Phospho-FGFR1/2/3/4 (Tyr653+Tyr654) Antibody - #AF8210
| Product: | Phospho-FGFR1/2/3/4 (Tyr653+Tyr654) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF8210 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-FGFR1/2/3/4 (Tyr653+Tyr654) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
| Prediction: | Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken, Xenopus |
| Mol.Wt.: | 92KD; 92kD,88kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P11362 | P21802 | P22607 | P22455 |
| RRID: | AB_2840272 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF8210, RRID:AB_2840272.
Fold/Unfold
Basic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; bFGF-R-1; BFGFR; CD331; CEK; FGFBR; FGFR 1; FGFR-1; FGFR1; FGFR1/PLAG1 fusion; FGFR1_HUMAN; fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; FLG; FLT-2; FLT2; Fms-like gene; Fms-like tyrosine kinase 2; fms-related tyrosine kinase 2; HBGFR; heparin-binding growth factor receptor; HH2; HRTFDS; hydroxyaryl-protein kinase; KAL2; N-SAM; OGD; Proto-oncogene c-Fgr; bacteria-expressed kinase; BBDS; BEK; BEK fibroblast growth factor receptor; BFR1; CD332; CD332 antigen; CEK3; CFD1; Craniofacial dysostosis 1; ECT1; FGF receptor; FGFR 2; FGFR-2; Fgfr2; FGFR2_HUMAN; Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2; Hydroxyaryl protein kinase; Jackson Weiss syndrome; JWS; K SAM; K-sam; Keratinocyte growth factor receptor 2; Keratinocyte growth factor receptor; KGFR; KSAM; protein tyrosine kinase, receptor like 14; soluble FGFR4 variant 4; TK14; TK25; ACH; CD 333; CD333; CD333 antigen; CEK 2; CEK2; FGFR 3; FGFR-3; FGFR3; FGFR3_HUMAN; Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (achondroplasia thanatophoric dwarfism); Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3; Heparin binding growth factor receptor; HSFGFR3EX; Hydroxyaryl protein kinase; JTK 4; JTK4; MFR 3; SAM 3; Tyrosine kinase JTK 4; Tyrosine kinase JTK4; Z FGFR 3; CD 334; CD334; CD334 antigen; fc13h 10; fc13h10; Fgfr 4; FGFR-4; Fgfr4; FGFR4_HUMAN; Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4; Hydroxyaryl protein kinase; JTK 2; JTK2; MGC20292; Protein tyrosine kinase; TKF; Tyrosine kinase related to fibroblast growth factor receptor; Tyrosylprotein kinase;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human FGFR1/2/3/4 around the phosphorylation site of Tyr653+Tyr654.
P11362(FGFR1_HUMAN) >>Visit HPA database.
P21802(FGFR2_HUMAN) >>Visit HPA database.
Detected in astrocytoma, neuroblastoma and adrenal cortex cell lines. Some isoforms are detected in foreskin fibroblast cell lines, however isoform 17, isoform 18 and isoform 19 are not detected in these cells.
P22607 FGFR3_HUMAN:Expressed in brain, kidney and testis. Very low or no expression in spleen, heart, and muscle. In 20- to 22-week old fetuses it is expressed at high level in kidney, lung, small intestine and brain, and to a lower degree in spleen, liver, and muscle. Isoform 2 is detected in epithelial cells. Isoform 1 is not detected in epithelial cells. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are detected in fibroblastic cells.
P22455 FGFR4_HUMAN:Expressed in gastrointestinal epithelial cells, pancreas, and gastric and pancreatic cancer cell lines.
