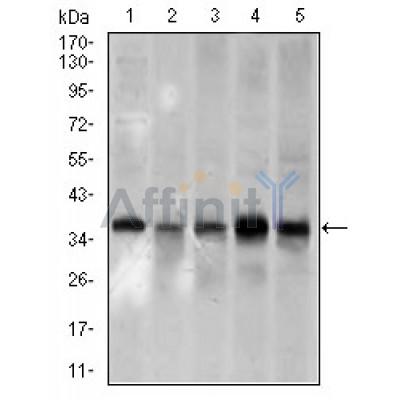
PCNA Antibody - #BF0704
| Product: | PCNA Antibody |
| Catalog: | BF0704 |
| Description: | Mouse monoclonal antibody to PCNA |
| Application: | WB IHC ELISA |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Mol.Wt.: | 29/35kDa; 29kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P12004 |
| RRID: | AB_2843434 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0704, RRID:AB_2843434.
Fold/Unfold
ATLD2; cb16; Cyclin; DNA polymerase delta auxiliary protein; etID36690.10; fa28e03; fb36g03; HGCN8729; MGC8367; Mutagen-sensitive 209 protein; OTTHUMP00000030189; OTTHUMP00000030190; PCNA; Pcna/cyclin; PCNA_HUMAN; PCNAR; Polymerase delta accessory protein; Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; wu:fa28e03; wu:fb36g03;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human PCNA (AA: 53-196 ) expressed in E. Coli.
- P12004 PCNA_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MFEARLVQGSILKKVLEALKDLINEACWDISSSGVNLQSMDSSHVSLVQLTLRSEGFDTYRCDRNLAMGVNLTSMSKILKCAGNEDIITLRAEDNADTLALVFEAPNQEKVSDYEMKLMDLDVEQLGIPEQEYSCVVKMPSGEFARICRDLSHIGDAVVISCAKDGVKFSASGELGNGNIKLSQTSNVDKEEEAVTIEMNEPVQLTFALRYLNFFTKATPLSSTVTLSMSADVPLVVEYKIADMGHLKYYLAPKIEDEEGS
Research Backgrounds
Auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase delta and is involved in the control of eukaryotic DNA replication by increasing the polymerase's processibility during elongation of the leading strand. Induces a robust stimulatory effect on the 3'-5' exonuclease and 3'-phosphodiesterase, but not apurinic-apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease, APEX2 activities. Has to be loaded onto DNA in order to be able to stimulate APEX2. Plays a key role in DNA damage response (DDR) by being conveniently positioned at the replication fork to coordinate DNA replication with DNA repair and DNA damage tolerance pathways. Acts as a loading platform to recruit DDR proteins that allow completion of DNA replication after DNA damage and promote postreplication repair: Monoubiquitinated PCNA leads to recruitment of translesion (TLS) polymerases, while 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of PCNA is involved in error-free pathway and employs recombination mechanisms to synthesize across the lesion.
Phosphorylated. Phosphorylation at Tyr-211 by EGFR stabilizes chromatin-associated PCNA.
Acetylated by CREBBP and p300/EP300; preferentially acetylated by CREBBP on Lys-80, Lys-13 and Lys-14 and on Lys-77 by p300/EP300 upon loading on chromatin in response to UV irradiation. Lysine acetylation disrupts association with chromatin, hence promoting PCNA ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation in response to UV damage in a CREBBP- and EP300-dependent manner. Acetylation disrupts interaction with NUDT15 and promotes degradation.
Ubiquitinated. Following DNA damage, can be either monoubiquitinated to stimulate direct bypass of DNA lesions by specialized DNA polymerases or polyubiquitinated to promote recombination-dependent DNA synthesis across DNA lesions by template switching mechanisms. Following induction of replication stress, monoubiquitinated by the UBE2B-RAD18 complex on Lys-164, leading to recruit translesion (TLS) polymerases, which are able to synthesize across DNA lesions in a potentially error-prone manner. An error-free pathway also exists and requires non-canonical polyubiquitination on Lys-164 through 'Lys-63' linkage of ubiquitin moieties by the E2 complex UBE2N-UBE2V2 and the E3 ligases, HLTF, RNF8 and SHPRH. This error-free pathway, also known as template switching, employs recombination mechanisms to synthesize across the lesion, using as a template the undamaged, newly synthesized strand of the sister chromatid. Monoubiquitination at Lys-164 also takes place in undamaged proliferating cells, and is mediated by the DCX(DTL) complex, leading to enhance PCNA-dependent translesion DNA synthesis. Sumoylated during S phase.
Methylated on glutamate residues by ARMT1/C6orf211.
Nucleus.
Note: Colocalizes with CREBBP, EP300 and POLD1 to sites of DNA damage (PubMed:24939902). Forms nuclear foci representing sites of ongoing DNA replication and vary in morphology and number during S phase. Together with APEX2, is redistributed in discrete nuclear foci in presence of oxidative DNA damaging agents.
Belongs to the PCNA family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Cell cycle. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Replication and repair > DNA replication.
· Genetic Information Processing > Replication and repair > Base excision repair.
· Genetic Information Processing > Replication and repair > Nucleotide excision repair.
· Genetic Information Processing > Replication and repair > Mismatch repair.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
References
Application: WB Species: rat Sample: Dental pulp fibroblasts
Application: WB Species: human Sample: passage 3 DPC
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.