SLC1A5 Antibody - #AF6610
| Product: | SLC1A5 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF6610 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to SLC1A5 |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 56 kDa; 57kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q15758 |
| RRID: | AB_2843431 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF6610, RRID:AB_2843431.
Fold/Unfold
ASCT2; AAAT; AAAT_HUMAN; ATB(0); ATBO; Baboon M7 virus receptor; FLJ31068; M7V1; M7VS1; Neutral amino acid transporter B(0); R16; RD114/simian type D retrovirus receptor; RDR; RDRC; SLC1A5; Sodium dependent neutral amino acid transporter type 2; Sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter type 2; Solute carrier family 1 (neutral amino acid transporter), member 5; Solute carrier family 1 member 5;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human SLC1A5, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- Q15758 AAAT_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MVADPPRDSKGLAAAEPTANGGLALASIEDQGAAAGGYCGSRDQVRRCLRANLLVLLTVVAVVAGVALGLGVSGAGGALALGPERLSAFVFPGELLLRLLRMIILPLVVCSLIGGAASLDPGALGRLGAWALLFFLVTTLLASALGVGLALALQPGAASAAINASVGAAGSAENAPSKEVLDSFLDLARNIFPSNLVSAAFRSYSTTYEERNITGTRVKVPVGQEVEGMNILGLVVFAIVFGVALRKLGPEGELLIRFFNSFNEATMVLVSWIMWYAPVGIMFLVAGKIVEMEDVGLLFARLGKYILCCLLGHAIHGLLVLPLIYFLFTRKNPYRFLWGIVTPLATAFGTSSSSATLPLMMKCVEENNGVAKHISRFILPIGATVNMDGAALFQCVAAVFIAQLSQQSLDFVKIITILVTATASSVGAAGIPAGGVLTLAIILEAVNLPVDHISLILAVDWLVDRSCTVLNVEGDALGAGLLQNYVDRTESRSTEPELIQVKSELPLDPLPVPTEEGNPLLKHYRGPAGDATVASEKESVM
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Sodium-dependent amino acids transporter that has a broad substrate specificity, with a preference for zwitterionic amino acids. It accepts as substrates all neutral amino acids, including glutamine, asparagine, and branched-chain and aromatic amino acids, and excludes methylated, anionic, and cationic amino acids. Through binding of the fusogenic protein syncytin-1/ERVW-1 may mediate trophoblasts syncytialization, the spontaneous fusion of their plasma membranes, an essential process in placental development.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a cell surface receptor for Feline endogenous virus RD114.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a cell surface receptor for Baboon M7 endogenous virus.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a cell surface receptor for type D simian retroviruses.
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Melanosome.
Note: Identified by mass spectrometry in melanosome fractions from stage I to stage IV.
Placenta, lung, skeletal muscle, kidney, pancreas, and intestine.
Belongs to the dicarboxylate/amino acid:cation symporter (DAACS) (TC 2.A.23) family. SLC1A5 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Central carbon metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Protein digestion and absorption.
References
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: EC cell
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: CCAs
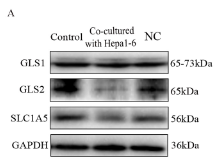
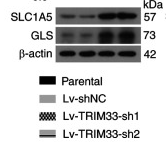
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and hepatoma cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.