- P11362 FGFR1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MWSWKCLLFWAVLVTATLCTARPSPTLPEQAQPWGAPVEVESFLVHPGDLLQLRCRLRDDVQSINWLRDGVQLAESNRTRITGEEVEVQDSVPADSGLYACVTSSPSGSDTTYFSVNVSDALPSSEDDDDDDDSSSEEKETDNTKPNRMPVAPYWTSPEKMEKKLHAVPAAKTVKFKCPSSGTPNPTLRWLKNGKEFKPDHRIGGYKVRYATWSIIMDSVVPSDKGNYTCIVENEYGSINHTYQLDVVERSPHRPILQAGLPANKTVALGSNVEFMCKVYSDPQPHIQWLKHIEVNGSKIGPDNLPYVQILKTAGVNTTDKEMEVLHLRNVSFEDAGEYTCLAGNSIGLSHHSAWLTVLEALEERPAVMTSPLYLEIIIYCTGAFLISCMVGSVIVYKMKSGTKKSDFHSQMAVHKLAKSIPLRRQVTVSADSSASMNSGVLLVRPSRLSSSGTPMLAGVSEYELPEDPRWELPRDRLVLGKPLGEGCFGQVVLAEAIGLDKDKPNRVTKVAVKMLKSDATEKDLSDLISEMEMMKMIGKHKNIINLLGACTQDGPLYVIVEYASKGNLREYLQARRPPGLEYCYNPSHNPEEQLSSKDLVSCAYQVARGMEYLASKKCIHRDLAARNVLVTEDNVMKIADFGLARDIHHIDYYKKTTNGRLPVKWMAPEALFDRIYTHQSDVWSFGVLLWEIFTLGGSPYPGVPVEELFKLLKEGHRMDKPSNCTNELYMMMRDCWHAVPSQRPTFKQLVEDLDRIVALTSNQEYLDLSMPLDQYSPSFPDTRSSTCSSGEDSVFSHEPLPEEPCLPRHPAQLANGGLKRR
- P21802 FGFR2_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MVSWGRFICLVVVTMATLSLARPSFSLVEDTTLEPEEPPTKYQISQPEVYVAAPGESLEVRCLLKDAAVISWTKDGVHLGPNNRTVLIGEYLQIKGATPRDSGLYACTASRTVDSETWYFMVNVTDAISSGDDEDDTDGAEDFVSENSNNKRAPYWTNTEKMEKRLHAVPAANTVKFRCPAGGNPMPTMRWLKNGKEFKQEHRIGGYKVRNQHWSLIMESVVPSDKGNYTCVVENEYGSINHTYHLDVVERSPHRPILQAGLPANASTVVGGDVEFVCKVYSDAQPHIQWIKHVEKNGSKYGPDGLPYLKVLKAAGVNTTDKEIEVLYIRNVTFEDAGEYTCLAGNSIGISFHSAWLTVLPAPGREKEITASPDYLEIAIYCIGVFLIACMVVTVILCRMKNTTKKPDFSSQPAVHKLTKRIPLRRQVTVSAESSSSMNSNTPLVRITTRLSSTADTPMLAGVSEYELPEDPKWEFPRDKLTLGKPLGEGCFGQVVMAEAVGIDKDKPKEAVTVAVKMLKDDATEKDLSDLVSEMEMMKMIGKHKNIINLLGACTQDGPLYVIVEYASKGNLREYLRARRPPGMEYSYDINRVPEEQMTFKDLVSCTYQLARGMEYLASQKCIHRDLAARNVLVTENNVMKIADFGLARDINNIDYYKKTTNGRLPVKWMAPEALFDRVYTHQSDVWSFGVLMWEIFTLGGSPYPGIPVEELFKLLKEGHRMDKPANCTNELYMMMRDCWHAVPSQRPTFKQLVEDLDRILTLTTNEEYLDLSQPLEQYSPSYPDTRSSCSSGDDSVFSPDPMPYEPCLPQYPHINGSVKT
- P22607 FGFR3_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MGAPACALALCVAVAIVAGASSESLGTEQRVVGRAAEVPGPEPGQQEQLVFGSGDAVELSCPPPGGGPMGPTVWVKDGTGLVPSERVLVGPQRLQVLNASHEDSGAYSCRQRLTQRVLCHFSVRVTDAPSSGDDEDGEDEAEDTGVDTGAPYWTRPERMDKKLLAVPAANTVRFRCPAAGNPTPSISWLKNGREFRGEHRIGGIKLRHQQWSLVMESVVPSDRGNYTCVVENKFGSIRQTYTLDVLERSPHRPILQAGLPANQTAVLGSDVEFHCKVYSDAQPHIQWLKHVEVNGSKVGPDGTPYVTVLKTAGANTTDKELEVLSLHNVTFEDAGEYTCLAGNSIGFSHHSAWLVVLPAEEELVEADEAGSVYAGILSYGVGFFLFILVVAAVTLCRLRSPPKKGLGSPTVHKISRFPLKRQVSLESNASMSSNTPLVRIARLSSGEGPTLANVSELELPADPKWELSRARLTLGKPLGEGCFGQVVMAEAIGIDKDRAAKPVTVAVKMLKDDATDKDLSDLVSEMEMMKMIGKHKNIINLLGACTQGGPLYVLVEYAAKGNLREFLRARRPPGLDYSFDTCKPPEEQLTFKDLVSCAYQVARGMEYLASQKCIHRDLAARNVLVTEDNVMKIADFGLARDVHNLDYYKKTTNGRLPVKWMAPEALFDRVYTHQSDVWSFGVLLWEIFTLGGSPYPGIPVEELFKLLKEGHRMDKPANCTHDLYMIMRECWHAAPSQRPTFKQLVEDLDRVLTVTSTDEYLDLSAPFEQYSPGGQDTPSSSSSGDDSVFAHDLLPPAPPSSGGSRT
- P22455 FGFR4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MRLLLALLGVLLSVPGPPVLSLEASEEVELEPCLAPSLEQQEQELTVALGQPVRLCCGRAERGGHWYKEGSRLAPAGRVRGWRGRLEIASFLPEDAGRYLCLARGSMIVLQNLTLITGDSLTSSNDDEDPKSHRDPSNRHSYPQQAPYWTHPQRMEKKLHAVPAGNTVKFRCPAAGNPTPTIRWLKDGQAFHGENRIGGIRLRHQHWSLVMESVVPSDRGTYTCLVENAVGSIRYNYLLDVLERSPHRPILQAGLPANTTAVVGSDVELLCKVYSDAQPHIQWLKHIVINGSSFGADGFPYVQVLKTADINSSEVEVLYLRNVSAEDAGEYTCLAGNSIGLSYQSAWLTVLPEEDPTWTAAAPEARYTDIILYASGSLALAVLLLLAGLYRGQALHGRHPRPPATVQKLSRFPLARQFSLESGSSGKSSSSLVRGVRLSSSGPALLAGLVSLDLPLDPLWEFPRDRLVLGKPLGEGCFGQVVRAEAFGMDPARPDQASTVAVKMLKDNASDKDLADLVSEMEVMKLIGRHKNIINLLGVCTQEGPLYVIVECAAKGNLREFLRARRPPGPDLSPDGPRSSEGPLSFPVLVSCAYQVARGMQYLESRKCIHRDLAARNVLVTEDNVMKIADFGLARGVHHIDYYKKTSNGRLPVKWMAPEALFDRVYTHQSDVWSFGILLWEIFTLGGSPYPGIPVEELFSLLREGHRMDRPPHCPPELYGLMRECWHAAPSQRPTFKQLVEALDKVLLAVSEEYLDLRLTFGPYSPSGGDASSTCSSSDSVFSHDPLPLGSSSFPFGSGVQT
