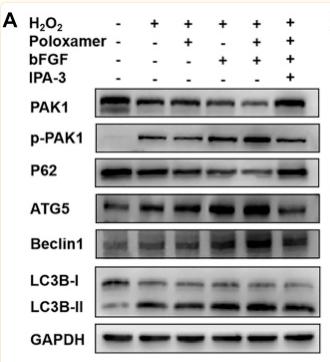
Phospho-PAK1 /PAK2 (Thr423/Thr402) Antibody - #AF4463
| Product: | Phospho-PAK1 /PAK2 (Thr423/Thr402) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF4463 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-PAK1 /PAK2 (Thr423/Thr402) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 61-67kDa (PAK2),68-74 kDa (PAK1/3); 61kD,58kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q13153 | Q13177 |
| RRID: | AB_2844520 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF4463, RRID:AB_2844520.
Fold/Unfold
ADRB2; Alpha PAK; Alpha-PAK; MGC130000; MGC130001; p21 activated kinase 1; p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac) activated kinase 1; p21-activated kinase 1; p21/Cdc42/Rac1 activated kinase 1 (yeast Ste20 related); p21/Cdc42/Rac1-activated kinase 1 (STE20 homolog, yeast); p65 PAK; p65-PAK; P68-PAK; PAK alpha; PAK-1; Pak1; PAK1_HUMAN; Paka; PAKalpha; Protein kinase MUK2; Rac/p21-activated kinase; Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1; STE20 homolog yeast; C-t-PAK2; CB422; EC 2.7.11.1; Gamma PAK; Gamma-PAK; hPAK65; Kinase; p21 (CDKN1A) activated kinase 2; p21 (CDKN1A)-activated kinase 2a; p21 activated kinase 2; p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 2; p21 protein Cdc42 Rac activated kinase 2; p21-activated kinase 2; p21-activated kinase, 65-KD; p21-activated protein kinase I; p21CDKN1A activated kinase 2; p27; p34; p58; p65PAK; PAK 2; PAK-2; PAK-2p34; Pak2; PAK2_HUMAN; PAK65; PAKgamma; S6 H4 kinase; S6/H4 kinase; Serine threonine protein kinase PAK 2; Serine/threonine protein kinase PAK 2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human PAK1 around the phosphorylation site of Thr423.
Overexpressed in gastric cancer cells and tissues (at protein level) (PubMed:25766321).
Q13177 PAK2_HUMAN:Ubiquitously expressed. Higher levels seen in skeletal muscle, ovary, thymus and spleen.
- Q13153 PAK1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSNNGLDIQDKPPAPPMRNTSTMIGAGSKDAGTLNHGSKPLPPNPEEKKKKDRFYRSILPGDKTNKKKEKERPEISLPSDFEHTIHVGFDAVTGEFTGMPEQWARLLQTSNITKSEQKKNPQAVLDVLEFYNSKKTSNSQKYMSFTDKSAEDYNSSNALNVKAVSETPAVPPVSEDEDDDDDDATPPPVIAPRPEHTKSVYTRSVIEPLPVTPTRDVATSPISPTENNTTPPDALTRNTEKQKKKPKMSDEEILEKLRSIVSVGDPKKKYTRFEKIGQGASGTVYTAMDVATGQEVAIKQMNLQQQPKKELIINEILVMRENKNPNIVNYLDSYLVGDELWVVMEYLAGGSLTDVVTETCMDEGQIAAVCRECLQALEFLHSNQVIHRDIKSDNILLGMDGSVKLTDFGFCAQITPEQSKRSTMVGTPYWMAPEVVTRKAYGPKVDIWSLGIMAIEMIEGEPPYLNENPLRALYLIATNGTPELQNPEKLSAIFRDFLNRCLEMDVEKRGSAKELLQHQFLKIAKPLSSLTPLIAAAKEATKNNH
- Q13177 PAK2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSDNGELEDKPPAPPVRMSSTIFSTGGKDPLSANHSLKPLPSVPEEKKPRHKIISIFSGTEKGSKKKEKERPEISPPSDFEHTIHVGFDAVTGEFTGMPEQWARLLQTSNITKLEQKKNPQAVLDVLKFYDSNTVKQKYLSFTPPEKDGFPSGTPALNAKGTEAPAVVTEEEDDDEETAPPVIAPRPDHTKSIYTRSVIDPVPAPVGDSHVDGAAKSLDKQKKKTKMTDEEIMEKLRTIVSIGDPKKKYTRYEKIGQGASGTVFTATDVALGQEVAIKQINLQKQPKKELIINEILVMKELKNPNIVNFLDSYLVGDELFVVMEYLAGGSLTDVVTETCMDEAQIAAVCRECLQALEFLHANQVIHRDIKSDNVLLGMEGSVKLTDFGFCAQITPEQSKRSTMVGTPYWMAPEVVTRKAYGPKVDIWSLGIMAIEMVEGEPPYLNENPLRALYLIATNGTPELQNPEKLSPIFRDFLNRCLEMDVEKRGSAKELLQHPFLKLAKPLSSLTPLIMAAKEAMKSNR
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Protein kinase involved in intracellular signaling pathways downstream of integrins and receptor-type kinases that plays an important role in cytoskeleton dynamics, in cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, apoptosis, mitosis, and in vesicle-mediated transport processes. Can directly phosphorylate BAD and protects cells against apoptosis. Activated by interaction with CDC42 and RAC1. Functions as GTPase effector that links the Rho-related GTPases CDC42 and RAC1 to the JNK MAP kinase pathway. Phosphorylates and activates MAP2K1, and thereby mediates activation of downstream MAP kinases. Involved in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, actin stress fibers and of focal adhesion complexes. Phosphorylates the tubulin chaperone TBCB and thereby plays a role in the regulation of microtubule biogenesis and organization of the tubulin cytoskeleton. Plays a role in the regulation of insulin secretion in response to elevated glucose levels. Part of a ternary complex that contains PAK1, DVL1 and MUSK that is important for MUSK-dependent regulation of AChR clustering during the formation of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Activity is inhibited in cells undergoing apoptosis, potentially due to binding of CDC2L1 and CDC2L2. Phosphorylates MYL9/MLC2. Phosphorylates RAF1 at 'Ser-338' and 'Ser-339' resulting in: activation of RAF1, stimulation of RAF1 translocation to mitochondria, phosphorylation of BAD by RAF1, and RAF1 binding to BCL2. Phosphorylates SNAI1 at 'Ser-246' promoting its transcriptional repressor activity by increasing its accumulation in the nucleus. In podocytes, promotes NR3C2 nuclear localization. Required for atypical chemokine receptor ACKR2-induced phosphorylation of LIMK1 and cofilin (CFL1) and for the up-regulation of ACKR2 from endosomal compartment to cell membrane, increasing its efficiency in chemokine uptake and degradation. In synapses, seems to mediate the regulation of F-actin cluster formation performed by SHANK3, maybe through CFL1 phosphorylation and inactivation. Plays a role in RUFY3-mediated facilitating gastric cancer cells migration and invasion. In response to DNA damage, phosphorylates MORC2 which activates its ATPase activity and facilitates chromatin remodeling.
