RXR alpha Antibody - #DF8459
| Product: | RXR alpha Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF8459 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to RXR alpha |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 51kDa; 51kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P19793 |
| RRID: | AB_2841695 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF8459, RRID:AB_2841695.
Fold/Unfold
FLJ00280; FLJ00318; FLJ16020; FLJ16733; MGC102720; NR2B1; Nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group B member 1; OTTHUMP00000022510; Retinoic acid receptor RXR alpha; Retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha; Retinoid X nuclear receptor alpha; Retinoid X receptor alpha; RXR alpha1; Rxra; RXRA_HUMAN; RXRalpha1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human RXR alpha, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Expressed in lung fibroblasts (at protein level) (PubMed:30216632). Expressed in monocytes (PubMed:26463675). Highly expressed in liver, also found in kidney and brain (PubMed:24275569, PubMed:2159111, PubMed:14702039).
- P19793 RXRA_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDTKHFLPLDFSTQVNSSLTSPTGRGSMAAPSLHPSLGPGIGSPGQLHSPISTLSSPINGMGPPFSVISSPMGPHSMSVPTTPTLGFSTGSPQLSSPMNPVSSSEDIKPPLGLNGVLKVPAHPSGNMASFTKHICAICGDRSSGKHYGVYSCEGCKGFFKRTVRKDLTYTCRDNKDCLIDKRQRNRCQYCRYQKCLAMGMKREAVQEERQRGKDRNENEVESTSSANEDMPVERILEAELAVEPKTETYVEANMGLNPSSPNDPVTNICQAADKQLFTLVEWAKRIPHFSELPLDDQVILLRAGWNELLIASFSHRSIAVKDGILLATGLHVHRNSAHSAGVGAIFDRVLTELVSKMRDMQMDKTELGCLRAIVLFNPDSKGLSNPAEVEALREKVYASLEAYCKHKYPEQPGRFAKLLLRLPALRSIGLKCLEHLFFFKLIGDTPIDTFLMEMLEAPHQMT
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Receptor for retinoic acid that acts as a transcription factor. Forms homo- or heterodimers with retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and binds to target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, to regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RAR/RXR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5 to regulate transcription. The high affinity ligand for retinoid X receptors (RXRs) is 9-cis retinoic acid. In the absence of ligand, the RXR-RAR heterodimers associate with a multiprotein complex containing transcription corepressors that induce histone deacetylation, chromatin condensation and transcriptional suppression. On ligand binding, the corepressors dissociate from the receptors and coactivators are recruited leading to transcriptional activation. Serves as a common heterodimeric partner for a number of nuclear receptors, such as RARA, RARB and PPARA. The RXRA/RARB heterodimer can act as a transcriptional repressor or transcriptional activator, depending on the RARE DNA element context. The RXRA/PPARA heterodimer is required for PPARA transcriptional activity on fatty acid oxidation genes such as ACOX1 and the P450 system genes. Together with RARA, positively regulates microRNA-10a expression, thereby inhibiting the GATA6/VCAM1 signaling response to pulsatile shear stress in vascular endothelial cells. Acts as an enhancer of RARA binding to RARE DNA element. May facilitate the nuclear import of heterodimerization partners such as VDR and NR4A1. Promotes myelin debris phagocytosis and remyelination by macrophages. Plays a role in the attenuation of the innate immune system in response to viral infections, possibly by negatively regulating the transcription of antiviral genes such as type I IFN genes. Involved in the regulation of calcium signaling by repressing ITPR2 gene expression, thereby controlling cellular senescence.
Acetylated by EP300; acetylation enhances DNA binding and transcriptional activity.
Phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues mainly in the N-terminal modulating domain (By similarity). Constitutively phosphorylated on Ser-21 in the presence or absence of ligand (By similarity). Under stress conditions, hyperphosphorylated by activated JNK on Ser-56, Ser-70, Thr-82 and Ser-260 (By similarity). Phosphorylated on Ser-27, in vitro, by PKA. This phosphorylation is required for repression of cAMP-mediated transcriptional activity of RARA.
Sumoylation negatively regulates transcriptional activity. Desumoylated specifically by SENP6.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Mitochondrion.
Note: Localization to the nucleus is enhanced by vitamin D3 (PubMed:15509776). Nuclear localization may be enhanced by the interaction with heterodimerization partner VDR (PubMed:12145331). Translocation to the mitochondrion upon interaction with NR4A1 (PubMed:17761950, PubMed:15509776). Increased nuclear localization upon pulsatile shear stress (PubMed:28167758).
Expressed in lung fibroblasts (at protein level). Expressed in monocytes. Highly expressed in liver, also found in kidney and brain.
Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain (AF1 domain), a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal ligand-binding domain (AF2 domain).
Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR2 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Transcriptional misregulation in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Thyroid cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Non-small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > PPAR signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Adipocytokine signaling pathway.
References
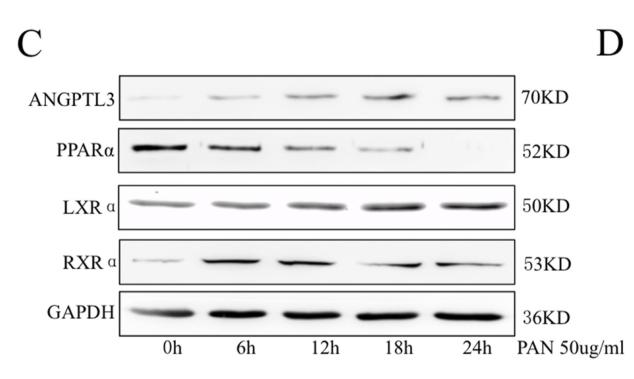
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: podocytes
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.