Catenin-beta Antibody - #BF0319
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0319, RRID:AB_2833506.
Fold/Unfold
Beta catenin; Beta-catenin; Cadherin associated protein; Catenin (cadherin associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa; Catenin beta 1; Catenin beta-1; CATNB; CHBCAT; CTNB1_HUMAN; CTNNB; CTNNB1; DKFZp686D02253; FLJ25606; FLJ37923; OTTHUMP00000162082; OTTHUMP00000165222; OTTHUMP00000165223; OTTHUMP00000209288; OTTHUMP00000209289;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human CTNNB1 expressed in E. Coli.
Expressed in several hair follicle cell types: basal and peripheral matrix cells, and cells of the outer and inner root sheaths. Expressed in colon. Present in cortical neurons (at protein level). Expressed in breast cancer tissues (at protein level) (PubMed:29367600).
- P35222 CTNB1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MATQADLMELDMAMEPDRKAAVSHWQQQSYLDSGIHSGATTTAPSLSGKGNPEEEDVDTSQVLYEWEQGFSQSFTQEQVADIDGQYAMTRAQRVRAAMFPETLDEGMQIPSTQFDAAHPTNVQRLAEPSQMLKHAVVNLINYQDDAELATRAIPELTKLLNDEDQVVVNKAAVMVHQLSKKEASRHAIMRSPQMVSAIVRTMQNTNDVETARCTAGTLHNLSHHREGLLAIFKSGGIPALVKMLGSPVDSVLFYAITTLHNLLLHQEGAKMAVRLAGGLQKMVALLNKTNVKFLAITTDCLQILAYGNQESKLIILASGGPQALVNIMRTYTYEKLLWTTSRVLKVLSVCSSNKPAIVEAGGMQALGLHLTDPSQRLVQNCLWTLRNLSDAATKQEGMEGLLGTLVQLLGSDDINVVTCAAGILSNLTCNNYKNKMMVCQVGGIEALVRTVLRAGDREDITEPAICALRHLTSRHQEAEMAQNAVRLHYGLPVVVKLLHPPSHWPLIKATVGLIRNLALCPANHAPLREQGAIPRLVQLLVRAHQDTQRRTSMGGTQQQFVEGVRMEEIVEGCTGALHILARDVHNRIVIRGLNTIPLFVQLLYSPIENIQRVAAGVLCELAQDKEAAEAIEAEGATAPLTELLHSRNEGVATYAAAVLFRMSEDKPQDYKKRLSVELTSSLFRTEPMAWNETADLGLDIGAQGEPLGYRQDDPSYRSFHSGGYGQDALGMDPMMEHEMGGHHPGADYPVDGLPDLGHAQDLMDGLPPGDSNQLAWFDTDL
Research Backgrounds
Key downstream component of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. In the absence of Wnt, forms a complex with AXIN1, AXIN2, APC, CSNK1A1 and GSK3B that promotes phosphorylation on N-terminal Ser and Thr residues and ubiquitination of CTNNB1 via BTRC and its subsequent degradation by the proteasome. In the presence of Wnt ligand, CTNNB1 is not ubiquitinated and accumulates in the nucleus, where it acts as a coactivator for transcription factors of the TCF/LEF family, leading to activate Wnt responsive genes. Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion, as component of an E-cadherin:catenin adhesion complex. Acts as a negative regulator of centrosome cohesion. Involved in the CDK2/PTPN6/CTNNB1/CEACAM1 pathway of insulin internalization. Blocks anoikis of malignant kidney and intestinal epithelial cells and promotes their anchorage-independent growth by down-regulating DAPK2. Disrupts PML function and PML-NB formation by inhibiting RANBP2-mediated sumoylation of PML. Promotes neurogenesis by maintaining sympathetic neuroblasts within the cell cycle (By similarity).
Phosphorylation at Ser-552 by AMPK promotes stabilizion of the protein, enhancing TCF/LEF-mediated transcription (By similarity). Phosphorylation by GSK3B requires prior phosphorylation of Ser-45 by another kinase. Phosphorylation proceeds then from Thr-41 to Ser-37 and Ser-33. Phosphorylated by NEK2. EGF stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation. Phosphorylation on Tyr-654 decreases CDH1 binding and enhances TBP binding. Phosphorylated on Ser-33 and Ser-37 by HIPK2 and GSK3B, this phosphorylation triggers proteasomal degradation. Phosphorylation on Ser-191 and Ser-246 by CDK5. Phosphorylation by CDK2 regulates insulin internalization. Phosphorylation by PTK6 at Tyr-64, Tyr-142, Tyr-331 and/or Tyr-333 with the predominant site at Tyr-64 is not essential for inhibition of transcriptional activity.
