HSPA6 Antibody - #DF8465
| Product: | HSPA6 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF8465 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to HSPA6 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse |
| Mol.Wt.: | 71 kDa; 71kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P17066 |
| RRID: | AB_2841698 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF8465, RRID:AB_2841698.
Fold/Unfold
Heat shock 70 kDa protein 6; Heat shock 70 kDa protein B'; Heat shock 70 kDa protein B''; heat shock 70kD protein 6 (HSP70B'); Heat shock 70kDa protein 6; HSP70B'; HSP70B-Prime; HSP76_HUMAN; HSPA6; OTTHUMP00000032372;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human HSPA6, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- P17066 HSP76_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MQAPRELAVGIDLGTTYSCVGVFQQGRVEILANDQGNRTTPSYVAFTDTERLVGDAAKSQAALNPHNTVFDAKRLIGRKFADTTVQSDMKHWPFRVVSEGGKPKVRVCYRGEDKTFYPEEISSMVLSKMKETAEAYLGQPVKHAVITVPAYFNDSQRQATKDAGAIAGLNVLRIINEPTAAAIAYGLDRRGAGERNVLIFDLGGGTFDVSVLSIDAGVFEVKATAGDTHLGGEDFDNRLVNHFMEEFRRKHGKDLSGNKRALRRLRTACERAKRTLSSSTQATLEIDSLFEGVDFYTSITRARFEELCSDLFRSTLEPVEKALRDAKLDKAQIHDVVLVGGSTRIPKVQKLLQDFFNGKELNKSINPDEAVAYGAAVQAAVLMGDKCEKVQDLLLLDVAPLSLGLETAGGVMTTLIQRNATIPTKQTQTFTTYSDNQPGVFIQVYEGERAMTKDNNLLGRFELSGIPPAPRGVPQIEVTFDIDANGILSVTATDRSTGKANKITITNDKGRLSKEEVERMVHEAEQYKAEDEAQRDRVAAKNSLEAHVFHVKGSLQEESLRDKIPEEDRRKMQDKCREVLAWLEHNQLAEKEEYEHQKRELEQICRPIFSRLYGGPGVPGGSSCGTQARQGDPSTGPIIEEVD
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Molecular chaperone implicated in a wide variety of cellular processes, including protection of the proteome from stress, folding and transport of newly synthesized polypeptides, activation of proteolysis of misfolded proteins and the formation and dissociation of protein complexes. Plays a pivotal role in the protein quality control system, ensuring the correct folding of proteins, the re-folding of misfolded proteins and controlling the targeting of proteins for subsequent degradation. This is achieved through cycles of ATP binding, ATP hydrolysis and ADP release, mediated by co-chaperones. The affinity for polypeptides is regulated by its nucleotide bound state. In the ATP-bound form, it has a low affinity for substrate proteins. However, upon hydrolysis of the ATP to ADP, it undergoes a conformational change that increases its affinity for substrate proteins. It goes through repeated cycles of ATP hydrolysis and nucleotide exchange, which permits cycles of substrate binding and release.
The N-terminal nucleotide binding domain (NBD) (also known as the ATPase domain) is responsible for binding and hydrolyzing ATP. The C-terminal substrate-binding domain (SBD) (also known as peptide-binding domain) binds to the client/substrate proteins. The two domains are allosterically coupled so that, when ATP is bound to the NBD, the SBD binds relatively weakly to clients. When ADP is bound in the NBD, a conformational change enhances the affinity of the SBD for client proteins.
Belongs to the heat shock protein 70 family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Transcription > Spliceosome.
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Legionellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Antigen processing and presentation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
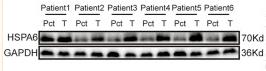
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: glioma tissues and matched para-carcinoma tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.