E-cadherin Antibody - #AF7718
| Product: | E-cadherin Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF7718 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to E-cadherin |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 120kDa; 97kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P12830 |
| RRID: | AB_2844082 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF7718, RRID:AB_2844082.
Fold/Unfold
Arc 1; CADH1_HUMAN; Cadherin 1; cadherin 1 type 1 E-cadherin; Cadherin1; CAM 120/80; CD 324; CD324; CD324 antigen; cdh1; CDHE; E-Cad/CTF3; E-cadherin; ECAD; Epithelial cadherin; epithelial calcium dependant adhesion protein; LCAM; Liver cell adhesion molecule; UVO; Uvomorulin;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human E-cadherin, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- P12830 CADH1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MGPWSRSLSALLLLLQVSSWLCQEPEPCHPGFDAESYTFTVPRRHLERGRVLGRVNFEDCTGRQRTAYFSLDTRFKVGTDGVITVKRPLRFHNPQIHFLVYAWDSTYRKFSTKVTLNTVGHHHRPPPHQASVSGIQAELLTFPNSSPGLRRQKRDWVIPPISCPENEKGPFPKNLVQIKSNKDKEGKVFYSITGQGADTPPVGVFIIERETGWLKVTEPLDRERIATYTLFSHAVSSNGNAVEDPMEILITVTDQNDNKPEFTQEVFKGSVMEGALPGTSVMEVTATDADDDVNTYNAAIAYTILSQDPELPDKNMFTINRNTGVISVVTTGLDRESFPTYTLVVQAADLQGEGLSTTATAVITVTDTNDNPPIFNPTTYKGQVPENEANVVITTLKVTDADAPNTPAWEAVYTILNDDGGQFVVTTNPVNNDGILKTAKGLDFEAKQQYILHVAVTNVVPFEVSLTTSTATVTVDVLDVNEAPIFVPPEKRVEVSEDFGVGQEITSYTAQEPDTFMEQKITYRIWRDTANWLEINPDTGAISTRAELDREDFEHVKNSTYTALIIATDNGSPVATGTGTLLLILSDVNDNAPIPEPRTIFFCERNPKPQVINIIDADLPPNTSPFTAELTHGASANWTIQYNDPTQESIILKPKMALEVGDYKINLKLMDNQNKDQVTTLEVSVCDCEGAAGVCRKAQPVEAGLQIPAILGILGGILALLILILLLLLFLRRRAVVKEPLLPPEDDTRDNVYYYDEEGGGEEDQDFDLSQLHRGLDARPEVTRNDVAPTLMSVPRYLPRPANPDEIGNFIDENLKAADTDPTAPPYDSLLVFDYEGSGSEAASLSSLNSSESDKDQDYDYLNEWGNRFKKLADMYGGGEDD
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Cadherins are calcium-dependent cell adhesion proteins. They preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells; cadherins may thus contribute to the sorting of heterogeneous cell types. CDH1 is involved in mechanisms regulating cell-cell adhesions, mobility and proliferation of epithelial cells. Has a potent invasive suppressor role. It is a ligand for integrin alpha-E/beta-7.
E-Cad/CTF2 promotes non-amyloidogenic degradation of Abeta precursors. Has a strong inhibitory effect on APP C99 and C83 production.
(Microbial infection) Serves as a receptor for Listeria monocytogenes; internalin A (InlA) binds to this protein and promotes uptake of the bacteria.
During apoptosis or with calcium influx, cleaved by a membrane-bound metalloproteinase (ADAM10), PS1/gamma-secretase and caspase-3. Processing by the metalloproteinase, induced by calcium influx, causes disruption of cell-cell adhesion and the subsequent release of beta-catenin into the cytoplasm. The residual membrane-tethered cleavage product is rapidly degraded via an intracellular proteolytic pathway. Cleavage by caspase-3 releases the cytoplasmic tail resulting in disintegration of the actin microfilament system. The gamma-secretase-mediated cleavage promotes disassembly of adherens junctions. During development of the cochlear organ of Corti, cleavage by ADAM10 at adherens junctions promotes pillar cell separation (By similarity).
N-glycosylation at Asn-637 is essential for expression, folding and trafficking. Addition of bisecting N-acetylglucosamine by MGAT3 modulates its cell membrane location.
Ubiquitinated by a SCF complex containing SKP2, which requires prior phosphorylation by CK1/CSNK1A1. Ubiquitinated by CBLL1/HAKAI, requires prior phosphorylation at Tyr-754.
O-glycosylated. O-manosylated by TMTC1, TMTC2, TMTC3 or TMTC4. Thr-285 and Thr-509 are O-mannosylated by TMTC2 or TMTC4 but not TMTC1 or TMTC3.
Cell junction>Adherens junction. Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Endosome. Golgi apparatus>trans-Golgi network.
Note: Colocalizes with DLGAP5 at sites of cell-cell contact in intestinal epithelial cells. Anchored to actin microfilaments through association with alpha-, beta- and gamma-catenin. Sequential proteolysis induced by apoptosis or calcium influx, results in translocation from sites of cell-cell contact to the cytoplasm. Colocalizes with RAB11A endosomes during its transport from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane.
Non-neural epithelial tissues.
Three calcium ions are usually bound at the interface of each cadherin domain and rigidify the connections, imparting a strong curvature to the full-length ectodomain.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Endometrial cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Thyroid cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Bladder cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
References
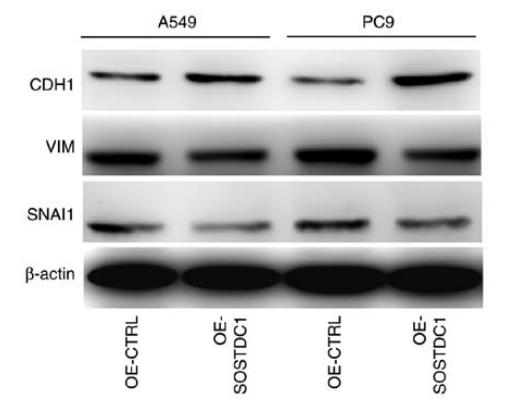
Application: WB Species: human Sample: A549 and PC9 cells
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: MG-63 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.