Gli1 Antibody - #DF7523
| Product: | Gli1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7523 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Gli1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 118 kDa; 118kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P08151 |
| RRID: | AB_2841022 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7523, RRID:AB_2841022.
Fold/Unfold
Gli 1; GLI; GLI family zinc finger 1; GLI Kruppel family member 1; gli1; GLI1_HUMAN; Glioma associated oncogene 1; Glioma associated oncogene homolog 1 (zinc finger protein); Glioma associated oncogene homolog; Glioma-associated oncogene; Oncogene GLI; Zfp 5; Zfp5; Zinc finger protein GLI 1; Zinc finger protein GLI1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Gli1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Detected in testis (at protein level) (PubMed:2105456). Testis, myometrium and fallopian tube. Also expressed in the brain with highest expression in the cerebellum, optic nerve and olfactory tract (PubMed:19878745). Isoform 1 is detected in brain, spleen, pancreas, liver, kidney and placenta; isoform 2 is not detectable in these tissues (PubMed:19706761).
- P08151 GLI1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MFNSMTPPPISSYGEPCCLRPLPSQGAPSVGTEGLSGPPFCHQANLMSGPHSYGPARETNSCTEGPLFSSPRSAVKLTKKRALSISPLSDASLDLQTVIRTSPSSLVAFINSRCTSPGGSYGHLSIGTMSPSLGFPAQMNHQKGPSPSFGVQPCGPHDSARGGMIPHPQSRGPFPTCQLKSELDMLVGKCREEPLEGDMSSPNSTGIQDPLLGMLDGREDLEREEKREPESVYETDCRWDGCSQEFDSQEQLVHHINSEHIHGERKEFVCHWGGCSRELRPFKAQYMLVVHMRRHTGEKPHKCTFEGCRKSYSRLENLKTHLRSHTGEKPYMCEHEGCSKAFSNASDRAKHQNRTHSNEKPYVCKLPGCTKRYTDPSSLRKHVKTVHGPDAHVTKRHRGDGPLPRAPSISTVEPKREREGGPIREESRLTVPEGAMKPQPSPGAQSSCSSDHSPAGSAANTDSGVEMTGNAGGSTEDLSSLDEGPCIAGTGLSTLRRLENLRLDQLHQLRPIGTRGLKLPSLSHTGTTVSRRVGPPVSLERRSSSSSSISSAYTVSRRSSLASPFPPGSPPENGASSLPGLMPAQHYLLRARYASARGGGTSPTAASSLDRIGGLPMPPWRSRAEYPGYNPNAGVTRRASDPAQAADRPAPARVQRFKSLGCVHTPPTVAGGGQNFDPYLPTSVYSPQPPSITENAAMDARGLQEEPEVGTSMVGSGLNPYMDFPPTDTLGYGGPEGAAAEPYGARGPGSLPLGPGPPTNYGPNPCPQQASYPDPTQETWGEFPSHSGLYPGPKALGGTYSQCPRLEHYGQVQVKPEQGCPVGSDSTGLAPCLNAHPSEGPPHPQPLFSHYPQPSPPQYLQSGPYTQPPPDYLPSEPRPCLDFDSPTHSTGQLKAQLVCNYVQSQQELLWEGGGREDAPAQEPSYQSPKFLGGSQVSPSRAKAPVNTYGPGFGPNLPNHKSGSYPTPSPCHENFVVGANRASHRAAAPPRLLPPLPTCYGPLKVGGTNPSCGHPEVGRLGGGPALYPPPEGQVCNPLDSLDLDNTQLDFVAILDEPQGLSPPPSHDQRGSSGHTPPPSGPPNMAVGNMSVLLRSLPGETEFLNSSA
Research Backgrounds
Acts as a transcriptional activator. Binds to the DNA consensus sequence 5'-GACCACCCA-3'. Regulates the transcription of specific genes during normal development. Plays a role in craniofacial development and digital development, as well as development of the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. Mediates SHH signaling. Plays a role in cell proliferation and differentiation via its role in SHH signaling.
Acts as a transcriptional activator, but activates a different set of genes than isoform 1. Activates expression of CD24, unlike isoform 1. Mediates SHH signaling. Promotes cancer cell migration.
Phosphorylated in vitro by ULK3.
Acetylation at Lys-518 down-regulates transcriptional activity. Deacetylated by HDAC1.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Tethered in the cytoplasm by binding to SUFU (PubMed:10806483). Activation and translocation to the nucleus is promoted by interaction with STK36 (PubMed:10806483). Phosphorylation by ULK3 may promote nuclear localization (PubMed:19878745). Translocation to the nucleus is promoted by interaction with ZIC1 (PubMed:11238441).
