CDC20 Antibody - #AF4759
| Product: | CDC20 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF4759 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CDC20 |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 50kDa; 55kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q12834 |
| RRID: | AB_2844753 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF4759, RRID:AB_2844753.
Fold/Unfold
bA276H19.3; Cdc 20; CDC20; CDC20 cell division cycle 20 homolog; CDC20_HUMAN; CDC20A; Cell division cycle 20; Cell division cycle 20 homolog (S. cerevisiae); Cell division cycle 20 homolog; Cell division cycle protein 20 homolog; fizzy; MGC102824; p55CDC;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CDC20, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
- Q12834 CDC20_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAQFAFESDLHSLLQLDAPIPNAPPARWQRKAKEAAGPAPSPMRAANRSHSAGRTPGRTPGKSSSKVQTTPSKPGGDRYIPHRSAAQMEVASFLLSKENQPENSQTPTKKEHQKAWALNLNGFDVEEAKILRLSGKPQNAPEGYQNRLKVLYSQKATPGSSRKTCRYIPSLPDRILDAPEIRNDYYLNLVDWSSGNVLAVALDNSVYLWSASSGDILQLLQMEQPGEYISSVAWIKEGNYLAVGTSSAEVQLWDVQQQKRLRNMTSHSARVGSLSWNSYILSSGSRSGHIHHHDVRVAEHHVATLSGHSQEVCGLRWAPDGRHLASGGNDNLVNVWPSAPGEGGWVPLQTFTQHQGAVKAVAWCPWQSNVLATGGGTSDRHIRIWNVCSGACLSAVDAHSQVCSILWSPHYKELISGHGFAQNQLVIWKYPTMAKVAELKGHTSRVLSLTMSPDGATVASAAADETLRLWRCFELDPARRREREKASAAKSSLIHQGIR
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Required for full ubiquitin ligase activity of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) and may confer substrate specificity upon the complex. Is regulated by MAD2L1: in metaphase the MAD2L1-CDC20-APC/C ternary complex is inactive and in anaphase the CDC20-APC/C binary complex is active in degrading substrates. The CDC20-APC/C complex positively regulates the formation of synaptic vesicle clustering at active zone to the presynaptic membrane in postmitotic neurons. CDC20-APC/C-induced degradation of NEUROD2 induces presynaptic differentiation.
Acetylated. Deacetylated at Lys-66 by SIRT2; deacetylation enhances the interaction of CDC20 with CDC27, leading to activation of anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C).
Phosphorylated during mitosis, probably by maturation promoting factor (MPF). Phosphorylated by BUB1 at Ser-41; Ser-72; Ser-92; Ser-153; Thr-157 and Ser-161. Phosphorylated by NEK2.
Dephosphorylated by CTDP1.
Ubiquitinated and degraded by the proteasome during spindle assembly checkpoint. Deubiquitinated by USP44, leading to stabilize the MAD2L1-CDC20-APC/C ternary complex, thereby preventing premature activation of the APC/C. Ubiquitinated at Lys-490 during prometaphase. Ubiquitination at Lys-485 and Lys-490 has no effect on its ability to bind the APC/C complex.
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Spindle pole.
Belongs to the WD repeat CDC20/Fizzy family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Oocyte meiosis. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Viral carcinogenesis.
References
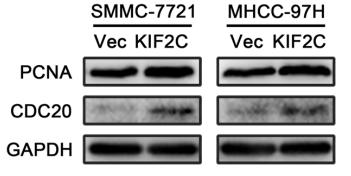
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: ovarian cancer cell
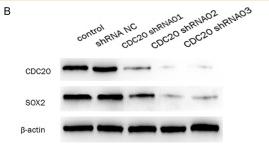
Application: WB Species: human Sample: HCCcell
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.