AFfirm™ GRP78 Mouse monoclonal Antibody - #BF8024
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Fold/Unfold
78 kDa glucose regulated protein; 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein; AL022860; AU019543; BIP; D2Wsu141e; D2Wsu17e; Endoplasmic reticulum lumenal Ca(2+)-binding protein grp78; Endoplasmic reticulum lumenal Ca2+ binding protein grp78; Epididymis secretory sperm binding protein Li 89n; FLJ26106; Glucose Regulated Protein 78kDa; GRP 78; GRP-78; GRP78; GRP78_HUMAN; Heat shock 70 kDa protein 5; Heat Shock 70kDa Protein 5; Heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 5; HEL S 89n; Hsce70; HSPA 5; HSPA5; Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Binding Protein; Immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein; mBiP; MIF2; Sez7;
Immunogens
A synthesized peptide derived from human GRP78, corresponding to a region within C-terminal amino acids.
- P11021 BIP_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MKLSLVAAMLLLLSAARAEEEDKKEDVGTVVGIDLGTTYSCVGVFKNGRVEIIANDQGNRITPSYVAFTPEGERLIGDAAKNQLTSNPENTVFDAKRLIGRTWNDPSVQQDIKFLPFKVVEKKTKPYIQVDIGGGQTKTFAPEEISAMVLTKMKETAEAYLGKKVTHAVVTVPAYFNDAQRQATKDAGTIAGLNVMRIINEPTAAAIAYGLDKREGEKNILVFDLGGGTFDVSLLTIDNGVFEVVATNGDTHLGGEDFDQRVMEHFIKLYKKKTGKDVRKDNRAVQKLRREVEKAKRALSSQHQARIEIESFYEGEDFSETLTRAKFEELNMDLFRSTMKPVQKVLEDSDLKKSDIDEIVLVGGSTRIPKIQQLVKEFFNGKEPSRGINPDEAVAYGAAVQAGVLSGDQDTGDLVLLDVCPLTLGIETVGGVMTKLIPRNTVVPTKKSQIFSTASDNQPTVTIKVYEGERPLTKDNHLLGTFDLTGIPPAPRGVPQIEVTFEIDVNGILRVTAEDKGTGNKNKITITNDQNRLTPEEIERMVNDAEKFAEEDKKLKERIDTRNELESYAYSLKNQIGDKEKLGGKLSSEDKETMEKAVEEKIEWLESHQDADIEDFKAKKKELEEIVQPIISKLYGSAGPPPTGEEDTAEKDEL
Research Backgrounds
Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone that plays a key role in protein folding and quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Involved in the correct folding of proteins and degradation of misfolded proteins via its interaction with DNAJC10/ERdj5, probably to facilitate the release of DNAJC10/ERdj5 from its substrate (By similarity). Acts as a key repressor of the ERN1/IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response (UPR). In the unstressed endoplasmic reticulum, recruited by DNAJB9/ERdj4 to the luminal region of ERN1/IRE1, leading to disrupt the dimerization of ERN1/IRE1, thereby inactivating ERN1/IRE1 (By similarity). Accumulation of misfolded protein in the endoplasmic reticulum causes release of HSPA5/BiP from ERN1/IRE1, allowing homodimerization and subsequent activation of ERN1/IRE1 (By similarity). Plays an auxiliary role in post-translational transport of small presecretory proteins across endoplasmic reticulum (ER). May function as an allosteric modulator for SEC61 channel-forming translocon complex, likely cooperating with SEC62 to enable the productive insertion of these precursors into SEC61 channel. Appears to specifically regulate translocation of precursors having inhibitory residues in their mature region that weaken channel gating.
AMPylated by FICD. In unstressed cells, AMPylation at Thr-518 by FICD inactivates the chaperome activity: AMPylated form is locked in a relatively inert state and only weakly stimulated by J domain-containing proteins (By similarity). In response to endoplasmic reticulum stress, de-AMPylation by the same protein, FICD, restores the chaperone activity (By similarity).
Endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Melanosome. Cytoplasm.
Note: Identified by mass spectrometry in melanosome fractions from stage I to stage IV.
The interdomain linker regulates the chaperone activity by mediating the formation of homooligomers. Homooligomers are formed by engagement of the interdomain linker of one HSPA5/BiP molecule as a typical substrate of an adjacent HSPA5/BiP molecule. HSPA5/BiP oligomerization inactivates participating HSPA5/BiP protomers. HSPA5/BiP oligomers probably act as reservoirs to store HSPA5/BiP molecules when they are not needed by the cell. When the levels of unfolded proteins rise, cells can rapidly break up these oligomers to make active monomers.
Belongs to the heat shock protein 70 family.
Research Fields
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein export.
· Genetic Information Processing > Folding, sorting and degradation > Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Neurodegenerative diseases > Prion diseases.
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Antigen processing and presentation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Thyroid hormone synthesis.
References
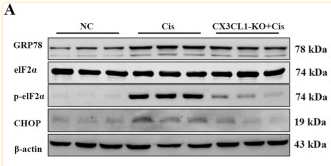
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample: kidney tissues
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.