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Detected in testis (at protein level). Testis, myometrium and fallopian tube. Also expressed in the brain with highest expression in the cerebellum, optic nerve and olfactory tract. Isoform 1 is detected in brain, spleen, pancreas, liver, kidney and placenta; isoform 2 is not detectable in these tissues.
Belongs to the GLI C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hedgehog signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Basal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
References
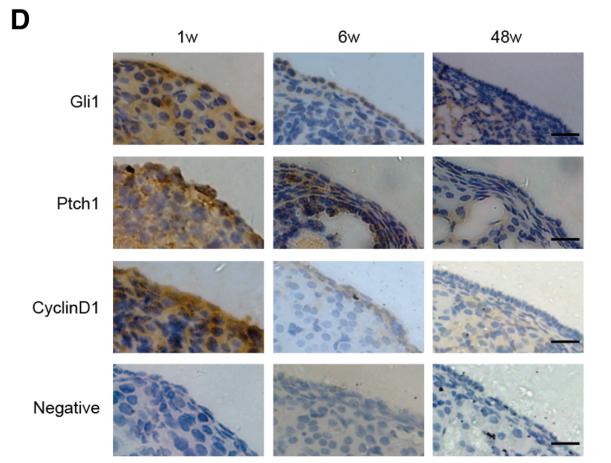
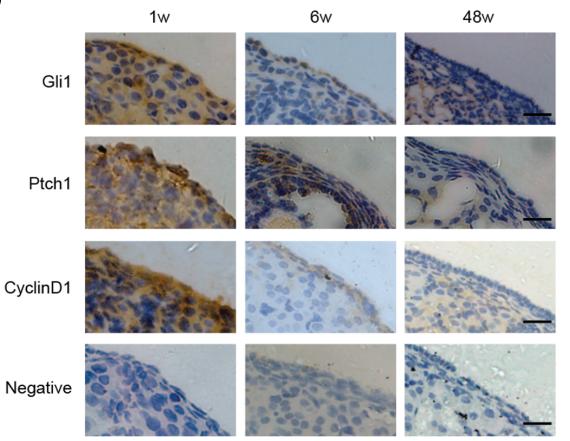
Application: IHC Species: mouse Sample: ovarian
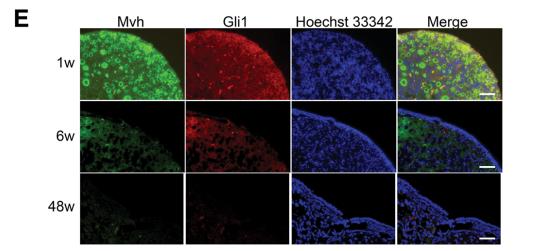
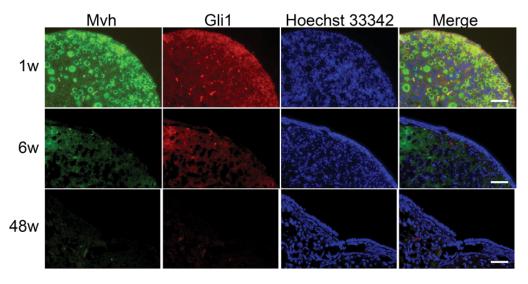
Application: IF/ICC Species: mouse Sample: ovarian
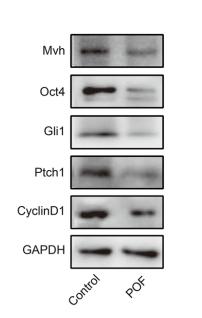
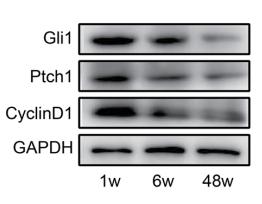
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: ovarian
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: ovaries
Application: IHC Species: mouse Sample: ovaries
Application: IF/ICC Species: mouse Sample: ovaries
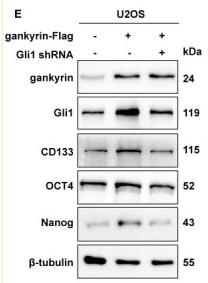
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: U2OS cells
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample: epithelial cells
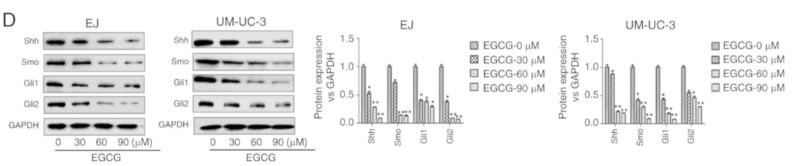
Application: WB Species: human Sample: Bladder CSCs
Application: WB Species: human Sample: HIBECs
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.