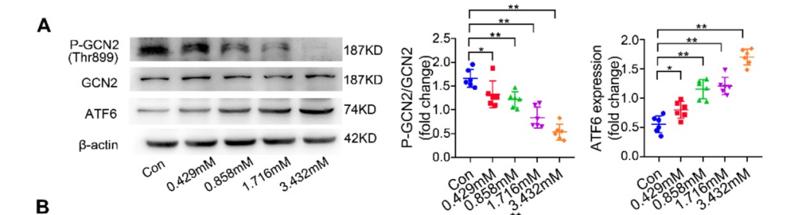
Phospho-GCN2 (Thr899) Antibody - #AF8154
| Product: | Phospho-GCN2 (Thr899) Antibody |
| Catalog: | AF8154 |
| Description: | Rabbit polyclonal antibody to Phospho-GCN2 (Thr899) |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Prediction: | Pig, Bovine, Horse, Sheep, Rabbit, Dog, Chicken |
| Mol.Wt.: | 190~230kDa; 187kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | Q9P2K8 |
| RRID: | AB_2840216 |
Related Downloads
Protocols
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF8154, RRID:AB_2840216.
Fold/Unfold
E2AK4_HUMAN; Eif2ak4; Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 2 alpha kinase 4; Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 4; GCN2; GCN2 eIF2alpha kinase; GCN2 like protein; GCN2-like protein; KIAA1338; MGCN2;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human GCN2 around the phosphorylation site of Thr899.
Widely expressed (PubMed:10504407). Expressed in lung, smooth muscle cells and macrophages (PubMed:24292273).
- Q9P2K8 E2AK4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAGGRGAPGRGRDEPPESYPQRQDHELQALEAIYGADFQDLRPDACGPVKEPPEINLVLYPQGLTGEEVYVKVDLRVKCPPTYPDVVPEIELKNAKGLSNESVNLLKSRLEELAKKHCGEVMIFELAYHVQSFLSEHNKPPPKSFHEEMLERRAQEEQQRLLEAKRKEEQEQREILHEIQRRKEEIKEEKKRKEMAKQERLEIASLSNQDHTSKKDPGGHRTAAILHGGSPDFVGNGKHRANSSGRSRRERQYSVCNSEDSPGSCEILYFNMGSPDQLMVHKGKCIGSDEQLGKLVYNALETATGGFVLLYEWVLQWQKKMGPFLTSQEKEKIDKCKKQIQGTETEFNSLVKLSHPNVVRYLAMNLKEQDDSIVVDILVEHISGVSLAAHLSHSGPIPVHQLRRYTAQLLSGLDYLHSNSVVHKVLSASNVLVDAEGTVKITDYSISKRLADICKEDVFEQTRVRFSDNALPYKTGKKGDVWRLGLLLLSLSQGQECGEYPVTIPSDLPADFQDFLKKCVCLDDKERWSPQQLLKHSFINPQPKMPLVEQSPEDSEGQDYVETVIPSNRLPSAAFFSETQRQFSRYFIEFEELQLLGKGAFGAVIKVQNKLDGCCYAVKRIPINPASRQFRRIKGEVTLLSRLHHENIVRYYNAWIERHERPAGPGTPPPDSGPLAKDDRAARGQPASDTDGLDSVEAAAPPPILSSSVEWSTSGERSASARFPATGPGSSDDEDDDEDEHGGVFSQSFLPASDSESDIIFDNEDENSKSQNQDEDCNEKNGCHESEPSVTTEAVHYLYIQMEYCEKSTLRDTIDQGLYRDTVRLWRLFREILDGLAYIHEKGMIHRDLKPVNIFLDSDDHVKIGDFGLATDHLAFSADSKQDDQTGDLIKSDPSGHLTGMVGTALYVSPEVQGSTKSAYNQKVDLFSLGIIFFEMSYHPMVTASERIFVLNQLRDPTSPKFPEDFDDGEHAKQKSVISWLLNHDPAKRPTATELLKSELLPPPQMEESELHEVLHHTLTNVDGKAYRTMMAQIFSQRISPAIDYTYDSDILKGNFSIRTAKMQQHVCETIIRIFKRHGAVQLCTPLLLPRNRQIYEHNEAALFMDHSGMLVMLPFDLRIPFARYVARNNILNLKRYCIERVFRPRKLDRFHPKELLECAFDIVTSTTNSFLPTAEIIYTIYEIIQEFPALQERNYSIYLNHTMLLKAILLHCGIPEDKLSQVYIILYDAVTEKLTRREVEAKFCNLSLSSNSLCRLYKFIEQKGDLQDLMPTINSLIKQKTGIAQLVKYGLKDLEEVVGLLKKLGIKLQVLINLGLVYKVQQHNGIIFQFVAFIKRRQRAVPEILAAGGRYDLLIPQFRGPQALGPVPTAIGVSIAIDKISAAVLNMEESVTISSCDLLVVSVGQMSMSRAINLTQKLWTAGITAEIMYDWSQSQEELQEYCRHHEITYVALVSDKEGSHVKVKSFEKERQTEKRVLETELVDHVLQKLRTKVTDERNGREASDNLAVQNLKGSFSNASGLFEIHGATVVPIVSVLAPEKLSASTRRRYETQVQTRLQTSLANLHQKSSEIEILAVDLPKETILQFLSLEWDADEQAFNTTVKQLLSRLPKQRYLKLVCDEIYNIKVEKKVSVLFLYSYRDDYYRILF
Predictions
Score>80(red) has high confidence and is suggested to be used for WB detection. *The prediction model is mainly based on the alignment of immunogen sequences, the results are for reference only, not as the basis of quality assurance.
High(score>80) Medium(80>score>50) Low(score<50) No confidence
Research Backgrounds