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation and migration. Required for normal mesoderm patterning and correct axial organization during embryonic development, normal skeletogenesis and normal development of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal system. Phosphorylates PLCG1, FRS2, GAB1 and SHB. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Promotes phosphorylation of SHC1, STAT1 and PTPN11/SHP2. In the nucleus, enhances RPS6KA1 and CREB1 activity and contributes to the regulation of transcription. FGFR1 signaling is down-regulated by IL17RD/SEF, and by FGFR1 ubiquitination, internalization and degradation.
Autophosphorylated. Binding of FGF family members together with heparan sulfate proteoglycan or heparin promotes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation on tyrosine residues. Autophosphorylation occurs in trans between the two FGFR molecules present in the dimer and proceeds in a highly ordered manner. Initial autophosphorylation at Tyr-653 increases the kinase activity by a factor of 50 to 100. After this, Tyr-583 becomes phosphorylated, followed by phosphorylation of Tyr-463, Tyr-766, Tyr-583 and Tyr-585. In a third stage, Tyr-654 is autophosphorylated, resulting in a further tenfold increase of kinase activity. Phosphotyrosine residues provide docking sites for interacting proteins and so are crucial for FGFR1 function and its regulation.
Ubiquitinated. FGFR1 is rapidly ubiquitinated by NEDD4 after autophosphorylation, leading to internalization and lysosomal degradation. CBL is recruited to activated FGFR1 via FRS2 and GRB2, and mediates ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of FGFR1.
N-glycosylated in the endoplasmic reticulum. The N-glycan chains undergo further maturation to an Endo H-resistant form in the Golgi apparatus.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Nucleus. Cytoplasm>Cytosol. Cytoplasmic vesicle.
Note: After ligand binding, both receptor and ligand are rapidly internalized. Can translocate to the nucleus after internalization, or by translocation from the endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi apparatus to the cytosol, and from there to the nucleus.
Detected in astrocytoma, neuroblastoma and adrenal cortex cell lines. Some isoforms are detected in foreskin fibroblast cell lines, however isoform 17, isoform 18 and isoform 19 are not detected in these cells.
The second and third Ig-like domains directly interact with fibroblast growth factors (FGF) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Isoforms lacking the first Ig-like domain have higher affinity for fibroblast growth factors (FGF) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans than isoforms with all three Ig-like domains.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. Fibroblast growth factor receptor subfamily.
