Bone Sialoprotein Antibody - #DF7738
| Product: | Bone Sialoprotein Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7738 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Bone Sialoprotein |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 35 kDa.; 35kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P21815 |
| RRID: | AB_2841206 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7738, RRID:AB_2841206.
Fold/Unfold
BNSP; Bone sialoprotein 2; Bone sialoprotein II; BSP; BSP II; BSPII; Cell binding sialoprotein; Cell-binding sialoprotein; IBSP; Integrin binding sialoprotein; Integrin-binding sialoprotein; SIAL_HUMAN; SPII;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Bone Sialoprotein, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
- P21815 SIAL_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MKTALILLSILGMACAFSMKNLHRRVKIEDSEENGVFKYRPRYYLYKHAYFYPHLKRFPVQGSSDSSEENGDDSSEEEEEEEETSNEGENNEESNEDEDSEAENTTLSATTLGYGEDATPGTGYTGLAAIQLPKKAGDITNKATKEKESDEEEEEEEEGNENEESEAEVDENEQGINGTSTNSTEAENGNGSSGGDNGEEGEEESVTGANAEDTTETGRQGKGTSKTTTSPNGGFEPTTPPQVYRTTSPPFGKTTTVEYEGEYEYTGANEYDNGYEIYESENGEPRGDNYRAYEDEYSYFKGQGYDGYDGQNYYHHQ
Research Backgrounds
Binds tightly to hydroxyapatite. Appears to form an integral part of the mineralized matrix. Probably important to cell-matrix interaction. Promotes Arg-Gly-Asp-dependent cell attachment.
N-glycosylated; glycans consist of sialylated and core-fucosylated bi-, tri- and tetraantennary chains.
O-glycosylated at eight sites; mucin-type glycans contain Gal, GlcNAc, GalNAc and terminal NeuAc.
Sulfated on either Tyr-313 or Tyr-314.
Secreted.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > ECM-receptor interaction. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
References
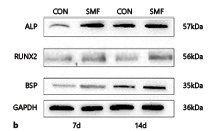
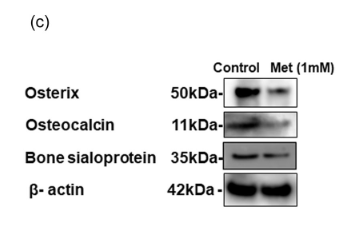
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: VSMCs
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: PDLSCs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.