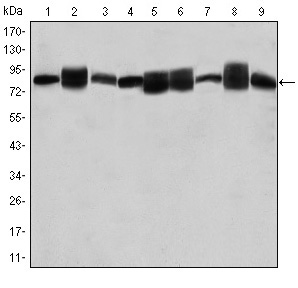
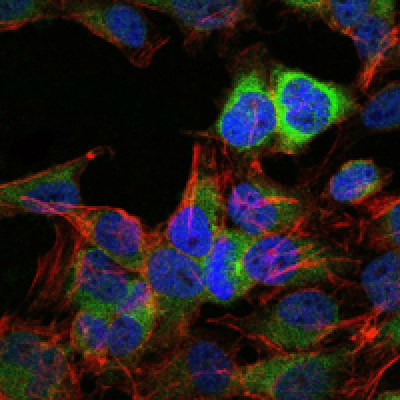
HSP90AB1 Antibody - #BF0215
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0215, RRID:AB_2833923.
Fold/Unfold
90 kda heat shock protein beta HSP90 beta; D6S182; FLJ26984; Heat shock 84 kDa; Heat shock 90kD protein 1, beta; Heat shock 90kDa protein 1 beta; Heat shock protein 90 alpha family class B member 1; Heat shock protein 90 kDa; Heat shock protein 90kDa alpha (cytosolic) class B member 1; Heat shock protein 90kDa alpha family class B member 1; Heat shock protein beta; Heat shock protein HSP 90 beta; Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta; HS90B_HUMAN; HSP 84; HSP 90; HSP 90 b; HSP 90b; HSP84; HSP90 BETA; hsp90ab1; HSP90B; HSPC2; HSPCB;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human HSP90AB1 expressed in E. Coli.
- P08238 HS90B_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MPEEVHHGEEEVETFAFQAEIAQLMSLIINTFYSNKEIFLRELISNASDALDKIRYESLTDPSKLDSGKELKIDIIPNPQERTLTLVDTGIGMTKADLINNLGTIAKSGTKAFMEALQAGADISMIGQFGVGFYSAYLVAEKVVVITKHNDDEQYAWESSAGGSFTVRADHGEPIGRGTKVILHLKEDQTEYLEERRVKEVVKKHSQFIGYPITLYLEKEREKEISDDEAEEEKGEKEEEDKDDEEKPKIEDVGSDEEDDSGKDKKKKTKKIKEKYIDQEELNKTKPIWTRNPDDITQEEYGEFYKSLTNDWEDHLAVKHFSVEGQLEFRALLFIPRRAPFDLFENKKKKNNIKLYVRRVFIMDSCDELIPEYLNFIRGVVDSEDLPLNISREMLQQSKILKVIRKNIVKKCLELFSELAEDKENYKKFYEAFSKNLKLGIHEDSTNRRRLSELLRYHTSQSGDEMTSLSEYVSRMKETQKSIYYITGESKEQVANSAFVERVRKRGFEVVYMTEPIDEYCVQQLKEFDGKSLVSVTKEGLELPEDEEEKKKMEESKAKFENLCKLMKEILDKKVEKVTISNRLVSSPCCIVTSTYGWTANMERIMKAQALRDNSTMGYMMAKKHLEINPDHPIVETLRQKAEADKNDKAVKDLVVLLFETALLSSGFSLEDPQTHSNRIYRMIKLGLGIDEDEVAAEEPNAAVPDEIPPLEGDEDASRMEEVD
Research Backgrounds
Molecular chaperone that promotes the maturation, structural maintenance and proper regulation of specific target proteins involved for instance in cell cycle control and signal transduction. Undergoes a functional cycle that is linked to its ATPase activity. This cycle probably induces conformational changes in the client proteins, thereby causing their activation. Interacts dynamically with various co-chaperones that modulate its substrate recognition, ATPase cycle and chaperone function. Engages with a range of client protein classes via its interaction with various co-chaperone proteins or complexes, that act as adapters, simultaneously able to interact with the specific client and the central chaperone itself. Recruitment of ATP and co-chaperone followed by client protein forms a functional chaperone. After the completion of the chaperoning process, properly folded client protein and co-chaperone leave HSP90 in an ADP-bound partially open conformation and finally, ADP is released from HSP90 which acquires an open conformation for the next cycle. Apart from its chaperone activity, it also plays a role in the regulation of the transcription machinery. HSP90 and its co-chaperones modulate transcription at least at three different levels. In the first place, they alter the steady-state levels of certain transcription factors in response to various physiological cues. Second, they modulate the activity of certain epigenetic modifiers, such as histone deacetylases or DNA methyl transferases, and thereby respond to the change in the environment. Third, they participate in the eviction of histones from the promoter region of certain genes and thereby turn on gene expression. Antagonizes STUB1-mediated inhibition of TGF-beta signaling via inhibition of STUB1-mediated SMAD3 ubiquitination and degradation. Promotes cell differentiation by chaperoning BIRC2 and thereby protecting from auto-ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasomal machinery. Main chaperone that is involved in the phosphorylation/activation of the STAT1 by chaperoning both JAK2 and PRKCE under heat shock and in turn, activates its own transcription.
Ubiquitinated in the presence of STUB1-UBE2D1 complex (in vitro).
ISGylated.
S-nitrosylated; negatively regulates the ATPase activity.
Phosphorylation at Tyr-301 by SRC is induced by lipopolysaccharide. Phosphorylation at Ser-226 and Ser-255 inhibits AHR interaction.
Methylated by SMYD2; facilitates dimerization and chaperone complex formation; promotes cancer cell proliferation.
Cleaved following oxidative stress resulting in HSP90AB1 protein radicals formation; disrupts the chaperoning function and the degradation of its client proteins.
Cytoplasm. Melanosome. Nucleus. Secreted. Cell membrane.
Note: Identified by mass spectrometry in melanosome fractions from stage I to stage IV (PubMed:17081065). Translocates with BIRC2 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm during differentiation (PubMed:18239673). Secreted when associated with TGFB1 processed form (LAP) (PubMed:20599762).
The TPR repeat-binding motif mediates interaction with TPR repeat-containing proteins.
Belongs to the heat shock protein 90 family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Necroptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Antigen processing and presentation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > NOD-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
Application: IHC Species: human Sample: HCC cells
Application: WB Species: human Sample: PLC-PRF-5 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.