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays an essential role in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and apoptosis, and in the regulation of embryonic development. Required for normal embryonic patterning, trophoblast function, limb bud development, lung morphogenesis, osteogenesis and skin development. Plays an essential role in the regulation of osteoblast differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis, and is required for normal skeleton development. Promotes cell proliferation in keratinocytes and immature osteoblasts, but promotes apoptosis in differentiated osteoblasts. Phosphorylates PLCG1, FRS2 and PAK4. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. FGFR2 signaling is down-regulated by ubiquitination, internalization and degradation. Mutations that lead to constitutive kinase activation or impair normal FGFR2 maturation, internalization and degradation lead to aberrant signaling. Over-expressed FGFR2 promotes activation of STAT1.
Autophosphorylated. Binding of FGF family members together with heparan sulfate proteoglycan or heparin promotes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation on several tyrosine residues. Autophosphorylation occurs in trans between the two FGFR molecules present in the dimer. Phosphorylation at Tyr-769 is essential for interaction with PLCG1.
N-glycosylated in the endoplasmic reticulum. The N-glycan chains undergo further maturation to an Endo H-resistant form in the Golgi apparatus.
Ubiquitinated. FGFR2 is rapidly ubiquitinated after autophosphorylation, leading to internalization and degradation. Subject to degradation both in lysosomes and by the proteasome.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Golgi apparatus. Cytoplasmic vesicle.
Note: Detected on osteoblast plasma membrane lipid rafts. After ligand binding, the activated receptor is rapidly internalized and degraded.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Note: After ligand binding, the activated receptor is rapidly internalized and degraded.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Note: After ligand binding, the activated receptor is rapidly internalized and degraded.
Secreted.
Secreted.
The second and third Ig-like domains directly interact with fibroblast growth factors (FGF) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Alternative splicing events affecting the third Ig-like domain are crucial for ligand selectivity.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. Fibroblast growth factor receptor subfamily.
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays an essential role in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Plays an essential role in the regulation of chondrocyte differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis, and is required for normal skeleton development. Regulates both osteogenesis and postnatal bone mineralization by osteoblasts. Promotes apoptosis in chondrocytes, but can also promote cancer cell proliferation. Required for normal development of the inner ear. Phosphorylates PLCG1, CBL and FRS2. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Plays a role in the regulation of vitamin D metabolism. Mutations that lead to constitutive kinase activation or impair normal FGFR3 maturation, internalization and degradation lead to aberrant signaling. Over-expressed or constitutively activated FGFR3 promotes activation of PTPN11/SHP2, STAT1, STAT5A and STAT5B. Secreted isoform 3 retains its capacity to bind FGF1 and FGF2 and hence may interfere with FGF signaling.
Autophosphorylated. Binding of FGF family members together with heparan sulfate proteoglycan or heparin promotes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation on tyrosine residues. Autophosphorylation occurs in trans between the two FGFR molecules present in the dimer. Phosphorylation at Tyr-724 is essential for stimulation of cell proliferation and activation of PIK3R1, STAT1 and MAP kinase signaling. Phosphorylation at Tyr-760 is required for interaction with PIK3R1 and PLCG1.
Ubiquitinated. Is rapidly ubiquitinated after ligand binding and autophosphorylation, leading to receptor internalization and degradation. Subject to both proteasomal and lysosomal degradation.
N-glycosylated in the endoplasmic reticulum. The N-glycan chains undergo further maturation to an Endo H-resistant form in the Golgi apparatus.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Endoplasmic reticulum.
Note: The activated receptor is rapidly internalized and degraded. Detected in intracellular vesicles after internalization of the autophosphorylated receptor.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Secreted.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein.
Expressed in brain, kidney and testis. Very low or no expression in spleen, heart, and muscle. In 20- to 22-week old fetuses it is expressed at high level in kidney, lung, small intestine and brain, and to a lower degree in spleen, liver, and muscle. Isoform 2 is detected in epithelial cells. Isoform 1 is not detected in epithelial cells. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are detected in fibroblastic cells.
The second and third Ig-like domains directly interact with fibroblast growth factors (FGF) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. Fibroblast growth factor receptor subfamily.
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation and migration, and in regulation of lipid metabolism, bile acid biosynthesis, glucose uptake, vitamin D metabolism and phosphate homeostasis. Required for normal down-regulation of the expression of CYP7A1, the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid synthesis, in response to FGF19. Phosphorylates PLCG1 and FRS2. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Promotes SRC-dependent phosphorylation of the matrix protease MMP14 and its lysosomal degradation. FGFR4 signaling is down-regulated by receptor internalization and degradation; MMP14 promotes internalization and degradation of FGFR4. Mutations that lead to constitutive kinase activation or impair normal FGFR4 inactivation lead to aberrant signaling.
