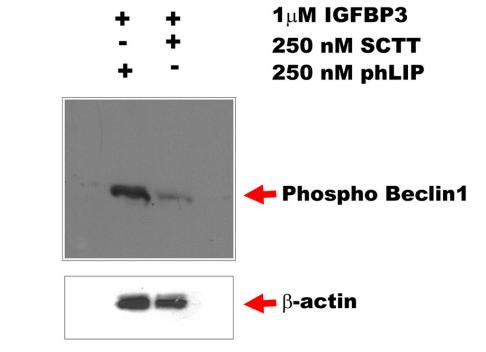
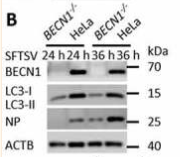
Phospho-Beclin 1 (Ser90/Ser93/Ser96) Antibody - #AF7386
| Product: | Phospho-Beclin 1 (Ser90/Ser93/Ser96) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF7386 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-Beclin 1 (Ser90/Ser93/Ser96) |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 60kDa; 52kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q14457 |
| RRID: | AB_2843826 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF7386, RRID:AB_2843826.
Fold/Unfold
APG6; ATG 6; ATG6; ATG6 autophagy related 6 homolog; Bcl-2-interacting protein beclin; Beclin 1 (coiled coil moesin like BCL2 interacting protein); Beclin 1 autophagy related; Beclin-1; Beclin1; BECN 1; Becn1; BECN1_HUMAN; Coiled coil myosin like BCL2 interacting protein; Coiled-coil myosin-like BCL2-interacting protein; GT197; Protein GT197; VPS 30; VPS30;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Beclin 1 around the phosphorylation site of Ser90/93/96.
- Q14457 BECN1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MEGSKTSNNSTMQVSFVCQRCSQPLKLDTSFKILDRVTIQELTAPLLTTAQAKPGETQEEETNSGEEPFIETPRQDGVSRRFIPPARMMSTESANSFTLIGEASDGGTMENLSRRLKVTGDLFDIMSGQTDVDHPLCEECTDTLLDQLDTQLNVTENECQNYKRCLEILEQMNEDDSEQLQMELKELALEEERLIQELEDVEKNRKIVAENLEKVQAEAERLDQEEAQYQREYSEFKRQQLELDDELKSVENQMRYAQTQLDKLKKTNVFNATFHIWHSGQFGTINNFRLGRLPSVPVEWNEINAAWGQTVLLLHALANKMGLKFQRYRLVPYGNHSYLESLTDKSKELPLYCSGGLRFFWDNKFDHAMVAFLDCVQQFKEEVEKGETRFCLPYRMDVEKGKIEDTGGSGGSYSIKTQFNSEEQWTKALKFMLTNLKWGLAWVSSQFYNK
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Plays a central role in autophagy. Acts as core subunit of the PI3K complex that mediates formation of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate; different complex forms are believed to play a role in multiple membrane trafficking pathways: PI3KC3-C1 is involved in initiation of autophagosomes and PI3KC3-C2 in maturation of autophagosomes and endocytosis. Involved in regulation of degradative endocytic trafficking and required for the abcission step in cytokinesis, probably in the context of PI3KC3-C2. Essential for the formation of PI3KC3-C2 but not PI3KC3-C1 PI3K complex forms. Involved in endocytosis. Protects against infection by a neurovirulent strain of Sindbis virus. May play a role in antiviral host defense.
Beclin-1-C 35 kDa localized to mitochondria can promote apoptosis; it induces the mitochondrial translocation of BAX and the release of proapoptotic factors.
Phosphorylation at Thr-119 by DAPK1 reduces its interaction with BCL2 and BCL2L1 and promotes induction of autophagy. In response to autophagic stimuli, phosphorylated at serine residues by AMPK in an ATG14-dependent manner, and this phosphorylation is critical for maximally efficient autophagy.
Polyubiquitinated by NEDD4, both with 'Lys-11'- and 'Lys-63'-linkages. 'Lys-11'-linked polyubiquitination leads to degradation and is enhanced when the stabilizing interaction partner VPS34 is depleted. Deubiquitinated by USP10 and USP13, leading to stabilize the PIK3C3/VPS34-containing complexes. Polyubiquitinated at Lys-402 with 'Lys-48'-linkages. 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination of Lys-402 leads to degradation. Deubiquitinated by ATXN3, leading to stabilization.
Proteolytically processed by caspases including CASP8 and CASP3; the C-terminal fragments lack autophagy-inducing capacity and are proposed to induce apoptosis. Thus the cleavage is proposed to be an determinant to switch from autophagy to apoptosis pathways affecting cellular homeostasis including viral infections and survival of tumor cells.
Cytoplasm. Golgi apparatus>trans-Golgi network membrane>Peripheral membrane protein. Endosome membrane>Peripheral membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane>Peripheral membrane protein. Mitochondrion membrane>Peripheral membrane protein. Endosome. Cytoplasmic vesicle>Autophagosome.
Note: Interaction with ATG14 promotes translocation to autophagosomes. Expressed in dendrites and cell bodies of cerebellar Purkinje cells (By similarity).
Mitochondrion. Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Mitochondrion.
Ubiquitous.
The coiled coil domain can form antiparallel homodimers and mediates dimerization with the coiled coil domains of ATG14 or UVRAG involved in the formation of PI3K complexes.
The C-terminal evolutionary conserved domain (ECD) contains poly-Gln-binding domains such as the ATXN3 poly-Gln motif, consistent with structural docking models revealing two highly scored poly-Gln-binding pockets in the ECD (PubMed:28445460). As some binding is observed with BECN1 lacking the ECD, other domains of BECN1 may also interact with ATXN3 (PubMed:28445460).
Belongs to the beclin family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - other. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HeLa cells and WT cells
Application: IF/ICC Species: Human Sample: HeLa cells and WT cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample: MCF7 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.