Raptor Antibody - #DF7527
| Product: | Raptor Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7527 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Raptor |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 149kDa; 149kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q8N122 |
| RRID: | AB_2841026 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7527, RRID:AB_2841026.
Fold/Unfold
KIAA1303; KOG1; Mip1; P150 target of rapamycin (TOR) scaffold protein; p150 target of rapamycin (TOR) scaffold protein containing WD repeats; P150 target of rapamycin (TOR)-scaffold protein; Raptor; Regulatory associated protein of mTOR; Regulatory associated protein of MTOR complex 1; Regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; RPTOR; RPTOR_HUMAN;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Raptor, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Highly expressed in skeletal muscle, and in a lesser extent in brain, lung, small intestine, kidney and placenta. Isoform 3 is widely expressed, with highest levels in nasal mucosa and pituitary and lowest in spleen.
- Q8N122 RPTOR_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MESEMLQSPLLGLGEEDEADLTDWNLPLAFMKKRHCEKIEGSKSLAQSWRMKDRMKTVSVALVLCLNVGVDPPDVVKTTPCARLECWIDPLSMGPQKALETIGANLQKQYENWQPRARYKQSLDPTVDEVKKLCTSLRRNAKEERVLFHYNGHGVPRPTVNGEVWVFNKNYTQYIPLSIYDLQTWMGSPSIFVYDCSNAGLIVKSFKQFALQREQELEVAAINPNHPLAQMPLPPSMKNCIQLAACEATELLPMIPDLPADLFTSCLTTPIKIALRWFCMQKCVSLVPGVTLDLIEKIPGRLNDRRTPLGELNWIFTAITDTIAWNVLPRDLFQKLFRQDLLVASLFRNFLLAERIMRSYNCTPVSSPRLPPTYMHAMWQAWDLAVDICLSQLPTIIEEGTAFRHSPFFAEQLTAFQVWLTMGVENRNPPEQLPIVLQVLLSQVHRLRALDLLGRFLDLGPWAVSLALSVGIFPYVLKLLQSSARELRPLLVFIWAKILAVDSSCQADLVKDNGHKYFLSVLADPYMPAEHRTMTAFILAVIVNSYHTGQEACLQGNLIAICLEQLNDPHPLLRQWVAICLGRIWQNFDSARWCGVRDSAHEKLYSLLSDPIPEVRCAAVFALGTFVGNSAERTDHSTTIDHNVAMMLAQLVSDGSPMVRKELVVALSHLVVQYESNFCTVALQFIEEEKNYALPSPATTEGGSLTPVRDSPCTPRLRSVSSYGNIRAVATARSLNKSLQNLSLTEESGGAVAFSPGNLSTSSSASSTLGSPENEEHILSFETIDKMRRASSYSSLNSLIGVSFNSVYTQIWRVLLHLAADPYPEVSDVAMKVLNSIAYKATVNARPQRVLDTSSLTQSAPASPTNKGVHIHQAGGSPPASSTSSSSLTNDVAKQPVSRDLPSGRPGTTGPAGAQYTPHSHQFPRTRKMFDKGPEQTADDADDAAGHKSFISATVQTGFCDWSARYFAQPVMKIPEEHDLESQIRKEREWRFLRNSRVRRQAQQVIQKGITRLDDQIFLNRNPGVPSVVKFHPFTPCIAVADKDSICFWDWEKGEKLDYFHNGNPRYTRVTAMEYLNGQDCSLLLTATDDGAIRVWKNFADLEKNPEMVTAWQGLSDMLPTTRGAGMVVDWEQETGLLMSSGDVRIVRIWDTDREMKVQDIPTGADSCVTSLSCDSHRSLIVAGLGDGSIRVYDRRMALSECRVMTYREHTAWVVKASLQKRPDGHIVSVSVNGDVRIFDPRMPESVNVLQIVKGLTALDIHPQADLIACGSVNQFTAIYNSSGELINNIKYYDGFMGQRVGAISCLAFHPHWPHLAVGSNDYYISVYSVEKRVR
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Involved in the control of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) activity which regulates cell growth and survival, and autophagy in response to nutrient and hormonal signals; functions as a scaffold for recruiting mTORC1 substrates. mTORC1 is activated in response to growth factors or amino acids. Growth factor-stimulated mTORC1 activation involves a AKT1-mediated phosphorylation of TSC1-TSC2, which leads to the activation of the RHEB GTPase that potently activates the protein kinase activity of mTORC1. Amino acid-signaling to mTORC1 requires its relocalization to the lysosomes mediated by the Ragulator complex and the Rag GTPases. Activated mTORC1 up-regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylating key regulators of mRNA translation and ribosome synthesis. mTORC1 phosphorylates EIF4EBP1 and releases it from inhibiting the elongation initiation factor 4E (eiF4E). mTORC1 phosphorylates and activates S6K1 at 'Thr-389', which then promotes protein synthesis by phosphorylating PDCD4 and targeting it for degradation. Involved in ciliogenesis.