N-glycosylated. Full maturation of the glycan chains in the Golgi is essential for high affinity interaction with FGF19.
Ubiquitinated. Subject to proteasomal degradation when not fully glycosylated.
Autophosphorylated. Binding of FGF family members together with heparan sulfate proteoglycan or heparin promotes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation on tyrosine residues. Autophosphorylation occurs in trans between the two FGFR molecules present in the dimer.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Endosome. Endoplasmic reticulum.
Note: Internalized from the cell membrane to recycling endosomes, and from there back to the cell membrane.
Secreted.
Cytoplasm.
Expressed in gastrointestinal epithelial cells, pancreas, and gastric and pancreatic cancer cell lines.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. Fibroblast growth factor receptor subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Ras signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > MicroRNAs in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Melanoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Bladder cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Central carbon metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
References
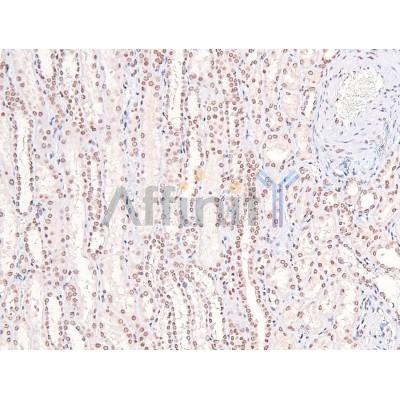
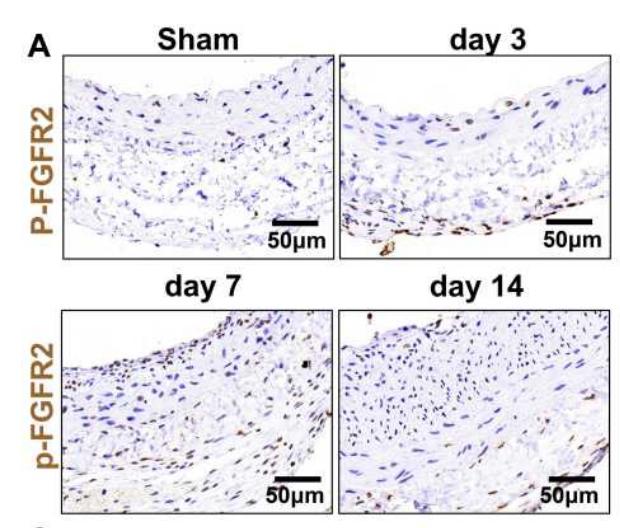
Application: IHC Species: Rat Sample: VSMCs
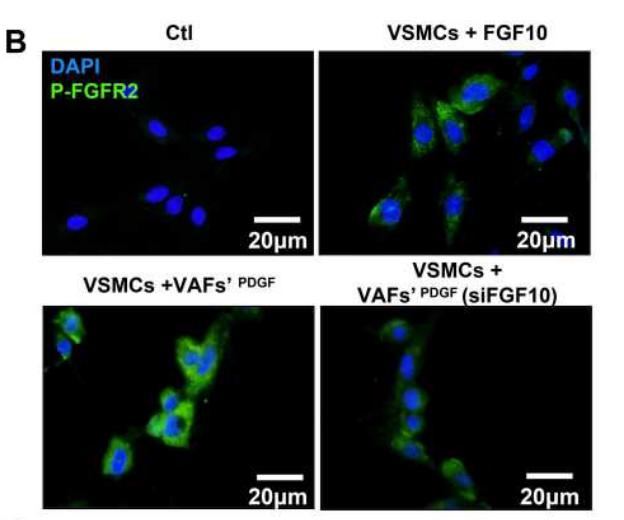
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample: VSMCs
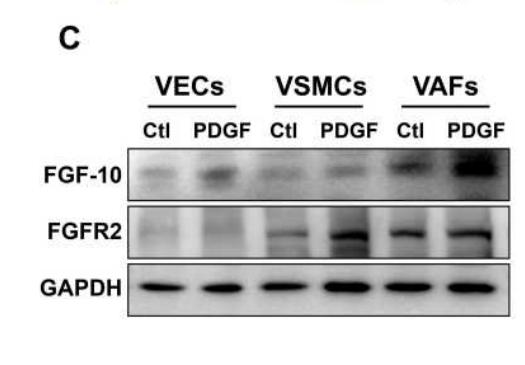
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample: VSMCs
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: 3T3-L1 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.