Metabolic-stress sensing protein kinase that phosphorylates the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF-2-alpha/EIF2S1) on 'Ser-52' in response to low amino acid availability. Plays a role as an activator of the integrated stress response (ISR) required for adapatation to amino acid starvation. Converts phosphorylated eIF-2-alpha/EIF2S1 either to a competitive inhibitor of the translation initiation factor eIF-2B, leading to a global protein synthesis repression, and thus to a reduced overall utilization of amino acids, or to a translational initiation activation of specific mRNAs, such as the transcriptional activator ATF4, and hence allowing ATF4-mediated reprogramming of amino acid biosynthetic gene expression to alleviate nutrient depletion. Binds uncharged tRNAs (By similarity). Involved in cell cycle arrest by promoting cyclin D1 mRNA translation repression after the unfolded protein response pathway (UPR) activation or cell cycle inhibitor CDKN1A/p21 mRNA translation activation in response to amino acid deprivation. Plays a role in the consolidation of synaptic plasticity, learning as well as formation of long-term memory. Plays a role in neurite outgrowth inhibition. Plays a proapoptotic role in response to glucose deprivation. Promotes global cellular protein synthesis repression in response to UV irradiation independently of the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK/JNK) and p38 MAPK signaling pathways (By similarity). Plays a role in the antiviral response against alphavirus infection; impairs early viral mRNA translation of the incoming genomic virus RNA, thus preventing alphavirus replication (By similarity).
(Microbial infection) Plays a role in modulating the adaptive immune response to yellow fever virus infection; promotes dendritic cells to initiate autophagy and antigene presentation to both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cells under amino acid starvation.
Autophosphorylated; autophosphorylation on Thr-899 is increased upon amino acid starvation and in UV irradiation cells and inhibited in presence of IMPACT.
Cytoplasm.
Widely expressed. Expressed in lung, smooth muscle cells and macrophages.
The histidyl-tRNA synthetase-like region and protein kinase domains are necessary for eIF-2-alpha kinase activity and eIF-2-alpha-mediated translational control. The histidyl-tRNA synthetase-like domain is necessary for binding to uncharged tRNAs. Kinase domain 1 is a degenerate kinase domain.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. GCN2 subfamily.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Autophagy - animal. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis C.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Measles.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Influenza A.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Epstein-Barr virus infection.
References
Application: WB Species: human Sample:
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: Heart
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.