Autophosphorylated in trans, meaning that in a dimer, one kinase molecule phosphorylates the other one. Activated by autophosphorylation at Thr-423 in response to a conformation change, triggered by interaction with GTP-bound CDC42 or RAC1. Activated by phosphorylation at Thr-423 by BRSK2 and by PDPK1. Phosphorylated by JAK2 in response to PRL; this increases PAK1 kinase activity. Phosphorylated at Ser-21 by PKB/AKT; this reduces interaction with NCK1 and association with focal adhesion sites. Upon DNA damage, phosphorylated at Thr-212 and translocates to the nucleoplasm. Phosphorylated at tyrosine residues, which can be enhanced by NTN1 (By similarity).
Cytoplasm. Cell junction>Focal adhesion. Cell membrane. Cell projection>Ruffle membrane. Cell projection>Invadopodium. Nucleus>Nucleoplasm. Chromosome.
Note: Colocalizes with RUFY3, F-actin and other core migration components in invadopodia at the cell periphery (PubMed:25766321). Recruited to the cell membrane by interaction with CDC42 and RAC1. Recruited to focal adhesions upon activation. Colocalized with CIB1 within membrane ruffles during cell spreading upon readhesion to fibronectin. Upon DNA damage, translocates to the nucleoplasm when phosphorylated at Thr-212 where is co-recruited with MORC2 on damaged chromatin (PubMed:23260667).
Overexpressed in gastric cancer cells and tissues (at protein level).
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family. STE20 subfamily.
Serine/threonine protein kinase that plays a role in a variety of different signaling pathways including cytoskeleton regulation, cell motility, cell cycle progression, apoptosis or proliferation. Acts as downstream effector of the small GTPases CDC42 and RAC1. Activation by the binding of active CDC42 and RAC1 results in a conformational change and a subsequent autophosphorylation on several serine and/or threonine residues. Full-length PAK2 stimulates cell survival and cell growth. Phosphorylates MAPK4 and MAPK6 and activates the downstream target MAPKAPK5, a regulator of F-actin polymerization and cell migration. Phosphorylates JUN and plays an important role in EGF-induced cell proliferation. Phosphorylates many other substrates including histone H4 to promote assembly of H3.3 and H4 into nucleosomes, BAD, ribosomal protein S6, or MBP. Additionally, associates with ARHGEF7 and GIT1 to perform kinase-independent functions such as spindle orientation control during mitosis. On the other hand, apoptotic stimuli such as DNA damage lead to caspase-mediated cleavage of PAK2, generating PAK-2p34, an active p34 fragment that translocates to the nucleus and promotes cellular apoptosis involving the JNK signaling pathway. Caspase-activated PAK2 phosphorylates MKNK1 and reduces cellular translation.
Full-length PAK2 is autophosphorylated when activated by CDC42/p21. Following cleavage, both peptides, PAK-2p27 and PAK-2p34, become highly autophosphorylated, with PAK-2p27 being phosphorylated on serine and PAK-2p34 on threonine residues, respectively. Autophosphorylation of PAK-2p27 can occur in the absence of any effectors and is dependent on phosphorylation of Thr-402, because PAK-2p27 is acting as an exogenous substrate.
During apoptosis proteolytically cleaved by caspase-3 or caspase-3-like proteases to yield active PAK-2p34.
Ubiquitinated, leading to its proteasomal degradation.
PAK-2p34 is myristoylated.
Cytoplasm.
Note: MYO18A mediates the cellular distribution of the PAK2-ARHGEF7-GIT1 complex to the inner surface of the cell membrane.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm>Perinuclear region. Membrane>Lipid-anchor.
Note: Interaction with ARHGAP10 probably changes PAK-2p34 location to cytoplasmic perinuclear region. Myristoylation changes PAK-2p34 location to the membrane.
Ubiquitously expressed. Higher levels seen in skeletal muscle, ovary, thymus and spleen.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family. STE20 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Renal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Chemokine signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Axon guidance. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis. (View pathway)
References
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: Schwann cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.