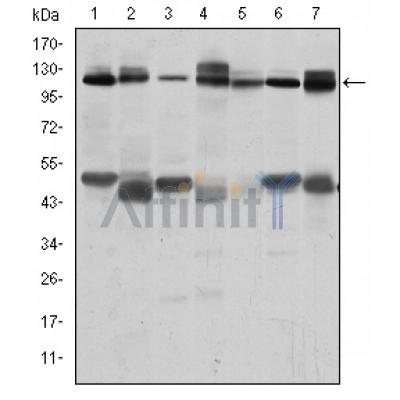
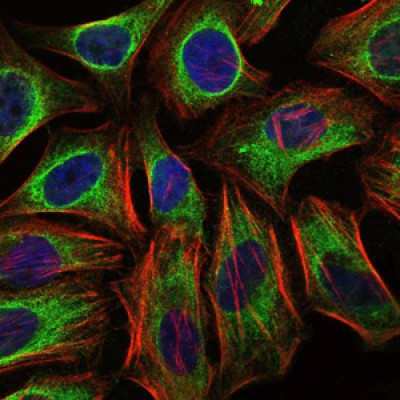
C-CBL Antibody - #BF0151
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0151, RRID:AB_2833939.
Fold/Unfold
4732447J05Rik; C CBL; Cas Br M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence; Casitas B lineage lymphoma proto oncogene; Casitas B-lineage lymphoma proto-oncogene; CBL 2; cbl; CBL_HUMAN; CBL2; E3 ubiquitin protein ligase CBL; E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL; Oncogene CBL2; Proto oncogene c CBL; Proto-oncogene c-CBL; RGD1561386; RING finger protein 55; RNF55; Signal transduction protein CBL;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human C-CBL expressed in E. Coli.
- P22681 CBL_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAGNVKKSSGAGGGSGSGGSGSGGLIGLMKDAFQPHHHHHHHLSPHPPGTVDKKMVEKCWKLMDKVVRLCQNPKLALKNSPPYILDLLPDTYQHLRTILSRYEGKMETLGENEYFRVFMENLMKKTKQTISLFKEGKERMYEENSQPRRNLTKLSLIFSHMLAELKGIFPSGLFQGDTFRITKADAAEFWRKAFGEKTIVPWKSFRQALHEVHPISSGLEAMALKSTIDLTCNDYISVFEFDIFTRLFQPWSSLLRNWNSLAVTHPGYMAFLTYDEVKARLQKFIHKPGSYIFRLSCTRLGQWAIGYVTADGNILQTIPHNKPLFQALIDGFREGFYLFPDGRNQNPDLTGLCEPTPQDHIKVTQEQYELYCEMGSTFQLCKICAENDKDVKIEPCGHLMCTSCLTSWQESEGQGCPFCRCEIKGTEPIVVDPFDPRGSGSLLRQGAEGAPSPNYDDDDDERADDTLFMMKELAGAKVERPPSPFSMAPQASLPPVPPRLDLLPQRVCVPSSASALGTASKAASGSLHKDKPLPVPPTLRDLPPPPPPDRPYSVGAESRPQRRPLPCTPGDCPSRDKLPPVPSSRLGDSWLPRPIPKVPVSAPSSSDPWTGRELTNRHSLPFSLPSQMEPRPDVPRLGSTFSLDTSMSMNSSPLVGPECDHPKIKPSSSANAIYSLAARPLPVPKLPPGEQCEGEEDTEYMTPSSRPLRPLDTSQSSRACDCDQQIDSCTYEAMYNIQSQAPSITESSTFGEGNLAAAHANTGPEESENEDDGYDVPKPPVPAVLARRTLSDISNASSSFGWLSLDGDPTTNVTEGSQVPERPPKPFPRRINSERKAGSCQQGSGPAASAATASPQLSSEIENLMSQGYSYQDIQKALVIAQNNIEMAKNILREFVSISSPAHVAT
Research Backgrounds
Adapter protein that functions as a negative regulator of many signaling pathways that are triggered by activation of cell surface receptors. Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, which accepts ubiquitin from specific E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and then transfers it to substrates promoting their degradation by the proteasome. Recognizes activated receptor tyrosine kinases, including KIT, FLT1, FGFR1, FGFR2, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, EGFR, CSF1R, EPHA8 and KDR and terminates signaling. Recognizes membrane-bound HCK, SRC and other kinases of the SRC family and mediates their ubiquitination and degradation. Participates in signal transduction in hematopoietic cells. Plays an important role in the regulation of osteoblast differentiation and apoptosis. Essential for osteoclastic bone resorption. The 'Tyr-731' phosphorylated form induces the activation and recruitment of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to the cell membrane in a signaling pathway that is critical for osteoclast function. May be functionally coupled with the E2 ubiquitin-protein ligase UB2D3. In association with CBLB, required for proper feedback inhibition of ciliary platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha (PDGFRA) signaling pathway via ubiquitination and internalization of PDGFRA (By similarity).
Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by ALK, EGFR, SYK, FYN and ZAP70 (By similarity). Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues in response to FLT1 and KIT signaling. Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by INSR and FGR. Phosphorylated on several tyrosine residues by constitutively activated FGFR3. Not phosphorylated at Tyr-731 by FGFR3. Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by activated CSF1R, PDGFRA and PDGFRB. Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by HCK.
Ubiquitinated, leading to its degradation via the proteasome. Ubiquitination is negatively regulated by IFT20.
Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Cell projection>Cilium. Golgi apparatus.
Note: Colocalizes with FGFR2 in lipid rafts at the cell membrane.
The RING-type zinc finger domain mediates binding to an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme.
The N-terminus is composed of the phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domain, a short linker region and the RING-type zinc finger. The PTB domain, which is also called TKB (tyrosine kinase binding) domain, is composed of three different subdomains: a four-helix bundle (4H), a calcium-binding EF hand and a divergent SH2 domain.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Endocytosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > ErbB signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Chronic myeloid leukemia. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Insulin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.