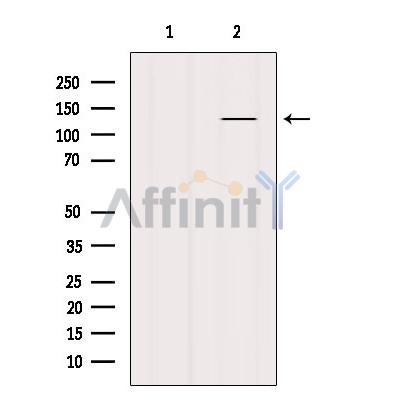
Bamacan Antibody - #DF7558
| Product: | Bamacan Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7558 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Bamacan |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 142kDa; 142kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9UQE7 |
| RRID: | AB_2841052 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7558, RRID:AB_2841052.
Fold/Unfold
BAM; Bamacan; Basement membrane associated chondroitin proteoglycan; Basement membrane-associated chondroitin proteoglycan; BMH; CDLS3; chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 6 (bamacan); Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 6; Chromosome associated polypeptide; Chromosome-associated polypeptide; CSPG 6; CSPG6; hCAP; Human chromosome associated polypeptide; im:7142991; SMC 3; SMC protein 3; SMC-3; smc3; SMC3_HUMAN; SMC3L1; Structural maintenance of chromosome 3; Structural maintenance of chromosomes 3; Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 3; u:fb22e01; wu:fc30d07;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Bamacan, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- Q9UQE7 SMC3_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MYIKQVIIQGFRSYRDQTIVDPFSSKHNVIVGRNGSGKSNFFYAIQFVLSDEFSHLRPEQRLALLHEGTGPRVISAFVEIIFDNSDNRLPIDKEEVSLRRVIGAKKDQYFLDKKMVTKNDVMNLLESAGFSRSNPYYIVKQGKINQMATAPDSQRLKLLREVAGTRVYDERKEESISLMKETEGKREKINELLKYIEERLHTLEEEKEELAQYQKWDKMRRALEYTIYNQELNETRAKLDELSAKRETSGEKSRQLRDAQQDARDKMEDIERQVRELKTKISAMKEEKEQLSAERQEQIKQRTKLELKAKDLQDELAGNSEQRKRLLKERQKLLEKIEEKQKELAETEPKFNSVKEKEERGIARLAQATQERTDLYAKQGRGSQFTSKEERDKWIKKELKSLDQAINDKKRQIAAIHKDLEDTEANKEKNLEQYNKLDQDLNEVKARVEELDRKYYEVKNKKDELQSERNYLWREENAEQQALAAKREDLEKKQQLLRAATGKAILNGIDSINKVLDHFRRKGINQHVQNGYHGIVMNNFECEPAFYTCVEVTAGNRLFYHIVDSDEVSTKILMEFNKMNLPGEVTFLPLNKLDVRDTAYPETNDAIPMISKLRYNPRFDKAFKHVFGKTLICRSMEVSTQLARAFTMDCITLEGDQVSHRGALTGGYYDTRKSRLELQKDVRKAEEELGELEAKLNENLRRNIERINNEIDQLMNQMQQIETQQRKFKASRDSILSEMKMLKEKRQQSEKTFMPKQRSLQSLEASLHAMESTRESLKAELGTDLLSQLSLEDQKRVDALNDEIRQLQQENRQLLNERIKLEGIITRVETYLNENLRKRLDQVEQELNELRETEGGTVLTATTSELEAINKRVKDTMARSEDLDNSIDKTEAGIKELQKSMERWKNMEKEHMDAINHDTKELEKMTNRQGMLLKKKEECMKKIRELGSLPQEAFEKYQTLSLKQLFRKLEQCNTELKKYSHVNKKALDQFVNFSEQKEKLIKRQEELDRGYKSIMELMNVLELRKYEAIQLTFKQVSKNFSEVFQKLVPGGKATLVMKKGDVEGSQSQDEGEGSGESERGSGSQSSVPSVDQFTGVGIRVSFTGKQGEMREMQQLSGGQKSLVALALIFAIQKCDPAPFYLFDEIDQALDAQHRKAVSDMIMELAVHAQFITTTFRPELLESADKFYGVKFRNKVSHIDVITAEMAKDFVEDDTTHG
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Central component of cohesin, a complex required for chromosome cohesion during the cell cycle. The cohesin complex may form a large proteinaceous ring within which sister chromatids can be trapped. At anaphase, the complex is cleaved and dissociates from chromatin, allowing sister chromatids to segregate. Cohesion is coupled to DNA replication and is involved in DNA repair. The cohesin complex plays also an important role in spindle pole assembly during mitosis and in chromosomes movement.
Phosphorylated at Ser-1083 in a SPO11-dependent manner.
Acetylation at Lys-105 and Lys-106 by ESCO1 is important for genome stability and S phase sister chromatid cohesion. Regulated by DSCC1, it is required for processive DNA synthesis, coupling sister chromatid cohesion establishment during S phase to DNA replication. Deacetylation by HDAC8, regulates release of the cohesin complex from chromatin.
Nucleus. Chromosome. Chromosome>Centromere.
Note: Associates with chromatin. Before prophase it is scattered along chromosome arms. During prophase, most of cohesin complexes dissociate from chromatin probably because of phosphorylation by PLK, except at centromeres, where cohesin complexes remain. At anaphase, the RAD21 subunit of the cohesin complex is cleaved, leading to the dissociation of the complex from chromosomes, allowing chromosome separation. The phosphorylated form at Ser-1083 is preferentially associated with unsynapsed chromosomal regions (By similarity).
The flexible SMC hinge domain, which separates the large intramolecular coiled coil regions, allows the heterotypic interaction with the corresponding domain of SMC1A or SMC1B, forming a V-shaped heterodimer. The two heads of the heterodimer are then connected by different ends of the cleavable RAD21 protein, forming a ring structure (By similarity).
Belongs to the SMC family. SMC3 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Oocyte meiosis. (View pathway)
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.