Phospho-Chk2 (Thr68) Antibody - #AF3036
| Product: | Phospho-Chk2 (Thr68) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF3036 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-Chk2 (Thr68) |
| Application: | WB IHC IF/ICC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 62kDa; 61kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | O96017 |
| RRID: | AB_2834325 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF3036, RRID:AB_2834325.
Fold/Unfold
CDS 1; Cds1; Cds1 homolog; Checkpoint kinase 2; Checkpoint like protein CHK2; CHEK 2; Chek2; Chk 2; CHK2 checkpoint homolog (S. pombe); CHK2 checkpoint homolog; CHK2_HUMAN; hCds1; HuCds 1; LFS 2; LFS2; PP1425; RAD 53; RAD53; Rad53 homolog; Serine/threonine protein kinase Chk2; Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human Chk2 around the phosphorylation site of Thr68.
High expression is found in testis, spleen, colon and peripheral blood leukocytes. Low expression is found in other tissues.
- O96017 CHK2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MSRESDVEAQQSHGSSACSQPHGSVTQSQGSSSQSQGISSSSTSTMPNSSQSSHSSSGTLSSLETVSTQELYSIPEDQEPEDQEPEEPTPAPWARLWALQDGFANLECVNDNYWFGRDKSCEYCFDEPLLKRTDKYRTYSKKHFRIFREVGPKNSYIAYIEDHSGNGTFVNTELVGKGKRRPLNNNSEIALSLSRNKVFVFFDLTVDDQSVYPKALRDEYIMSKTLGSGACGEVKLAFERKTCKKVAIKIISKRKFAIGSAREADPALNVETEIEILKKLNHPCIIKIKNFFDAEDYYIVLELMEGGELFDKVVGNKRLKEATCKLYFYQMLLAVQYLHENGIIHRDLKPENVLLSSQEEDCLIKITDFGHSKILGETSLMRTLCGTPTYLAPEVLVSVGTAGYNRAVDCWSLGVILFICLSGYPPFSEHRTQVSLKDQITSGKYNFIPEVWAEVSEKALDLVKKLLVVDPKARFTTEEALRHPWLQDEDMKRKFQDLLSEENESTALPQVLAQPSTSRKRPREGEAEGAETTKRPAVCAAVL
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Serine/threonine-protein kinase which is required for checkpoint-mediated cell cycle arrest, activation of DNA repair and apoptosis in response to the presence of DNA double-strand breaks. May also negatively regulate cell cycle progression during unperturbed cell cycles. Following activation, phosphorylates numerous effectors preferentially at the consensus sequence [L-X-R-X-X-S/T]. Regulates cell cycle checkpoint arrest through phosphorylation of CDC25A, CDC25B and CDC25C, inhibiting their activity. Inhibition of CDC25 phosphatase activity leads to increased inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of CDK-cyclin complexes and blocks cell cycle progression. May also phosphorylate NEK6 which is involved in G2/M cell cycle arrest. Regulates DNA repair through phosphorylation of BRCA2, enhancing the association of RAD51 with chromatin which promotes DNA repair by homologous recombination. Also stimulates the transcription of genes involved in DNA repair (including BRCA2) through the phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor FOXM1. Regulates apoptosis through the phosphorylation of p53/TP53, MDM4 and PML. Phosphorylation of p53/TP53 at 'Ser-20' by CHEK2 may alleviate inhibition by MDM2, leading to accumulation of active p53/TP53. Phosphorylation of MDM4 may also reduce degradation of p53/TP53. Also controls the transcription of pro-apoptotic genes through phosphorylation of the transcription factor E2F1. Tumor suppressor, it may also have a DNA damage-independent function in mitotic spindle assembly by phosphorylating BRCA1. Its absence may be a cause of the chromosomal instability observed in some cancer cells. Promotes the CCAR2-SIRT1 association and is required for CCAR2-mediated SIRT1 inhibition.
Phosphorylated. Phosphorylated at Ser-73 by PLK3 in response to DNA damage, promoting phosphorylation at Thr-68 by ATM and the G2/M transition checkpoint. Phosphorylation at Thr-68 induces homodimerization. Autophosphorylates at Thr-383 and Thr-387 in the T-loop/activation segment upon dimerization to become fully active and phosphorylate its substrates like for instance CDC25C. DNA damage-induced autophosphorylation at Ser-379 induces CUL1-mediated ubiquitination and regulates the pro-apoptotic function. Phosphorylation at Ser-456 also regulates ubiquitination. Phosphorylated by PLK4.
Ubiquitinated. CUL1-mediated ubiquitination regulates the pro-apoptotic function. Ubiquitination may also regulate protein stability. Ubiquitinated by RNF8 via 'Lys-48'-linked ubiquitination.
Nucleus.
Note: Isoform 10 is present throughout the cell.
Nucleus.
Nucleus.
Nucleus.
Nucleus.
Nucleus>PML body. Nucleus>Nucleoplasm.
Note: Recruited into PML bodies together with TP53.
High expression is found in testis, spleen, colon and peripheral blood leukocytes. Low expression is found in other tissues.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CHK2 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > p53 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cellular senescence. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
References
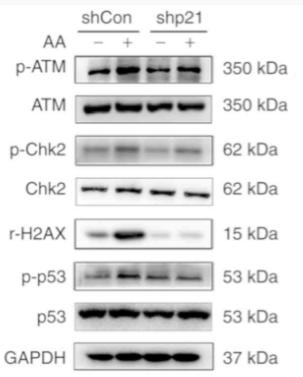
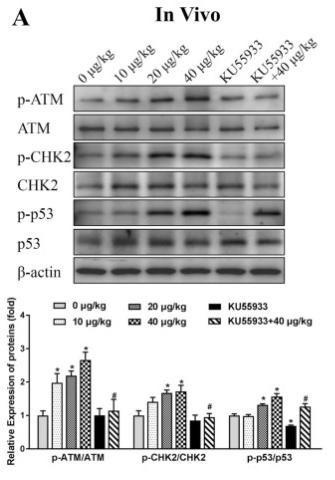
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: GC-1 cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample: HK-2 cells
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.