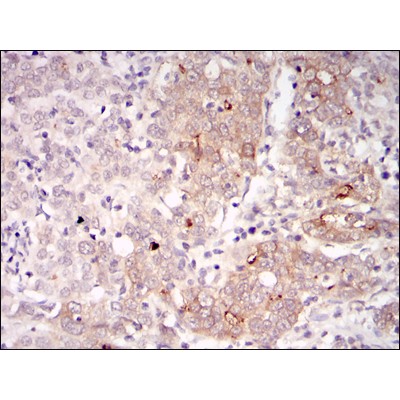
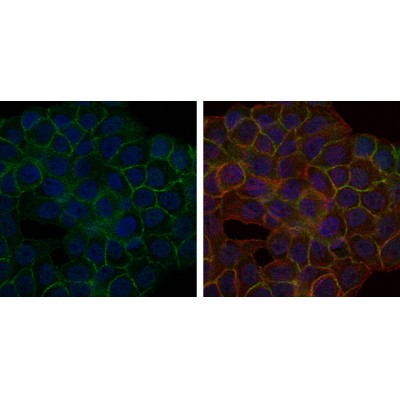
BLNK Antibody - #BF0686
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0686, RRID:AB_2833926.
Fold/Unfold
AGM4; B cell adapter containing SH2 domain protein; B cell adapter containing Src homology 2 domain protein; B cell adaptor containing SH2 domain; B cell linker; B cell linker protein; B cell-specific adaptor protein; B-cell activation; B-cell adapter containing a SH2 domain protein; B-cell adapter containing a Src homology 2 domain protein; B-cell linker protein; BASH; Bca; BLNK; BLNK s; BLNK_HUMAN; Cytoplasmic adapter protein; Ly 57; Ly57; Lymphocyte antigen 57; Lyw 57; Lyw57; MGC111051; SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein, 65-KD; SLP 65; SLP-65; SLP65; Src homology [SH2] domain-containing leukocyte protein of 65 kD; Src homology 2 domain containing leukocyte protein of 65 kDa; Src homology 2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 65 kDa;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human BLNK expressed in E. Coli.
Expressed in B-cell lineage and fibroblast cell lines (at protein level). Highest levels of expression in the spleen, with lower levels in the liver, kidney, pancreas, small intestines and colon.
- Q8WV28 BLNK_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MDKLNKITVPASQKLRQLQKMVHDIKNNEGGIMNKIKKLKVKAPPSVPRRDYASESPADEEEQWSDDFDSDYENPDEHSDSEMYVMPAEENADDSYEPPPVEQETRPVHPALPFARGEYIDNRSSQRHSPPFSKTLPSKPSWPSEKARLTSTLPALTALQKPQVPPKPKGLLEDEADYVVPVEDNDENYIHPTESSSPPPEKAPMVNRSTKPNSSTPASPPGTASGRNSGAWETKSPPPAAPSPLPRAGKKPTTPLKTTPVASQQNASSVCEEKPIPAERHRGSSHRQEAVQSPVFPPAQKQIHQKPIPLPRFTEGGNPTVDGPLPSFSSNSTISEQEAGVLCKPWYAGACDRKSAEEALHRSNKDGSFLIRKSSGHDSKQPYTLVVFFNKRVYNIPVRFIEATKQYALGRKKNGEEYFGSVAEIIRNHQHSPLVLIDSQNNTKDSTRLKYAVKVS
Research Backgrounds
Functions as a central linker protein, downstream of the B-cell receptor (BCR), bridging the SYK kinase to a multitude of signaling pathways and regulating biological outcomes of B-cell function and development. Plays a role in the activation of ERK/EPHB2, MAP kinase p38 and JNK. Modulates AP1 activation. Important for the activation of NF-kappa-B and NFAT. Plays an important role in BCR-mediated PLCG1 and PLCG2 activation and Ca(2+) mobilization and is required for trafficking of the BCR to late endosomes. However, does not seem to be required for pre-BCR-mediated activation of MAP kinase and phosphatidyl-inositol 3 (PI3) kinase signaling. May be required for the RAC1-JNK pathway. Plays a critical role in orchestrating the pro-B cell to pre-B cell transition. May play an important role in BCR-induced B-cell apoptosis.
Following BCR activation, phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by SYK and LYN. When phosphorylated, serves as a scaffold to assemble downstream targets of antigen activation, including PLCG1, VAV1, GRB2 and NCK1. Phosphorylation of Tyr-84, Tyr-178 and Tyr-189 facilitates PLCG1 binding. Phosphorylation of Tyr-96 facilitates BTK binding. Phosphorylation of Tyr-72 facilitates VAV1 and NCK1 binding. Phosphorylation is required for both Ca(2+) and MAPK signaling pathways.
Cytoplasm. Cell membrane.
Note: BCR activation results in the translocation to membrane fraction.
Expressed in B-cell lineage and fibroblast cell lines (at protein level). Highest levels of expression in the spleen, with lower levels in the liver, kidney, pancreas, small intestines and colon.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > NF-kappa B signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Primary immunodeficiency.
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > B cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.