GABBR2 Antibody - #DF7800
| Product: | GABBR2 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7800 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to GABBR2 |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 106kDa; 106kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | O75899 |
| RRID: | AB_2841255 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7800, RRID:AB_2841255.
Fold/Unfold
BcDNA:GH07312; CG6706; CT20836; D Gaba2; FLJ36928; G protein coupled receptor 51; G-protein coupled receptor 51; GAB B R2; GABA B R2; GABA B receptor 2; GABA-B receptor 2; GABA-B-R2; GABA-BR2; GABAB R2; GABABR 2; GABABR2; GABB R2; GABBR 2; Gabbr2; GABR2_HUMAN; Gamma aminobutyric acid B receptor 2; Gamma aminobutyric acid GABA B receptor 2; Gamma aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 2; Gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 2; Gb 2; Gb2; GH07312; GPR 51; GPR51; GPRC 3B; GPRC3B; HG 20; HG20; HRIHFB2099; Metabotropic GABA B receptor subtype 2; OTTHUMP00000021776; OTTHUMP00000063797; R2 SUBUNIT;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human GABBR2, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Highly expressed in brain, especially in cerebral cortex, thalamus, hippocampus, frontal, occipital and temporal lobe, occipital pole and cerebellum, followed by corpus callosum, caudate nucleus, spinal cord, amygdala and medulla (PubMed:10087195, PubMed:10328880, PubMed:10727622, PubMed:9872744). Weakly expressed in heart, testis and skeletal muscle (PubMed:10087195, PubMed:10727622).
- O75899 GABR2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MASPRSSGQPGPPPPPPPPPARLLLLLLLPLLLPLAPGAWGWARGAPRPPPSSPPLSIMGLMPLTKEVAKGSIGRGVLPAVELAIEQIRNESLLRPYFLDLRLYDTECDNAKGLKAFYDAIKYGPNHLMVFGGVCPSVTSIIAESLQGWNLVQLSFAATTPVLADKKKYPYFFRTVPSDNAVNPAILKLLKHYQWKRVGTLTQDVQRFSEVRNDLTGVLYGEDIEISDTESFSNDPCTSVKKLKGNDVRIILGQFDQNMAAKVFCCAYEENMYGSKYQWIIPGWYEPSWWEQVHTEANSSRCLRKNLLAAMEGYIGVDFEPLSSKQIKTISGKTPQQYEREYNNKRSGVGPSKFHGYAYDGIWVIAKTLQRAMETLHASSRHQRIQDFNYTDHTLGRIILNAMNETNFFGVTGQVVFRNGERMGTIKFTQFQDSREVKVGEYNAVADTLEIINDTIRFQGSEPPKDKTIILEQLRKISLPLYSILSALTILGMIMASAFLFFNIKNRNQKLIKMSSPYMNNLIILGGMLSYASIFLFGLDGSFVSEKTFETLCTVRTWILTVGYTTAFGAMFAKTWRVHAIFKNVKMKKKIIKDQKLLVIVGGMLLIDLCILICWQAVDPLRRTVEKYSMEPDPAGRDISIRPLLEHCENTHMTIWLGIVYAYKGLLMLFGCFLAWETRNVSIPALNDSKYIGMSVYNVGIMCIIGAAVSFLTRDQPNVQFCIVALVIIFCSTITLCLVFVPKLITLRTNPDAATQNRRFQFTQNQKKEDSKTSTSVTSVNQASTSRLEGLQSENHRLRMKITELDKDLEEVTMQLQDTPEKTTYIKQNHYQELNDILNLGNFTESTDGGKAILKNHLDQNPQLQWNTTEPSRTCKDPIEDINSPEHIQRRLSLQLPILHHAYLPSIGGVDASCVSPCVSPTASPRHRHVPPSFRVMVSGL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Component of a heterodimeric G-protein coupled receptor for GABA, formed by GABBR1 and GABBR2. Within the heterodimeric GABA receptor, only GABBR1 seems to bind agonists, while GABBR2 mediates coupling to G proteins. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase, stimulates phospholipase A2, activates potassium channels, inactivates voltage-dependent calcium-channels and modulates inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Plays a critical role in the fine-tuning of inhibitory synaptic transmission. Pre-synaptic GABA receptor inhibits neurotransmitter release by down-regulating high-voltage activated calcium channels, whereas postsynaptic GABA receptor decreases neuronal excitability by activating a prominent inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) conductance that underlies the late inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. Not only implicated in synaptic inhibition but also in hippocampal long-term potentiation, slow wave sleep, muscle relaxation and antinociception (Probable).
Cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell junction>Synapse>Postsynaptic cell membrane>Multi-pass membrane protein.
Note: Coexpression of GABBR1 and GABBR2 is required for GABBR1 maturation and transport to the plasma membrane. In contrast, GABBR2 does not depend on GABBR1 for transport to the cell membrane.
Highly expressed in brain, especially in cerebral cortex, thalamus, hippocampus, frontal, occipital and temporal lobe, occipital pole and cerebellum, followed by corpus callosum, caudate nucleus, spinal cord, amygdala and medulla. Weakly expressed in heart, testis and skeletal muscle.
Alpha-helical parts of the C-terminal intracellular region mediate heterodimeric interaction with GABBR1.
Belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 3 family. GABA-B receptor subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Morphine addiction.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > GABAergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Sensory system > Taste transduction.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
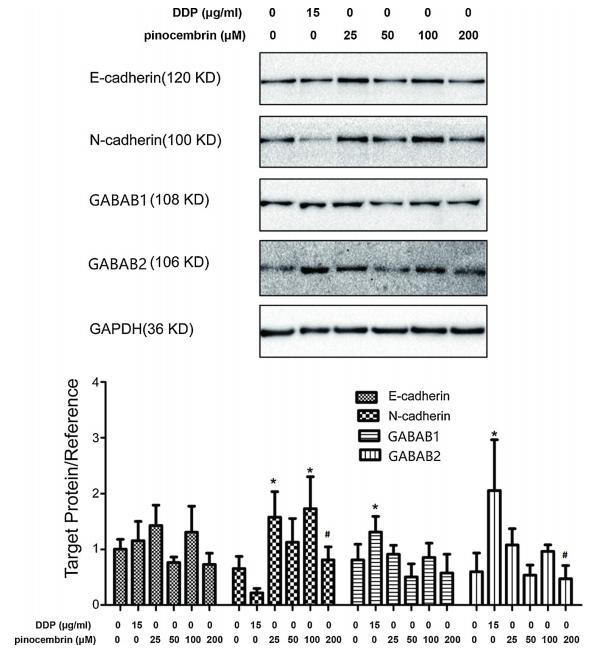
Application: WB Species: human Sample: SKOV3 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.