Phospho-TAZ (Ser89) Antibody - #AF4315
| Product: | Phospho-TAZ (Ser89) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF4315 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-TAZ (Ser89) |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 44kDa; 44kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9GZV5 |
| RRID: | AB_2844394 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF4315, RRID:AB_2844394.
Fold/Unfold
DKFZP586I1419; FLJ27004; FLJ45718; OTTHUMP00000215994; OTTHUMP00000215995; OTTHUMP00000215996; OTTHUMP00000216001; TAZ; Transcriptional co activator with PDZ binding motif; Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ binding motif; Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif; WW domain containing transcription regulator 1; WW domain containing transcription regulator protein 1; WW domain-containing transcription regulator protein 1; WWTR 1; WWTR1; WWTR1_HUMAN;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human TAZ around the phosphorylation site of Ser89.
Highly expressed in kidney, heart, placenta and lung. Expressed in the thyroid tissue.
- Q9GZV5 WWTR1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MNPASAPPPLPPPGQQVIHVTQDLDTDLEALFNSVMNPKPSSWRKKILPESFFKEPDSGSHSRQSSTDSSGGHPGPRLAGGAQHVRSHSSPASLQLGTGAGAAGSPAQQHAHLRQQSYDVTDELPLPPGWEMTFTATGQRYFLNHIEKITTWQDPRKAMNQPLNHMNLHPAVSSTPVPQRSMAVSQPNLVMNHQHQQQMAPSTLSQQNHPTQNPPAGLMSMPNALTTQQQQQQKLRLQRIQMERERIRMRQEELMRQEAALCRQLPMEAETLAPVQAAVNPPTMTPDMRSITNNSSDPFLNGGPYHSREQSTDSGLGLGCYSVPTTPEDFLSNVDEMDTGENAGQTPMNINPQQTRFPDFLDCLPGTNVDLGTLESEDLIPLFNDVESALNKSEPFLTWL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Transcriptional coactivator which acts as a downstream regulatory target in the Hippo signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ. WWTR1 enhances PAX8 and NKX2-1/TTF1-dependent gene activation. Regulates the nuclear accumulation of SMADS and has a key role in coupling them to the transcriptional machinery such as the mediator complex. Regulates embryonic stem-cell self-renewal, promotes cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Phosphorylated by LATS2 and STK3/MST2. Phosphorylation by LATS2 results in creation of 14-3-3 binding sites, retention in the cytoplasm, and functional inactivation. Phosphorylation results in the inhibition of transcriptional coactivation through YWHAZ-mediated nuclear export.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Note: Concentrates along specific portions of the plasma membrane, and accumulates in punctate nuclear bodies. When phosphorylated, is retained in cytoplasm by YWHAZ. Can be retained in the nucleus by MED15.
Highly expressed in kidney, heart, placenta and lung. Expressed in the thyroid tissue.
The PDZ-binding motif is essential for stimulated gene transcription. It localizes the protein into both punctate nuclear foci and plasma membrane-associated complexes (By similarity).
Binds to transcription factors via its WW domain.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
References
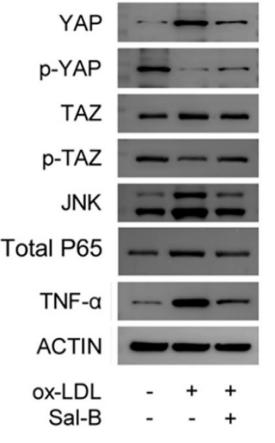
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: lung tissues
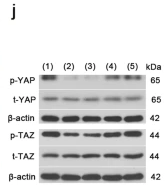
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: ECs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.