Tubulin alpha Antibody - #T0033
| Product: | Tubulin alpha Antibody |
| Catalog: | T0033 |
| Description: | Mouse monoclonal antibody to Tubulin alpha |
| Application: | WB ELISA |
| Cited expt.: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Zebrafish, Rabbit |
| Mol.Wt.: | 55KD; 50kD(Calculated). |
| Uniprot: | P68366 |
| RRID: | AB_2839424 |
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# T0033, RRID:AB_2839424.
Fold/Unfold
TUBA4A, Alpha-tubulin 1, TUBA1, Testis-specific alpha-tubulin, Tubulin, alpha 4a, H2-ALPHA, Tubulin alpha-1 chain, Tubulin alpha-4 chain, Tubulin alpha-4A chain, Tubulin H2-alpha, Tubulin, alpha 1
Immunogens
Peptide from Zebrafish alpha tubulin.
- P68366 TBA4A_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MRECISVHVGQAGVQMGNACWELYCLEHGIQPDGQMPSDKTIGGGDDSFTTFFCETGAGKHVPRAVFVDLEPTVIDEIRNGPYRQLFHPEQLITGKEDAANNYARGHYTIGKEIIDPVLDRIRKLSDQCTGLQGFLVFHSFGGGTGSGFTSLLMERLSVDYGKKSKLEFSIYPAPQVSTAVVEPYNSILTTHTTLEHSDCAFMVDNEAIYDICRRNLDIERPTYTNLNRLISQIVSSITASLRFDGALNVDLTEFQTNLVPYPRIHFPLATYAPVISAEKAYHEQLSVAEITNACFEPANQMVKCDPRHGKYMACCLLYRGDVVPKDVNAAIAAIKTKRSIQFVDWCPTGFKVGINYQPPTVVPGGDLAKVQRAVCMLSNTTAIAEAWARLDHKFDLMYAKRAFVHWYVGEGMEEGEFSEAREDMAALEKDYEEVGIDSYEDEDEGEE
Research Backgrounds
Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are polyglutamylated, resulting in polyglutamate chains on the gamma-carboxyl group. Polyglutamylation plays a key role in microtubule severing by spastin (SPAST). SPAST preferentially recognizes and acts on microtubules decorated with short polyglutamate tails: severing activity by SPAST increases as the number of glutamates per tubulin rises from one to eight, but decreases beyond this glutamylation threshold.
Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are monoglycylated but not polyglycylated due to the absence of functional TTLL10 in human. Monoglycylation is mainly limited to tubulin incorporated into axonemes (cilia and flagella). Both polyglutamylation and monoglycylation can coexist on the same protein on adjacent residues, and lowering glycylation levels increases polyglutamylation, and reciprocally. The precise function of monoglycylation is still unclear (Probable).
Acetylation of alpha chains at Lys-40 is located inside the microtubule lumen. This modification has been correlated with increased microtubule stability, intracellular transport and ciliary assembly.
Methylation of alpha chains at Lys-40 is found in mitotic microtubules and is required for normal mitosis and cytokinesis contributing to genomic stability.
Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton.
Belongs to the tubulin family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Phagosome. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Gap junction. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection.
References
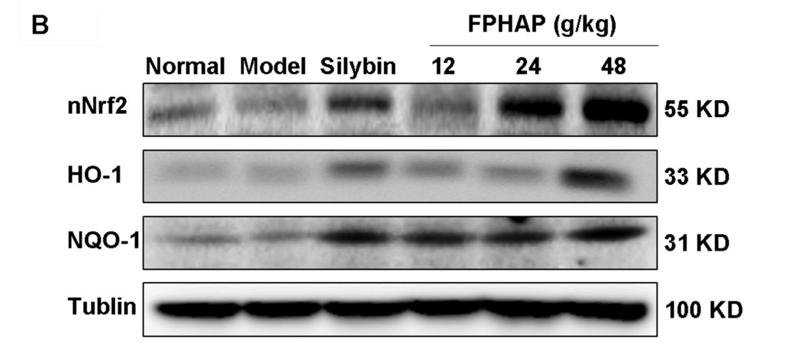
Application: WB Species: mice Sample: liver tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.