Ubiquitinated by the SCF(BTRC) E3 ligase complex when phosphorylated by GSK3B, leading to its degradation. Ubiquitinated by a E3 ubiquitin ligase complex containing UBE2D1, SIAH1, CACYBP/SIP, SKP1, APC and TBL1X, leading to its subsequent proteasomal degradation (By similarity).
S-nitrosylation at Cys-619 within adherens junctions promotes VEGF-induced, NO-dependent endothelial cell permeability by disrupting interaction with E-cadherin, thus mediating disassembly adherens junctions.
O-glycosylation at Ser-23 decreases nuclear localization and transcriptional activity, and increases localization to the plasma membrane and interaction with E-cadherin CDH1.
Deacetylated at Lys-49 by SIRT1.
Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton. Cell junction>Adherens junction. Cell junction. Cell membrane. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Microtubule organizing center>Centrosome. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Spindle pole. Cell junction>Synapse. Cytoplasm>Cytoskeleton>Cilium basal body.
Note: Colocalized with RAPGEF2 and TJP1 at cell-cell contacts (By similarity). Cytoplasmic when it is unstabilized (high level of phosphorylation) or bound to CDH1. Translocates to the nucleus when it is stabilized (low level of phosphorylation). Interaction with GLIS2 and MUC1 promotes nuclear translocation. Interaction with EMD inhibits nuclear localization. The majority of beta-catenin is localized to the cell membrane. In interphase, colocalizes with CROCC between CEP250 puncta at the proximal end of centrioles, and this localization is dependent on CROCC and CEP250. In mitosis, when NEK2 activity increases, it localizes to centrosomes at spindle poles independent of CROCC. Colocalizes with CDK5 in the cell-cell contacts and plasma membrane of undifferentiated and differentiated neuroblastoma cells. Interaction with FAM53B promotes translocation to the nucleus (PubMed:25183871).
Expressed in several hair follicle cell types: basal and peripheral matrix cells, and cells of the outer and inner root sheaths. Expressed in colon. Present in cortical neurons (at protein level). Expressed in breast cancer tissues (at protein level).
Belongs to the beta-catenin family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Adherens junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Wnt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Hippo signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Endometrial cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Prostate cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Thyroid cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Basal cell carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Hepatocellular carcinoma. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Gastric cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC).
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Leukocyte transendothelial migration. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Melanogenesis.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone signaling pathway. (View pathway)
References
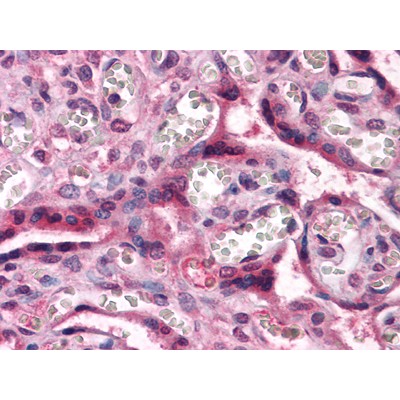
Application: IHC Species: zebrafish Sample: mesencephalon and medulla oblongata
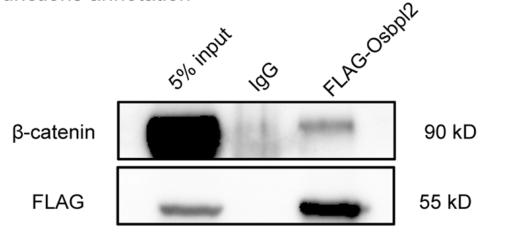
Application: WB Species: Mice Sample: WT cells and KO cells
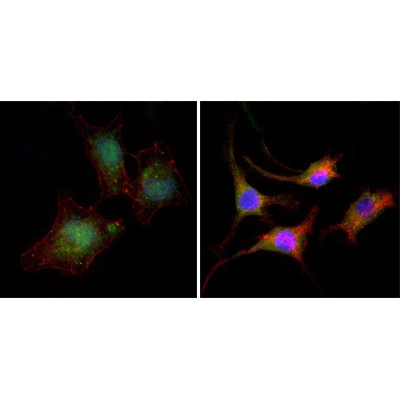
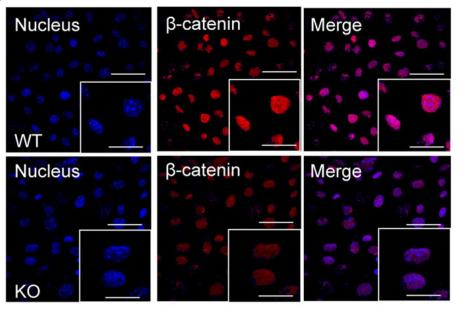
Application: IF/ICC Species: Mice Sample: WT cells and KO cells
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.