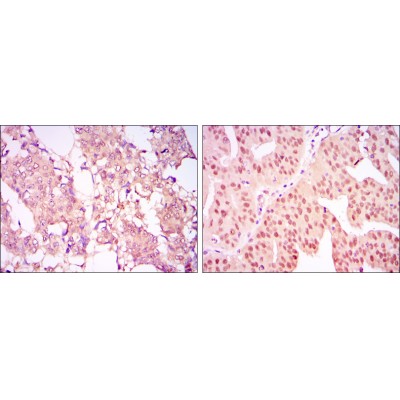
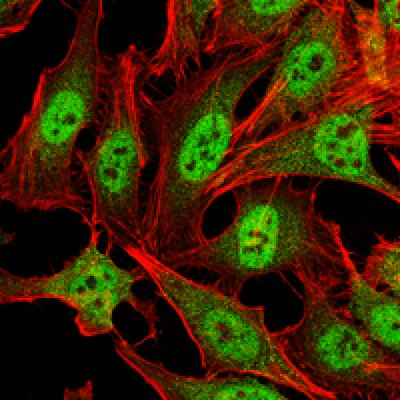
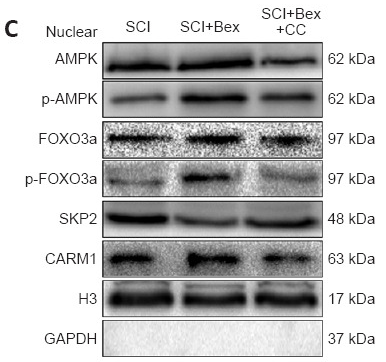
CARM1 Antibody - #BF0658
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0658, RRID:AB_2833878.
Fold/Unfold
carm1; CARM1_HUMAN; Coactivator associated arginine methyltransferase 1; Coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1; Histone arginine methyltransferase CARM 1; Histone arginine methyltransferase CARM1; Histone-arginine methyltransferase CARM1; PRMT 4; PRMT4; Protein arginine methyltransferase; Protein arginine N methyltransferase 4; Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 4;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human CARM1 expressed in E. Coli.
Overexpressed in prostate adenocarcinomas and high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia.
- Q86X55 CARM1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MAAAAAAVGPGAGGAGSAVPGGAGPCATVSVFPGARLLTIGDANGEIQRHAEQQALRLEVRAGPDSAGIALYSHEDVCVFKCSVSRETECSRVGKQSFIITLGCNSVLIQFATPNDFCSFYNILKTCRGHTLERSVFSERTEESSAVQYFQFYGYLSQQQNMMQDYVRTGTYQRAILQNHTDFKDKIVLDVGCGSGILSFFAAQAGARKIYAVEASTMAQHAEVLVKSNNLTDRIVVIPGKVEEVSLPEQVDIIISEPMGYMLFNERMLESYLHAKKYLKPSGNMFPTIGDVHLAPFTDEQLYMEQFTKANFWYQPSFHGVDLSALRGAAVDEYFRQPVVDTFDIRILMAKSVKYTVNFLEAKEGDLHRIEIPFKFHMLHSGLVHGLAFWFDVAFIGSIMTVWLSTAPTEPLTHWYQVRCLFQSPLFAKAGDTLSGTCLLIANKRQSYDISIVAQVDQTGSKSSNLLDLKNPFFRYTGTTPSPPPGSHYTSPSENMWNTGSTYNLSSGMAVAGMPTAYDLSSVIASGSSVGHNNLIPLANTGIVNHTHSRMGSIMSTGIVQGSSGAQGSGGGSTSAHYAVNSQFTMGGPAISMASPMSIPTNTMHYGS
Research Backgrounds
Methylates (mono- and asymmetric dimethylation) the guanidino nitrogens of arginyl residues in several proteins involved in DNA packaging, transcription regulation, pre-mRNA splicing, and mRNA stability. Recruited to promoters upon gene activation together with histone acetyltransferases from EP300/P300 and p160 families, methylates histone H3 at 'Arg-17' (H3R17me), forming mainly asymmetric dimethylarginine (H3R17me2a), leading to activate transcription via chromatin remodeling. During nuclear hormone receptor activation and TCF7L2/TCF4 activation, acts synergically with EP300/P300 and either one of the p160 histone acetyltransferases NCOA1/SRC1, NCOA2/GRIP1 and NCOA3/ACTR or CTNNB1/beta-catenin to activate transcription. During myogenic transcriptional activation, acts together with NCOA3/ACTR as a coactivator for MEF2C. During monocyte inflammatory stimulation, acts together with EP300/P300 as a coactivator for NF-kappa-B. Acts as coactivator for PPARG, promotes adipocyte differentiation and the accumulation of brown fat tissue. Plays a role in the regulation of pre-mRNA alternative splicing by methylation of splicing factors. Also seems to be involved in p53/TP53 transcriptional activation. Methylates EP300/P300, both at 'Arg-2142', which may loosen its interaction with NCOA2/GRIP1, and at 'Arg-580' and 'Arg-604' in the KIX domain, which impairs its interaction with CREB and inhibits CREB-dependent transcriptional activation. Also methylates arginine residues in RNA-binding proteins PABPC1, ELAVL1 and ELAV4, which may affect their mRNA-stabilizing properties and the half-life of their target mRNAs.
Auto-methylated on Arg-550. Methylation enhances transcription coactivator activity. Methylation is required for its role in the regulation of pre-mRNA alternative splicing (By similarity).
Phosphorylation at Ser-216 interferes with S-adenosyl-L-methionine binding and strongly reduces methyltransferase activity (By similarity). Phosphorylation at Ser-216 is strongly increased during mitosis, and decreases rapidly to a very low, basal level after entry into the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Phosphorylation at Ser-216 may promote location in the cytosol.
Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
Note: Mainly nuclear during the G1, S and G2 phases of the cell cycle. Cytoplasmic during mitosis, after breakup of the nuclear membrane.
Overexpressed in prostate adenocarcinomas and high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia.
Belongs to the class I-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily. Protein arginine N-methyltransferase family.
Research Fields
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
References
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: spinal cord
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: colorectal cancer cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.