Phospho-TORC2 (Ser171) Antibody - #AF8328
| Product: | Phospho-TORC2 (Ser171) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF8328 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-TORC2 (Ser171) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Zebrafish, Bovine, Horse, Rabbit, Dog |
| Mol.Wt.: | 70 KD; 73kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q53ET0 |
| RRID: | AB_2840390 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF8328, RRID:AB_2840390.
Fold/Unfold
CREB regulated transcription coactivator 2; CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2; CRTC2; CRTC2_HUMAN; RP11-422P24.6; TORC-2; torc2; Transducer of CREB protein 2; Transducer of regulated cAMP response element-binding protein; Transducer of regulated cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) 2; Transducer of regulated cAMP response element-binding protein 2; Transducer of regulated CREB protein 2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human TORC2 around the phosphorylation site of Ser171.
Most abundantly expressed in the thymus. Present in both B and T-lymphocytes. Highly expressed in HEK293T cells and in insulinomas. High levels also in spleen, ovary, muscle and lung, with highest levels in muscle. Lower levels found in brain, colon, heart, kidney, prostate, small intestine and stomach. Weak expression in liver and pancreas.
- Q53ET0 CRTC2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MATSGANGPGSATASASNPRKFSEKIALQKQRQAEETAAFEEVMMDIGSTRLQAQKLRLAYTRSSHYGGSLPNVNQIGSGLAEFQSPLHSPLDSSRSTRHHGLVERVQRDPRRMVSPLRRYTRHIDSSPYSPAYLSPPPESSWRRTMAWGNFPAEKGQLFRLPSALNRTSSDSALHTSVMNPSPQDTYPGPTPPSILPSRRGGILDGEMDPKVPAIEENLLDDKHLLKPWDAKKLSSSSSRPRSCEVPGINIFPSPDQPANVPVLPPAMNTGGSLPDLTNLHFPPPLPTPLDPEETAYPSLSGGNSTSNLTHTMTHLGISRGMGLGPGYDAPGLHSPLSHPSLQSSLSNPNLQASLSSPQPQLQGSHSHPSLPASSLARHVLPTTSLGHPSLSAPALSSSSSSSSTSSPVLGAPSYPASTPGASPHHRRVPLSPLSLLAGPADARRSQQQLPKQFSPTMSPTLSSITQGVPLDTSKLSTDQRLPPYPYSSPSLVLPTQPHTPKSLQQPGLPSQSCSVQSSGGQPPGRQSHYGTPYPPGPSGHGQQSYHRPMSDFNLGNLEQFSMESPSASLVLDPPGFSEGPGFLGGEGPMGGPQDPHTFNHQNLTHCSRHGSGPNIILTGDSSPGFSKEIAAALAGVPGFEVSAAGLELGLGLEDELRMEPLGLEGLNMLSDPCALLPDPAVEESFRSDRLQ
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Transcriptional coactivator for CREB1 which activates transcription through both consensus and variant cAMP response element (CRE) sites. Acts as a coactivator, in the SIK/TORC signaling pathway, being active when dephosphorylated and acts independently of CREB1 'Ser-133' phosphorylation. Enhances the interaction of CREB1 with TAF4. Regulates gluconeogenesis as a component of the LKB1/AMPK/TORC2 signaling pathway. Regulates the expression of specific genes such as the steroidogenic gene, StAR. Potent coactivator of PPARGC1A and inducer of mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells. Also coactivator for TAX activation of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) long terminal repeats (LTR).
Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation states of Ser-171 are required for regulating transduction of CREB activity. CRTCs/TORCs are inactive when phosphorylated, and active when dephosphorylated at this site. This primary site of phosphorylation, is regulated by cAMP and calcium levels and is dependent on the phosphorylation of SIKs (SIK1 and SIK2) by LKB1. Following adenylyl cyclase activation, dephosphorylated at Ser-171 by PPP3CA/calcineurin A resulting in CRTC2 dissociation from 14-3-3 proteins and PPP3CA (By similarity). Both insulin and AMPK increase this phosphorylation of CRTC2 while glucagon suppresses it. Phosphorylation at Ser-274 by MARK2 is induced under low glucose conditions and dephosphorylated in response to glucose influx. Phosphorylation at Ser-274 promotes interaction with 14-3-3 proteins and translocation to the cytoplasm.
Asymmetric dimethylation of arginine resisues by PRMT6 enhances the association of CRTC2 with CREB on the promoters of gluconeogenic genes.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Translocated from the nucleus to the cytoplasm on interaction of the phosphorylated form with 14-3-3 protein (PubMed:15454081). In response to cAMP levels and glucagon, relocated to the nucleus (PubMed:15454081).
Most abundantly expressed in the thymus. Present in both B and T-lymphocytes. Highly expressed in HEK293T cells and in insulinomas. High levels also in spleen, ovary, muscle and lung, with highest levels in muscle. Lower levels found in brain, colon, heart, kidney, prostate, small intestine and stomach. Weak expression in liver and pancreas.
Belongs to the TORC family.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > AMPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Endocrine and metabolic diseases > Insulin resistance.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Glucagon signaling pathway.
References
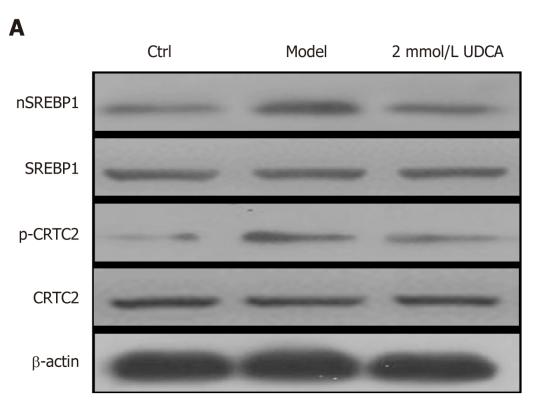
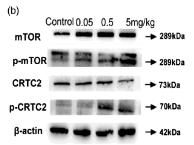
Application: WB Species: human Sample: LO2 cells
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.