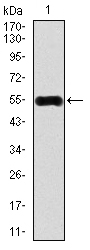
CAMK4 Antibody - #BF0007
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0007, RRID:AB_2833788.
Fold/Unfold
Brain Ca(2+) calmodulin dependent protein kinase type 4; Brain Ca(2+) calmodulin dependent protein kinase type IV; Brain Ca++-calmodulin dependent protein kinase type IV; Calcium / calmodulin dependent protein kinase type 4 catalytic chain; Calcium / calmodulin dependent protein kinase type IV catalytic chain; Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase IV; Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase type IV; Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV; CAM kinase 4; CAM kinase GR; CAM kinase IV; CAM kinase-GR; CaMK 4; CAMK GR; CaMK IV; Camk4; CaMKGR; IV; KCC4_HUMAN; MGC36771;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human CAMK4 expressed in E. Coli.
Expressed in brain, thymus, CD4 T-cells, testis and epithelial ovarian cancer tissue.
- Q16566 KCC4_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MLKVTVPSCSASSCSSVTASAAPGTASLVPDYWIDGSNRDALSDFFEVESELGRGATSIVYRCKQKGTQKPYALKVLKKTVDKKIVRTEIGVLLRLSHPNIIKLKEIFETPTEISLVLELVTGGELFDRIVEKGYYSERDAADAVKQILEAVAYLHENGIVHRDLKPENLLYATPAPDAPLKIADFGLSKIVEHQVLMKTVCGTPGYCAPEILRGCAYGPEVDMWSVGIITYILLCGFEPFYDERGDQFMFRRILNCEYYFISPWWDEVSLNAKDLVRKLIVLDPKKRLTTFQALQHPWVTGKAANFVHMDTAQKKLQEFNARRKLKAAVKAVVASSRLGSASSSHGSIQESHKASRDPSPIQDGNEDMKAIPEGEKIQGDGAQAAVKGAQAELMKVQALEKVKGADINAEEAPKMVPKAVEDGIKVADLELEEGLAEEKLKTVEEAAAPREGQGSSAVGFEVPQQDVILPEY
Research Backgrounds
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that operates in the calcium-triggered CaMKK-CaMK4 signaling cascade and regulates, mainly by phosphorylation, the activity of several transcription activators, such as CREB1, MEF2D, JUN and RORA, which play pivotal roles in immune response, inflammation, and memory consolidation. In the thymus, regulates the CD4(+)/CD8(+) double positive thymocytes selection threshold during T-cell ontogeny. In CD4 memory T-cells, is required to link T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling to the production of IL2, IFNG and IL4 (through the regulation of CREB and MEF2). Regulates the differentiation and survival phases of osteoclasts and dendritic cells (DCs). Mediates DCs survival by linking TLR4 and the regulation of temporal expression of BCL2. Phosphorylates the transcription activator CREB1 on 'Ser-133' in hippocampal neuron nuclei and contribute to memory consolidation and long term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus. Can activate the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK8/JNK1 and MAPK14/p38 and stimulate transcription through the phosphorylation of ELK1 and ATF2. Can also phosphorylate in vitro CREBBP, PRM2, MEF2A and STMN1/OP18.
Phosphorylated by CaMKK1 and CaMKK2 on Thr-200. Dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A. Autophosphorylated on Ser-12 and Ser-13.
Glycosylation at Ser-189 modulates the phosphorylation of CaMK4 at Thr-200 and negatively regulates its activity toward CREB1 in basal conditions and during early inomycin stimulation.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Note: Localized in hippocampal neuron nuclei. In spermatids, associated with chromatin and nuclear matrix (By similarity).
Expressed in brain, thymus, CD4 T-cells, testis and epithelial ovarian cancer tissue.
The autoinhibitory domain overlaps with the calmodulin binding region and interacts in the inactive folded state with the catalytic domain as a pseudosubstrate.
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CaMK subfamily.
Research Fields
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Calcium signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Apelin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Amphetamine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Alcoholism.
· Organismal Systems > Aging > Longevity regulating pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Long-term potentiation.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Neurotrophin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Cholinergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Aldosterone synthesis and secretion.
References
Application: WB Species: Human Sample: SW620 cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.