CD68 Antibody - #DF7518
| Product: | CD68 Antibody |
| Catalog: | DF7518 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CD68 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 37kD,70-140kD(glycosylated); 37kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P34810 |
| RRID: | AB_2841017 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# DF7518, RRID:AB_2841017.
Fold/Unfold
CD 68; CD68; CD68 antigen; CD68 molecule; CD68_HUMAN; DKFZp686M18236; gp11; Gp110; LAMP4; Macrophage antigen CD68 (microsialin); MACROPHAGE ANTIGEN CD68; Macrosialin; SCARD1; Scavenger receptor class D member 1;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CD68, corresponding to a region within the internal amino acids.
Highly expressed by blood monocytes and tissue macrophages. Also expressed in lymphocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Expressed in many tumor cell lines which could allow them to attach to selectins on vascular endothelium, facilitating their dissemination to secondary sites.
- P34810 CD68_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MRLAVLFSGALLGLLAAQGTGNDCPHKKSATLLPSFTVTPTVTESTGTTSHRTTKSHKTTTHRTTTTGTTSHGPTTATHNPTTTSHGNVTVHPTSNSTATSQGPSTATHSPATTSHGNATVHPTSNSTATSPGFTSSAHPEPPPPSPSPSPTSKETIGDYTWTNGSQPCVHLQAQIQIRVMYTTQGGGEAWGISVLNPNKTKVQGSCEGAHPHLLLSFPYGHLSFGFMQDLQQKVVYLSYMAVEYNVSFPHAAQWTFSAQNASLRDLQAPLGQSFSCSNSSIILSPAVHLDLLSLRLQAAQLPHTGVFGQSFSCPSDRSILLPLIIGLILLGLLALVLIAFCIIRRRPSAYQAL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Could play a role in phagocytic activities of tissue macrophages, both in intracellular lysosomal metabolism and extracellular cell-cell and cell-pathogen interactions. Binds to tissue- and organ-specific lectins or selectins, allowing homing of macrophage subsets to particular sites. Rapid recirculation of CD68 from endosomes and lysosomes to the plasma membrane may allow macrophages to crawl over selectin-bearing substrates or other cells.
N- and O-glycosylated.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Endosome membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Lysosome membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Highly expressed by blood monocytes and tissue macrophages. Also expressed in lymphocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Expressed in many tumor cell lines which could allow them to attach to selectins on vascular endothelium, facilitating their dissemination to secondary sites.
Belongs to the LAMP family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Lysosome. (View pathway)
References
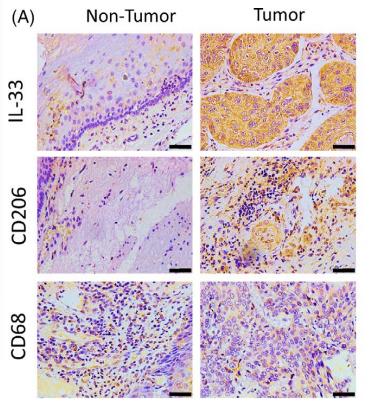
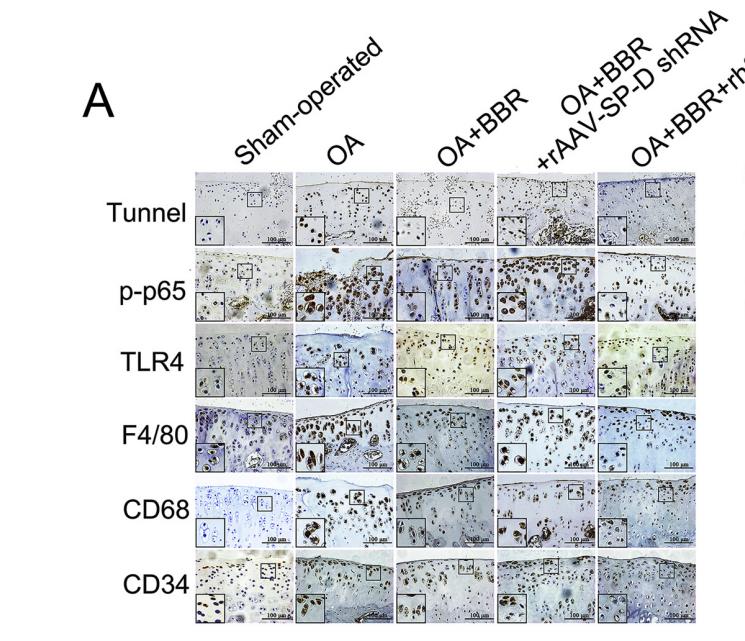
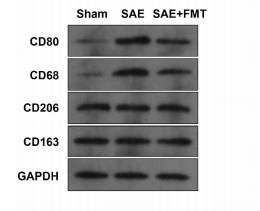
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample:
Application: IHC Species: rat Sample: knee joints
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.



















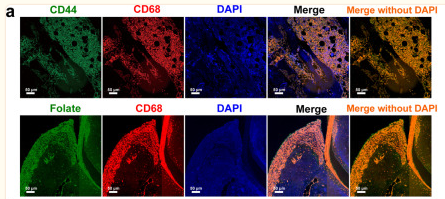

![Figure 3. MiR-22-3p induces macrophages into the M2 phenotype in ApoE–/– mice fed a high fat diet: (a) immunofluorescence staining (original magnification, × 40, bar = 50 μm) and quantitative analysis of macrophage accumulation and macrophage polarization by detection of (a) the macrophage marker cluster of differentiation (CD)68 and M1 marker inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and (b) the M2 markers CD206 and arginase (Arg)-1, in aortic sections from MiR-22-3p agomir or normal control (NC) mice; and (c) western blot and quantitative analysis of relative protein levels of the M1 markers (iNOS, interleukin [IL]-6, and tumour necrosis factor [TNF]-α) and M2 markers (Arg1 and CD206) in aortic sections from MiR-22-3p agomir or NC mice. CD68 Antibody - Figure 3.](http://img.affbiotech.cn/uploads/202403/c009a547f3113d92b315dc89b41d49f7.png)





