Shh Antibody - #DF7747
| Product: | Shh Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7747 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Shh |
| Application: | WB |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 51 kDa; 50kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q15465 |
| RRID: | AB_2841213 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7747, RRID:AB_2841213.
Fold/Unfold
HHG 1; HHG-1; HHG1; HLP 3; HLP3; Holoprosencephaly 3; HPE 3; HPE3; MCOPCB5; shh; SHH_HUMAN; SMMC I; SMMCI; Sonic Hedgehog (Drosophila) homolog; sonic hedgehog homolog (Drosophila); Sonic hedgehog homolog; Sonic hedgehog protein; Sonic hedgehog protein C-product; TPT; TPTPS;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Shh, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- Q15465 SHH_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MLLLARCLLLVLVSSLLVCSGLACGPGRGFGKRRHPKKLTPLAYKQFIPNVAEKTLGASGRYEGKISRNSERFKELTPNYNPDIIFKDEENTGADRLMTQRCKDKLNALAISVMNQWPGVKLRVTEGWDEDGHHSEESLHYEGRAVDITTSDRDRSKYGMLARLAVEAGFDWVYYESKAHIHCSVKAENSVAAKSGGCFPGSATVHLEQGGTKLVKDLSPGDRVLAADDQGRLLYSDFLTFLDRDDGAKKVFYVIETREPRERLLLTAAHLLFVAPHNDSATGEPEASSGSGPPSGGALGPRALFASRVRPGQRVYVVAERDGDRRLLPAAVHSVTLSEEAAGAYAPLTAQGTILINRVLASCYAVIEEHSWAHRAFAPFRLAHALLAALAPARTDRGGDSGGGDRGGGGGRVALTAPGAADAPGAGATAGIHWYSQLLYQIGTWLLDSEALHPLGMAVKSS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
The C-terminal part of the sonic hedgehog protein precursor displays an autoproteolysis and a cholesterol transferase activity (By similarity). Both activities result in the cleavage of the full-length protein into two parts (ShhN and ShhC) followed by the covalent attachment of a cholesterol moiety to the C-terminal of the newly generated ShhN (By similarity). Both activities occur in the reticulum endoplasmic (By similarity). Once cleaved, ShhC is degraded in the endoplasmic reticulum (By similarity).
The dually lipidated sonic hedgehog protein N-product (ShhNp) is a morphogen which is essential for a variety of patterning events during development. Induces ventral cell fate in the neural tube and somites. Involved in the patterning of the anterior-posterior axis of the developing limb bud (By similarity). Essential for axon guidance (By similarity). Binds to the patched (PTCH1) receptor, which functions in association with smoothened (SMO), to activate the transcription of target genes. In the absence of SHH, PTCH1 represses the constitutive signaling activity of SMO.
The C-terminal domain displays an autoproteolysis activity and a cholesterol transferase activity (By similarity). Both activities result in the cleavage of the full-length protein and covalent attachment of a cholesterol moiety to the C-terminal of the newly generated N-terminal fragment (ShhN) (By similarity). Cholesterylation is required for the sonic hedgehog protein N-product targeting to lipid rafts and multimerization. ShhN is the active species in both local and long-range signaling, whereas the C-product (ShhC) is degraded in the reticulum endoplasmic (By similarity).
N-palmitoylation by HHAT of ShhN is required for sonic hedgehog protein N-product multimerization and full activity (By similarity). It is a prerequisite for the membrane-proximal positioning and the subsequent shedding of this N-terminal peptide.
The lipidated N- and C-terminal peptides of ShhNp can be cleaved (shedding). The N-terminal palmitoylated peptide is cleaved at the Cardin-Weintraub (CW) motif site. The cleavage reduced the interactions with heparan sulfate. The cleavage is enhanced by SCUBE2.
Cell membrane>Lipid-anchor.
Note: The dual-lipidated sonic hedgehog protein N-product (ShhNp) is firmly tethered to the cell membrane where it forms multimers (PubMed:24522195). Further solubilization and release from the cell surface seem to be achieved through different mechanisms, including the interaction with DISP1 and SCUBE2, movement by lipoprotein particles, transport by cellular extensions called cytonemes or by the proteolytic removal of both terminal lipidated peptides (PubMed:26875496, PubMed:24522195).
Binds calcium and zinc ions; this stabilizes the protein fold and is essential for protein-protein interactions mediated by this domain.
The Cardin-Weintraub (CW) motif is required for heparan sulfate binding of the solubilized ShhNp (PubMed:23118222). The N-terminal palmitoylated peptide is cleaved at the heparan sulfate-binding Cardin-Weintraub (CW) motif site (PubMed:24522195). The cleavage reduced the interactions with heparan sulfate. The cleavage is enhanced by SCUBE2 (PubMed:24522195).
Belongs to the hedgehog family.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hedgehog signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Basal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Axon guidance. (View pathway)
References
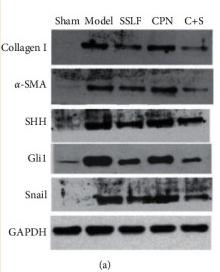
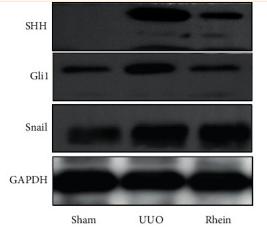
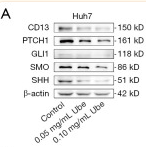
Application: WB Species: human Sample: HIBECs
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: liver cancer cell
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: renal tissues
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.