CD227/MUC1 Antibody - #AF8524
| Product: | CD227/MUC1 Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF8524 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to CD227/MUC1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Mol.Wt.: | 170kDa; 122kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P15941 |
| RRID: | AB_2840578 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF8524, RRID:AB_2840578.
Fold/Unfold
ADMCKD; ADMCKD1; Breast carcinoma associated antigen DF3; Breast carcinoma-associated antigen DF3; CA 15-3; CA15 3; CA15 3 antigen; CA15.3; Cancer antigen 15-3; Carcinoma associated mucin; Carcinoma-associated mucin; CD 227; CD227; DF3 antigen; EMA; Episialin; H23 antigen; H23AG; KL 6; KL-6; KL6; Krebs von den Lungen-6; MAM 6; MAM6; MCD; MCKD; MCKD1; Medullary cystic kidney disease 1 (autosomal dominant); Medullary cystic kidney disease, autosomal dominant; MUC 1; MUC-1; MUC-1/SEC; MUC-1/X; MUC1; MUC1-alpha; MUC1-beta; MUC1-CT; MUC1-NT; MUC1/ZD; MUC1_HUMAN; Mucin 1; Mucin 1 transmembrane; Mucin 1, cell surface associated; Mucin-1 subunit beta; Peanut reactive urinary mucin; Peanut-reactive urinary mucin; PEM; PEMT; Polymorphic epithelial mucin; PUM; Tumor associated epithelial membrane antigen; Tumor associated epithelial mucin; Tumor associated mucin; Tumor-associated epithelial membrane antigen; Tumor-associated mucin;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human CD227/MUC1, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
Expressed on the apical surface of epithelial cells, especially of airway passages, breast and uterus. Also expressed in activated and unactivated T-cells. Overexpressed in epithelial tumors, such as breast or ovarian cancer and also in non-epithelial tumor cells. Isoform Y is expressed in tumor cells only.
- P15941 MUC1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MTPGTQSPFFLLLLLTVLTVVTGSGHASSTPGGEKETSATQRSSVPSSTEKNAVSMTSSVLSSHSPGSGSSTTQGQDVTLAPATEPASGSAATWGQDVTSVPVTRPALGSTTPPAHDVTSAPDNKPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTSAPDNRPALGSTAPPVHNVTSASGSASGSASTLVHNGTSARATTTPASKSTPFSIPSHHSDTPTTLASHSTKTDASSTHHSSVPPLTSSNHSTSPQLSTGVSFFFLSFHISNLQFNSSLEDPSTDYYQELQRDISEMFLQIYKQGGFLGLSNIKFRPGSVVVQLTLAFREGTINVHDVETQFNQYKTEAASRYNLTISDVSVSDVPFPFSAQSGAGVPGWGIALLVLVCVLVALAIVYLIALAVCQCRRKNYGQLDIFPARDTYHPMSEYPTYHTHGRYVPPSSTDRSPYEKVSAGNGGSSLSYTNPAVAATSANL
Research Backgrounds
The alpha subunit has cell adhesive properties. Can act both as an adhesion and an anti-adhesion protein. May provide a protective layer on epithelial cells against bacterial and enzyme attack.
The beta subunit contains a C-terminal domain which is involved in cell signaling, through phosphorylations and protein-protein interactions. Modulates signaling in ERK, SRC and NF-kappa-B pathways. In activated T-cells, influences directly or indirectly the Ras/MAPK pathway. Promotes tumor progression. Regulates TP53-mediated transcription and determines cell fate in the genotoxic stress response. Binds, together with KLF4, the PE21 promoter element of TP53 and represses TP53 activity.
Highly glycosylated (N- and O-linked carbohydrates and sialic acid). O-glycosylated to a varying degree on serine and threonine residues within each tandem repeat, ranging from mono- to penta-glycosylation. The average density ranges from about 50% in human milk to over 90% in T47D breast cancer cells. Further sialylation occurs during recycling. Membrane-shed glycoproteins from kidney and breast cancer cells have preferentially sialyated core 1 structures, while secreted forms from the same tissues display mainly core 2 structures. The O-glycosylated content is overlapping in both these tissues with terminal fucose and galactose, 2- and 3-linked galactose, 3- and 3,6-linked GalNAc-ol and 4-linked GlcNAc predominating. Differentially O-glycosylated in breast carcinomas with 3,4-linked GlcNAc. N-glycosylation consists of high-mannose, acidic complex-type and hybrid glycans in the secreted form MUC1/SEC, and neutral complex-type in the transmembrane form, MUC1/TM.
Proteolytic cleavage in the SEA domain occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by an autoproteolytic mechanism and requires the full-length SEA domain as well as requiring a Ser, Thr or Cys residue at the P + 1 site. Cleavage at this site also occurs on isoform MUC1/X but not on isoform MUC1/Y. Ectodomain shedding is mediated by ADAM17.
Dual palmitoylation on cysteine residues in the CQC motif is required for recycling from endosomes back to the plasma membrane.
Phosphorylated on tyrosines and serine residues in the C-terminal. Phosphorylation on tyrosines in the C-terminal increases the nuclear location of MUC1 and beta-catenin. Phosphorylation by PKC delta induces binding of MUC1 to beta-catenin/CTNNB1 and thus decreases the formation of the beta-catenin/E-cadherin complex. Src-mediated phosphorylation inhibits interaction with GSK3B. Src- and EGFR-mediated phosphorylation on Tyr-1229 increases binding to beta-catenin/CTNNB1. GSK3B-mediated phosphorylation on Ser-1227 decreases this interaction but restores the formation of the beta-cadherin/E-cadherin complex. On T-cell receptor activation, phosphorylated by LCK. PDGFR-mediated phosphorylation increases nuclear colocalization of MUC1CT and CTNNB1.
The N-terminal sequence has been shown to begin at position 24 or 28.
Apical cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Note: Exclusively located in the apical domain of the plasma membrane of highly polarized epithelial cells. After endocytosis, internalized and recycled to the cell membrane. Located to microvilli and to the tips of long filopodial protusions.
Secreted.
Secreted.
Secreted.
Cell membrane. Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: On EGF and PDGFRB stimulation, transported to the nucleus through interaction with CTNNB1, a process which is stimulated by phosphorylation. On HRG stimulation, colocalizes with JUP/gamma-catenin at the nucleus.
Expressed on the apical surface of epithelial cells, especially of airway passages, breast and uterus. Also expressed in activated and unactivated T-cells. Overexpressed in epithelial tumors, such as breast or ovarian cancer and also in non-epithelial tumor cells. Isoform Y is expressed in tumor cells only.
References
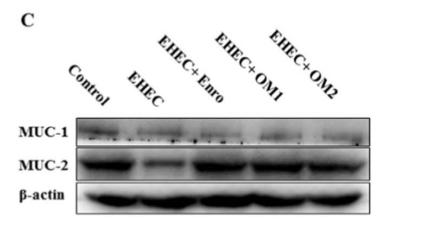
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: intestine
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.