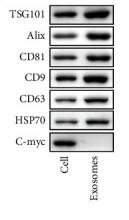
TSG101 Antibody - #DF8427
| Product: | TSG101 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF8427 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to TSG101 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 45 kDa; 44kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q99816 |
| RRID: | AB_2841675 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF8427, RRID:AB_2841675.
Fold/Unfold
ESCRT I complex subunit TSG101; ESCRT-I complex subunit TSG101; TS101_HUMAN; TSG 10; TSG 101; TSG10; Tsg101; Tumor susceptibility gene 10; Tumor susceptibility gene 101; Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein; Tumor susceptibility protein; Tumor susceptibility protein isoform 3; VPS 23; VPS23;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human TSG101, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- Q99816 TS101_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAVSESQLKKMVSKYKYRDLTVRETVNVITLYKDLKPVLDSYVFNDGSSRELMNLTGTIPVPYRGNTYNIPICLWLLDTYPYNPPICFVKPTSSMTIKTGKHVDANGKIYLPYLHEWKHPQSDLLGLIQVMIVVFGDEPPVFSRPISASYPPYQATGPPNTSYMPGMPGGISPYPSGYPPNPSGYPGCPYPPGGPYPATTSSQYPSQPPVTTVGPSRDGTISEDTIRASLISAVSDKLRWRMKEEMDRAQAELNALKRTEEDLKKGHQKLEEMVTRLDQEVAEVDKNIELLKKKDEELSSALEKMENQSENNDIDEVIIPTAPLYKQILNLYAEENAIEDTIFYLGEALRRGVIDLDVFLKHVRLLSRKQFQLRALMQKARKTAGLSDLY
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Component of the ESCRT-I complex, a regulator of vesicular trafficking process. Binds to ubiquitinated cargo proteins and is required for the sorting of endocytic ubiquitinated cargos into multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Mediates the association between the ESCRT-0 and ESCRT-I complex. Required for completion of cytokinesis; the function requires CEP55. May be involved in cell growth and differentiation. Acts as a negative growth regulator. Involved in the budding of many viruses through an interaction with viral proteins that contain a late-budding motif P-[ST]-A-P. This interaction is essential for viral particle budding of numerous retroviruses. Required for the exosomal release of SDCBP, CD63 and syndecan. It may also play a role in the extracellular release of microvesicles that differ from the exosomes.
Monoubiquitinated at multiple sites by LRSAM1 and by MGRN1. Ubiquitination inactivates it, possibly by regulating its shuttling between an active membrane-bound protein and an inactive soluble form. Ubiquitination by MGRN1 requires the presence of UBE2D1.
Cytoplasm. Early endosome membrane>Peripheral membrane protein>Cytoplasmic side. Late endosome membrane>Peripheral membrane protein. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Midbody>Midbody ring. Nucleus.
Note: Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis.
Heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal, kidney and pancreas.
The UEV domain is required for the interaction of the complex with ubiquitin. It also mediates the interaction with PTAP/PSAP motifs of HIV-1 P6 protein and human spumaretrovirus Gag protein.
The coiled coil domain may interact with stathmin.
The UEV domain binds ubiquitin and P-[ST]-A-P peptide motif independently.
Belongs to the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family. UEV subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
References
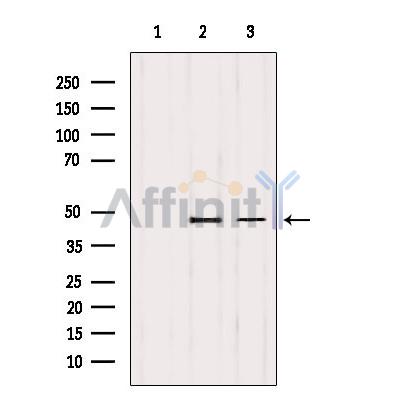
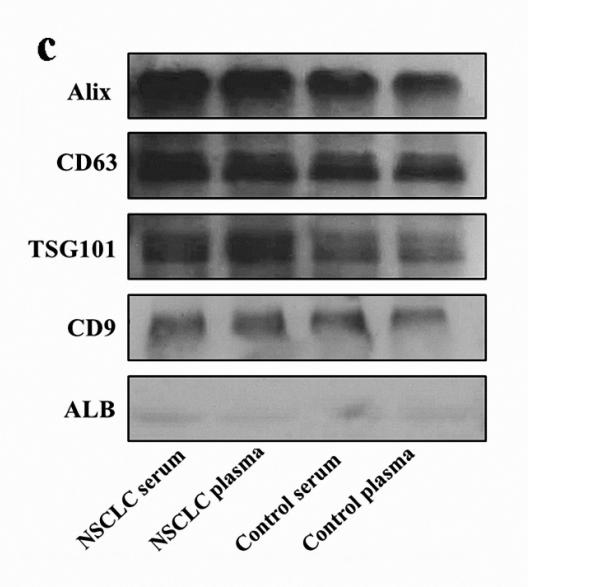
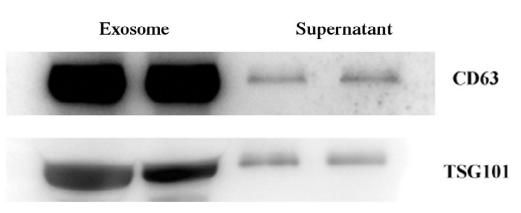
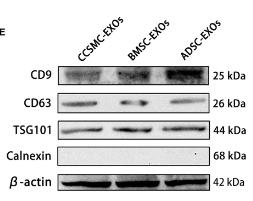
Application: WB Species: Human Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: BM-MSCs cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.