AGRN Antibody - #DF9181
| Product: | AGRN Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF9181 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to AGRN |
| Application: | WB IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 217kDa, 150 kDa; 217kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | O00468 |
| RRID: | AB_2842377 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF9181, RRID:AB_2842377.
Fold/Unfold
AGRIN; Agrin proteoglycan; AGRN; FLJ45064; OTTHUMP00000044043;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human AGRN, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Expressed in basement membranes of lung and kidney. Muscle- and neuron-specific isoforms are found. Isoforms (y+) with the 4 AA insert and (z+8) isoforms with the 8 AA insert are all neuron-specific. Isoforms (z+11) are found in both neuronal and non-neuronal tissues.
- O00468 AGRIN_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAGRSHPGPLRPLLPLLVVAACVLPGAGGTCPERALERREEEANVVLTGTVEEILNVDPVQHTYSCKVRVWRYLKGKDLVARESLLDGGNKVVISGFGDPLICDNQVSTGDTRIFFVNPAPPYLWPAHKNELMLNSSLMRITLRNLEEVEFCVEDKPGTHFTPVPPTPPDACRGMLCGFGAVCEPNAEGPGRASCVCKKSPCPSVVAPVCGSDASTYSNECELQRAQCSQQRRIRLLSRGPCGSRDPCSNVTCSFGSTCARSADGLTASCLCPATCRGAPEGTVCGSDGADYPGECQLLRRACARQENVFKKFDGPCDPCQGALPDPSRSCRVNPRTRRPEMLLRPESCPARQAPVCGDDGVTYENDCVMGRSGAARGLLLQKVRSGQCQGRDQCPEPCRFNAVCLSRRGRPRCSCDRVTCDGAYRPVCAQDGRTYDSDCWRQQAECRQQRAIPSKHQGPCDQAPSPCLGVQCAFGATCAVKNGQAACECLQACSSLYDPVCGSDGVTYGSACELEATACTLGREIQVARKGPCDRCGQCRFGALCEAETGRCVCPSECVALAQPVCGSDGHTYPSECMLHVHACTHQISLHVASAGPCETCGDAVCAFGAVCSAGQCVCPRCEHPPPGPVCGSDGVTYGSACELREAACLQQTQIEEARAGPCEQAECGSGGSGSGEDGDCEQELCRQRGGIWDEDSEDGPCVCDFSCQSVPGSPVCGSDGVTYSTECELKKARCESQRGLYVAAQGACRGPTFAPLPPVAPLHCAQTPYGCCQDNITAARGVGLAGCPSACQCNPHGSYGGTCDPATGQCSCRPGVGGLRCDRCEPGFWNFRGIVTDGRSGCTPCSCDPQGAVRDDCEQMTGLCSCKPGVAGPKCGQCPDGRALGPAGCEADASAPATCAEMRCEFGARCVEESGSAHCVCPMLTCPEANATKVCGSDGVTYGNECQLKTIACRQGLQISIQSLGPCQEAVAPSTHPTSASVTVTTPGLLLSQALPAPPGALPLAPSSTAHSQTTPPPSSRPRTTASVPRTTVWPVLTVPPTAPSPAPSLVASAFGESGSTDGSSDEELSGDQEASGGGSGGLEPLEGSSVATPGPPVERASCYNSALGCCSDGKTPSLDAEGSNCPATKVFQGVLELEGVEGQELFYTPEMADPKSELFGETARSIESTLDDLFRNSDVKKDFRSVRLRDLGPGKSVRAIVDVHFDPTTAFRAPDVARALLRQIQVSRRRSLGVRRPLQEHVRFMDFDWFPAFITGATSGAIAAGATARATTASRLPSSAVTPRAPHPSHTSQPVAKTTAAPTTRRPPTTAPSRVPGRRPPAPQQPPKPCDSQPCFHGGTCQDWALGGGFTCSCPAGRGGAVCEKVLGAPVPAFEGRSFLAFPTLRAYHTLRLALEFRALEPQGLLLYNGNARGKDFLALALLDGRVQLRFDTGSGPAVLTSAVPVEPGQWHRLELSRHWRRGTLSVDGETPVLGESPSGTDGLNLDTDLFVGGVPEDQAAVALERTFVGAGLRGCIRLLDVNNQRLELGIGPGAATRGSGVGECGDHPCLPNPCHGGAPCQNLEAGRFHCQCPPGRVGPTCADEKSPCQPNPCHGAAPCRVLPEGGAQCECPLGREGTFCQTASGQDGSGPFLADFNGFSHLELRGLHTFARDLGEKMALEVVFLARGPSGLLLYNGQKTDGKGDFVSLALRDRRLEFRYDLGKGAAVIRSREPVTLGAWTRVSLERNGRKGALRVGDGPRVLGESPKSRKVPHTVLNLKEPLYVGGAPDFSKLARAAAVSSGFDGAIQLVSLGGRQLLTPEHVLRQVDVTSFAGHPCTRASGHPCLNGASCVPREAAYVCLCPGGFSGPHCEKGLVEKSAGDVDTLAFDGRTFVEYLNAVTESELANEIPVPETLDSGALHSEKALQSNHFELSLRTEATQGLVLWSGKATERADYVALAIVDGHLQLSYNLGSQPVVLRSTVPVNTNRWLRVVAHREQREGSLQVGNEAPVTGSSPLGATQLDTDGALWLGGLPELPVGPALPKAYGTGFVGCLRDVVVGRHPLHLLEDAVTKPELRPCPTP
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
heparan sulfate basal lamina glycoprotein that plays a central role in the formation and the maintenance of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) and directs key events in postsynaptic differentiation. Component of the AGRN-LRP4 receptor complex that induces the phosphorylation and activation of MUSK. The activation of MUSK in myotubes induces the formation of NMJ by regulating different processes including the transcription of specific genes and the clustering of AChR in the postsynaptic membrane. Calcium ions are required for maximal AChR clustering. AGRN function in neurons is highly regulated by alternative splicing, glycan binding and proteolytic processing. Modulates calcium ion homeostasis in neurons, specifically by inducing an increase in cytoplasmic calcium ions. Functions differentially in the central nervous system (CNS) by inhibiting the alpha(3)-subtype of Na+/K+-ATPase and evoking depolarization at CNS synapses. This secreted isoform forms a bridge, after release from motor neurons, to basal lamina through binding laminin via the NtA domain.
