVDPLDSTSRIMDPNIVGSEHYDVARGVQKILQDYKSLQDIIAILGMDELSEEDKLTVSRARKIQRFLSQPFQVAEVFTGHMGKLVPLKETIKGFQQILAGEYDHLPEQAFYMVGPIEEAVAKADKLAEEHSS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core, and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Subunits alpha and beta form the catalytic core in F(1). Rotation of the central stalk against the surrounding alpha(3)beta(3) subunits leads to hydrolysis of ATP in three separate catalytic sites on the beta subunits.
Mitochondrion inner membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Matrix side.
Belongs to the ATPase alpha/beta chains family.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Alzheimer's disease.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Parkinson's disease.
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Huntington's disease.
· Metabolism > Energy metabolism > Oxidative phosphorylation.
· Metabolism > Global and overview maps > Metabolic pathways.
References
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.