KCNJ10 Antibody - #DF9260
| Product: | KCNJ10 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF9260 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to KCNJ10 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 43 kDa; 43kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P78508 |
| RRID: | AB_2842456 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF9260, RRID:AB_2842456.
Fold/Unfold
inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 10; ATP dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir4.1; ATP sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 10; ATP-dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir4.1; ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 10; BIRK10; Glial ATP dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channel KIR4.1; Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir1.2; Inward rectifier K+ channel KIR1.2; Inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir1.2; KCJ10_HUMAN; KCNJ 10; Kcnj10; KCNJ13 PEN; KIR1.2; KIR4.1; Potassium channel; Potassium channel inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 10; Potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 10; SESAME;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human KCNJ10, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P78508 KCJ10_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MTSVAKVYYSQTTQTESRPLMGPGIRRRRVLTKDGRSNVRMEHIADKRFLYLKDLWTTFIDMQWRYKLLLFSATFAGTWFLFGVVWYLVAVAHGDLLELDPPANHTPCVVQVHTLTGAFLFSLESQTTIGYGFRYISEECPLAIVLLIAQLVLTTILEIFITGTFLAKIARPKKRAETIRFSQHAVVASHNGKPCLMIRVANMRKSLLIGCQVTGKLLQTHQTKEGENIRLNQVNVTFQVDTASDSPFLILPLTFYHVVDETSPLKDLPLRSGEGDFELVLILSGTVESTSATCQVRTSYLPEEILWGYEFTPAISLSASGKYIADFSLFDQVVKVASPSGLRDSTVRYGDPEKLKLEESLREQAEKEGSALSVRISNV
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
May be responsible for potassium buffering action of glial cells in the brain. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. Can be blocked by extracellular barium and cesium (By similarity). In the kidney, together with KCNJ16, mediates basolateral K(+) recycling in distal tubules; this process is critical for Na(+) reabsorption at the tubules.
Membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Basolateral cell membrane.
Note: In kidney distal convoluted tubules, located in the basolateral membrane where it colocalizes with KCNJ16.
Expressed in kidney (at protein level).
Belongs to the inward rectifier-type potassium channel (TC 1.A.2.1) family. KCNJ10 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Organismal Systems > Digestive system > Gastric acid secretion.
References
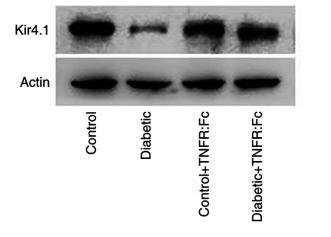
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: kidney tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.