transmembrane form that is the predominate form in neurons of the brain, induces dendritic filopodia and synapse formation in mature hippocampal neurons in large part due to the attached glycosaminoglycan chains and the action of Rho-family GTPases.
Isoform 1, isoform 4 and isoform 5: neuron-specific (z+) isoforms that contain C-terminal insertions of 8-19 AA are potent activators of AChR clustering. Isoform 5, agrin (z+8), containing the 8-AA insert, forms a receptor complex in myotubules containing the neuronal AGRN, the muscle-specific kinase MUSK and LRP4, a member of the LDL receptor family. The splicing factors, NOVA1 and NOVA2, regulate AGRN splicing and production of the 'z' isoforms.
Isoform 3 and isoform 6: lack any 'z' insert, are muscle-specific and may be involved in endothelial cell differentiation.
is involved in regulation of neurite outgrowth probably due to the presence of the glycosaminoglcan (GAG) side chains of heparan and chondroitin sulfate attached to the Ser/Thr- and Gly/Ser-rich regions. Also involved in modulation of growth factor signaling (By similarity).
this released fragment is important for agrin signaling and to exert a maximal dendritic filopodia-inducing effect. All 'z' splice variants (z+) of this fragment also show an increase in the number of filopodia.
Contains heparan and chondroitin sulfate chains and alpha-dystroglycan as well as N-linked and O-linked oligosaccharides. Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), present in the N-terminal 110 kDa fragment, are required for induction of filopodia in hippocampal neurons. The first cluster (Gly/Ser-rich) for GAG attachment contains heparan sulfate (HS) chains and the second cluster (Ser/Thr-rich), contains chondroitin sulfate (CS) chains. Heparin and heparin sulfate binding in the G3 domain is independent of calcium ions. Binds heparin with a stoichiometry of 2:1. Binds sialic acid with a stoichiometry of 1:1 and binding requires calcium ions (By similarity).
At synaptic junctions, cleaved at two conserved sites, alpha and beta, by neurotrypsin. Cleavage at the alpha-site produces the agrin N-terminal 110-kDa subunit and the agrin C-terminal 110-kDa subunit. Further cleavage of agrin C-terminal 110-kDa subunit at the beta site produces the C-terminal fragments, agrin C-terminal 90 kDa fragment and agrin C-terminal 22 kDa fragment. Excessive cleavage at the beta-site releases large amounts of the agrin C-terminal 22 kDa fragment leading to destabilization at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ).
Secreted>Extracellular space>Extracellular matrix.
Note: Synaptic basal lamina at the neuromuscular junction.
Cell junction>Synapse. Cell membrane>Single-pass type II membrane protein.
Expressed in basement membranes of lung and kidney. Muscle- and neuron-specific isoforms are found. Isoforms (y+) with the 4 AA insert and (z+8) isoforms with the 8 AA insert are all neuron-specific. Isoforms (z+11) are found in both neuronal and non-neuronal tissues.
The NtA domain, absent in TM-agrin, is required for binding laminin and connecting to basal lamina.
Both laminin G-like 2 (G2) and laminin G-like 3 (G3) domains are required for alpha-dystroglycan/DAG1 binding. G3 domain is required for C-terminal heparin, heparan sulfate and sialic acid binding (By similarity).
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > ECM-receptor interaction. (View pathway)
References
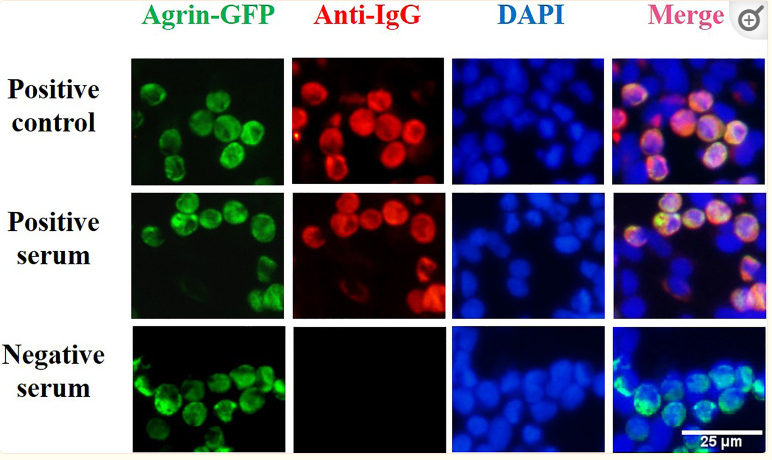
Application: IF/ICC Species: Human Sample: HEK293T cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.