KEAP1 Antibody - #BF0010
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0010, RRID:AB_2834071.
Fold/Unfold
Cytosolic inhibitor of Nrf2; INrf 2; INrf2; Keap 1; KEAP1; KEAP1_HUMAN; Kelch like ECH associated protein 1; Kelch like family member 19; Kelch like protein 19; Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; Kelch-like protein 19; KIAA0132; KLHL 19; KLHL19; MGC10630; MGC1114; MGC20887; MGC4407; MGC9454;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human KEAP1 expressed in E. Coli.
- Q14145 KEAP1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MQPDPRPSGAGACCRFLPLQSQCPEGAGDAVMYASTECKAEVTPSQHGNRTFSYTLEDHTKQAFGIMNELRLSQQLCDVTLQVKYQDAPAAQFMAHKVVLASSSPVFKAMFTNGLREQGMEVVSIEGIHPKVMERLIEFAYTASISMGEKCVLHVMNGAVMYQIDSVVRACSDFLVQQLDPSNAIGIANFAEQIGCVELHQRAREYIYMHFGEVAKQEEFFNLSHCQLVTLISRDDLNVRCESEVFHACINWVKYDCEQRRFYVQALLRAVRCHSLTPNFLQMQLQKCEILQSDSRCKDYLVKIFEELTLHKPTQVMPCRAPKVGRLIYTAGGYFRQSLSYLEAYNPSDGTWLRLADLQVPRSGLAGCVVGGLLYAVGGRNNSPDGNTDSSALDCYNPMTNQWSPCAPMSVPRNRIGVGVIDGHIYAVGGSHGCIHHNSVERYEPERDEWHLVAPMLTRRIGVGVAVLNRLLYAVGGFDGTNRLNSAECYYPERNEWRMITAMNTIRSGAGVCVLHNCIYAAGGYDGQDQLNSVERYDVETETWTFVAPMKHRRSALGITVHQGRIYVLGGYDGHTFLDSVECYDPDTDTWSEVTRMTSGRSGVGVAVTMEPCRKQIDQQNCTC
PTMs - Q14145 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ubiquitination | Uniprot | ||
| Y33 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K39 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T43 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y54 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T55 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T60 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K61 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K84 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y85 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K97 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K108 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T112 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K131 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| Y141 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| C273 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| T277 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K287 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| C288 | S-Nitrosylation | Uniprot | |
| S293 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| S295 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K298 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K312 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S599 | Phosphorylation | Q02156 (PRKCE) | Uniprot |
| S602 | Phosphorylation | Q02156 (PRKCE) | Uniprot |
| K615 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Substrate-specific adapter of a BCR (BTB-CUL3-RBX1) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that regulates the response to oxidative stress by targeting NFE2L2/NRF2 for ubiquitination. KEAP1 acts as a key sensor of oxidative and electrophilic stress: in normal conditions, the BCR(KEAP1) complex mediates ubiquitination and degradation of NFE2L2/NRF2, a transcription factor regulating expression of many cytoprotective genes. In response to oxidative stress, different electrophile metabolites trigger non-enzymatic covalent modifications of highly reactive cysteine residues in KEAP1, leading to inactivate the ubiquitin ligase activity of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, promoting NFE2L2/NRF2 nuclear accumulation and expression of phase II detoxifying enzymes. In response to selective autophagy, KEAP1 is sequestered in inclusion bodies following its interaction with SQSTM1/p62, leading to inactivation of the BCR(KEAP1) complex and activation of NFE2L2/NRF2. The BCR(KEAP1) complex also mediates ubiquitination of SQSTM1/p62, increasing SQSTM1/p62 sequestering activity and degradation. The BCR(KEAP1) complex also targets BPTF and PGAM5 for ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome.
Non-enzymatic covalent modifications of reactive cysteines by electrophile metabolites inactivate the BCR(KEAP1) complex. Accumulation of fumarate promotes the formation of cysteine S-succination (S-(2-succinyl)cysteine), leading to inactivate the BCR(KEAP1) complex and promote NFE2L2/NRF2 nuclear accumulation and activation (By similarity). Nitric oxide-dependent 8-Nitro-cGMP formation promotes cysteine guanylation (S-cGMP-cysteine), leading to NFE2L2/NRF2 nuclear accumulation and activation (By similarity). Itaconate, an anti-inflammatory metabolite generated in response to lipopolysaccharide, alkylates cysteines, activating NFE2L2/NRF2. Methylglyoxal, a reactive metabolite that accumulates when the glycolytic enzyme PGK1 is inhibited, promotes formation of a methylimidazole cross-link between proximal Cys-151 and Arg-135 on another KEAP1 molecule, resulting in an inactive dimer that inactivates the BCR(KEAP1) complex.
Degraded via a proteasomal-independent process during selective autophagy: interaction with phosphorylated SQSTM1/p62 sequesters KEAP1 in inclusion bodies, leading to its degradation.
Auto-ubiquitinated by the BCR(KEAP1) complex. Quinone-induced oxidative stress, but not sulforaphane, increases its ubiquitination. Ubiquitination and subsequent degradation is most pronounced following prolonged exposure of cells to oxidative stress, particularly in glutathione-deficient cells that are highly susceptible to oxidative stress.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Mainly cytoplasmic (PubMed:15601839). In response to selective autophagy, relocalizes to inclusion bodies following interaction with SQSTM1/p62 (PubMed:20452972).
Broadly expressed, with highest levels in skeletal muscle.
Component of the BCR(KEAP1) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, at least composed of 2 molecules of CUL3, 2 molecules of KEAP1, and RBX1. Interacts with NFE2L2/NRF2; the interaction is direct. Forms a ternary complex with NFE2L2/NRF2 and PGAM5. Interacts with (phosphorylated) SQSTM1/p62; the interaction is direct and inactivates the BCR(KEAP1) complex by sequestering it in inclusion bodies, promoting its degradation. Interacts with NFE2L1. Interacts with BPTF and PTMA. Interacts with MAP1LC3B. Interacts indirectly with ENC1. Interacts with SESN1 and SESN2. Interacts with HSP90AA1 and HSP90AB1.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with ebolavirus protein VP24; this interaction activates transcription factor NFE2L2/NRF2 by blocking its interaction with KEAP1.
KEAP1 contains reactive cysteine residues that act as sensors for endogenously produced and exogenously encountered small molecules, which react with sulfhydryl groups and modify the cysteine sensors, leading to impair ability of the BCR(KEAP1) complex to ubiquitinate target proteins.
The Kelch repeats mediate interaction with NFE2L2/NRF2, BPTF and PGAM5.
Belongs to the KEAP1 family.
Research Fields
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
References
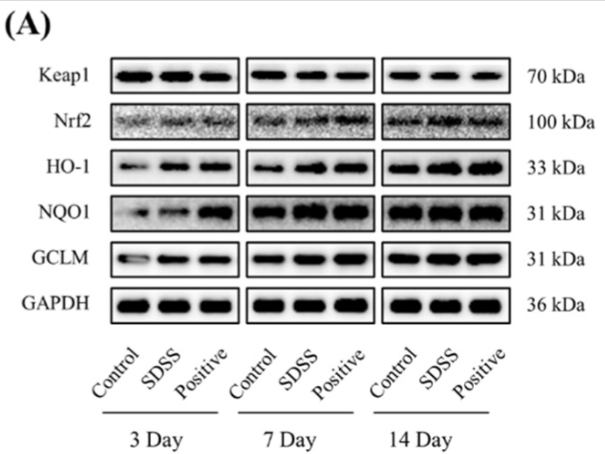
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.