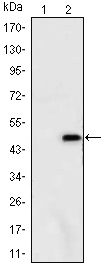
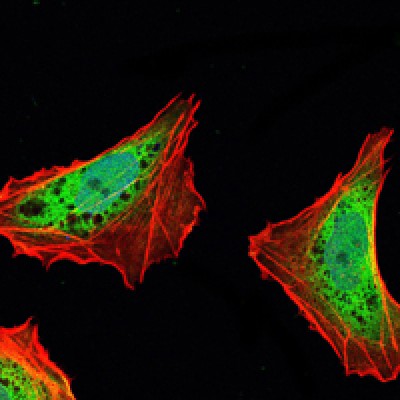
ATXN1 Antibody - #BF0249
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0249, RRID:AB_2833872.
Fold/Unfold
alternative ataxin1; Ataxin-1; ATX1; ATX1_HUMAN; Atxn1; D6S504E; OTTHUMP00000016065; SCA1; Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 protein;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human ATXN1 expressed in E. Coli.
- P54253 ATX1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MKSNQERSNECLPPKKREIPATSRSSEEKAPTLPSDNHRVEGTAWLPGNPGGRGHGGGRHGPAGTSVELGLQQGIGLHKALSTGLDYSPPSAPRSVPVATTLPAAYATPQPGTPVSPVQYAHLPHTFQFIGSSQYSGTYASFIPSQLIPPTANPVTSAVASAAGATTPSQRSQLEAYSTLLANMGSLSQTPGHKAEQQQQQQQQQQQQHQHQQQQQQQQQQQQQQHLSRAPGLITPGSPPPAQQNQYVHISSSPQNTGRTASPPAIPVHLHPHQTMIPHTLTLGPPSQVVMQYADSGSHFVPREATKKAESSRLQQAIQAKEVLNGEMEKSRRYGAPSSADLGLGKAGGKSVPHPYESRHVVVHPSPSDYSSRDPSGVRASVMVLPNSNTPAADLEVQQATHREASPSTLNDKSGLHLGKPGHRSYALSPHTVIQTTHSASEPLPVGLPATAFYAGTQPPVIGYLSGQQQAITYAGSLPQHLVIPGTQPLLIPVGSTDMEASGAAPAIVTSSPQFAAVPHTFVTTALPKSENFNPEALVTQAAYPAMVQAQIHLPVVQSVASPAAAPPTLPPYFMKGSIIQLANGELKKVEDLKTEDFIQSAEISNDLKIDSSTVERIEDSHSPGVAVIQFAVGEHRAQVSVEVLVEYPFFVFGQGWSSCCPERTSQLFDLPCSKLSVGDVCISLTLKNLKNGSVKKGQPVDPASVLLKHSKADGLAGSRHRYAEQENGINQGSAQMLSENGELKFPEKMGLPAAPFLTKIEPSKPAATRKRRWSAPESRKLEKSEDEPPLTLPKPSLIPQEVKICIEGRSNVGK
Research Backgrounds
Chromatin-binding factor that repress Notch signaling in the absence of Notch intracellular domain by acting as a CBF1 corepressor. Binds to the HEY promoter and might assist, along with NCOR2, RBPJ-mediated repression. Binds RNA in vitro. May be involved in RNA metabolism. In concert with CIC and ATXN1L, involved in brain development (By similarity).
Ubiquitinated by UBE3A, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. The presence of expanded poly-Gln repeats in spinocerebellar ataxia 1 (SCA1) patients impairs ubiquitination and degradation, leading to accumulation of ATXN1 in neurons and subsequent toxicity.
Phosphorylation at Ser-775 increases the pathogenicity of proteins with an expanded polyglutamine tract.
Sumoylation is dependent on nuclear localization and phosphorylation at Ser-775. It is reduced in the presence of an expanded polyglutamine tract.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Colocalizes with USP7 in the nucleus.
Widely expressed throughout the body.
The AXH domain is required for interaction with CIC.
Belongs to the ATXN1 family.
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.