Phospho-IRAK4 (Thr345/Ser346) Antibody - #DF7567
| Product: | Phospho-IRAK4 (Thr345/Ser346) Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7567 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-IRAK4 (Thr345/Ser346) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 60 kDa; 52kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9NWZ3 |
| RRID: | AB_2841060 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7567, RRID:AB_2841060.
Fold/Unfold
IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4; Interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase 4 mutant form 1; Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4; Interleukin1 receptor associated kinase 4; IPD1; IRAK 4; IRAK-4; IRAK4; IRAK4 mutated form 1; IRAK4_HUMAN; LOC 51135; NY REN 64; NY REN 64 antigen; NY-REN-64; REN64; Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-64;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human IRAK4 around the phosphorylation site of Thr345/Ser346.
- Q9NWZ3 IRAK4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MNKPITPSTYVRCLNVGLIRKLSDFIDPQEGWKKLAVAIKKPSGDDRYNQFHIRRFEALLQTGKSPTSELLFDWGTTNCTVGDLVDLLIQNEFFAPASLLLPDAVPKTANTLPSKEAITVQQKQMPFCDKDRTLMTPVQNLEQSYMPPDSSSPENKSLEVSDTRFHSFSFYELKNVTNNFDERPISVGGNKMGEGGFGVVYKGYVNNTTVAVKKLAAMVDITTEELKQQFDQEIKVMAKCQHENLVELLGFSSDGDDLCLVYVYMPNGSLLDRLSCLDGTPPLSWHMRCKIAQGAANGINFLHENHHIHRDIKSANILLDEAFTAKISDFGLARASEKFAQTVMTSRIVGTTAYMAPEALRGEITPKSDIYSFGVVLLEIITGLPAVDEHREPQLLLDIKEEIEDEEKTIEDYIDKKMNDADSTSVEAMYSVASQCLHEKKNKRPDIKKVQQLLQEMTAS
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays a critical role in initiating innate immune response against foreign pathogens. Involved in Toll-like receptor (TLR) and IL-1R signaling pathways. Is rapidly recruited by MYD88 to the receptor-signaling complex upon TLR activation to form the Myddosome together with IRAK2. Phosphorylates initially IRAK1, thus stimulating the kinase activity and intensive autophosphorylation of IRAK1. Phosphorylates E3 ubiquitin ligases Pellino proteins (PELI1, PELI2 and PELI3) to promote pellino-mediated polyubiquitination of IRAK1. Then, the ubiquitin-binding domain of IKBKG/NEMO binds to polyubiquitinated IRAK1 bringing together the IRAK1-MAP3K7/TAK1-TRAF6 complex and the NEMO-IKKA-IKKB complex. In turn, MAP3K7/TAK1 activates IKKs (CHUK/IKKA and IKBKB/IKKB) leading to NF-kappa-B nuclear translocation and activation. Alternatively, phosphorylates TIRAP to promote its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Phosphorylates NCF1 and regulates NADPH oxidase activation after LPS stimulation suggesting a similar mechanism during microbial infections.
Phosphorylated.
Cytoplasm.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family. Pelle subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pertussis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Tuberculosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Neurotrophin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
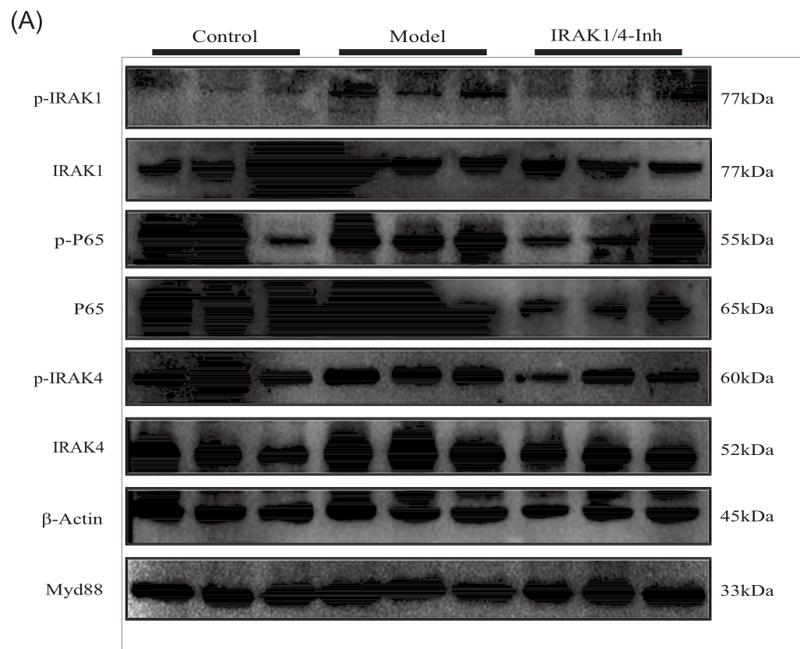
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: OPCs
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample: OPCs
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: HCT‐116 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.