Insulin-stimulated phosphorylation at Ser-863 by MTOR and MAPK8 up-regulates mTORC1 activity. Osmotic stress also induces phosphorylation at Ser-696, Thr-706 and Ser-863 by MAPK8. Ser-863 phosphorylation is required for phosphorylation at Ser-855 and Ser-859. In response to nutrient limitation, phosphorylated by AMPK; phosphorylation promotes interaction with 14-3-3 proteins, leading to negative regulation of the mTORC1 complex. In response to growth factors, phosphorylated at Ser-719, Ser-721 and Ser-722 by RPS6KA1, which stimulates mTORC1 activity.
Cytoplasm. Lysosome. Cytoplasmic granule.
Note: Targeting to lysosomes depends on amino acid availability. In arsenite-stressed cells, accumulates in stress granules when associated with SPAG5 and association with lysosomes is drastically decreased.
Highly expressed in skeletal muscle, and in a lesser extent in brain, lung, small intestine, kidney and placenta. Isoform 3 is widely expressed, with highest levels in nasal mucosa and pituitary and lowest in spleen.
Belongs to the WD repeat RAPTOR family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - other. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > mTOR signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
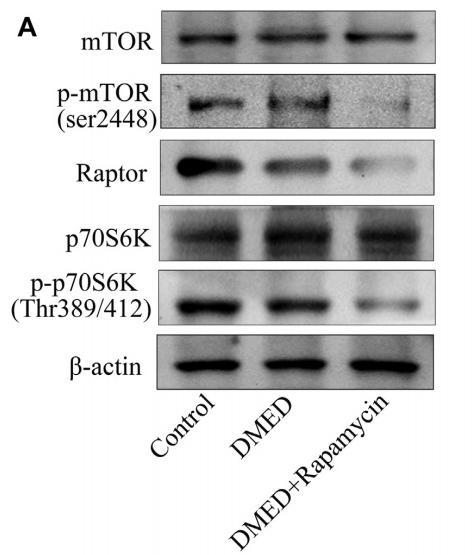
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
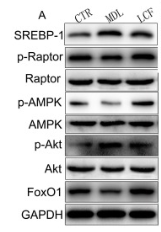
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
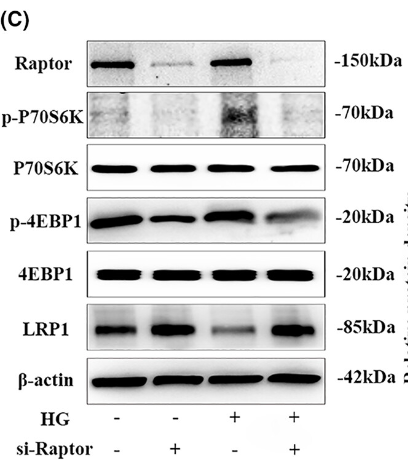
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: corpus cavernosum
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.