ITGB1 Antibody - #BF0336
Product Info
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
*Tips:
WB: For western blot detection of denatured protein samples. IHC: For immunohistochemical detection of paraffin sections (IHC-p) or frozen sections (IHC-f) of tissue samples. IF/ICC: For immunofluorescence detection of cell samples. ELISA(peptide): For ELISA detection of antigenic peptide.
Cite Format: Affinity Biosciences Cat# BF0336, RRID:AB_2833991.
Fold/Unfold
beta1 integrin; CD29; Fibronectin receptor subunit beta; FNRB; Glycoprotein IIa; GP IIa; GPIIA; Integrin beta-1; Integrin subunit beta 1; integrin VLA-4 beta subunit; Integrin, beta 1 (fibronectin receptor, beta polypeptide, antigen CD29 includes MDF2, MSK12); ITB1_HUMAN; ITGB1; MDF2; MSK12; OTTHUMP00000019420; Very late activation protein, beta polypeptide; VLA BETA; VLA-4 subunit beta; VLA-BETA; VLAB; VLAbeta;
Immunogens
Purified recombinant fragment of human ITGB1 expressed in E. Coli.
Isoform 1 is widely expressed, other isoforms are generally coexpressed with a more restricted distribution. Isoform 2 is expressed in skin, liver, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, placenta, umbilical vein endothelial cells, neuroblastoma cells, lymphoma cells, hepatoma cells and astrocytoma cells. Isoform 3 and isoform 4 are expressed in muscle, kidney, liver, placenta, cervical epithelium, umbilical vein endothelial cells, fibroblast cells, embryonal kidney cells, platelets and several blood cell lines. Isoform 4, rather than isoform 3, is selectively expressed in peripheral T-cells. Isoform 3 is expressed in non-proliferating and differentiated prostate gland epithelial cells and in platelets, on the surface of erythroleukemia cells and in various hematopoietic cell lines. Isoform 5 is expressed specifically in striated muscle (skeletal and cardiac muscle).
- P05556 ITB1_HUMAN:
- Protein BLAST With
- NCBI/
- ExPASy/
- Uniprot
MNLQPIFWIGLISSVCCVFAQTDENRCLKANAKSCGECIQAGPNCGWCTNSTFLQEGMPTSARCDDLEALKKKGCPPDDIENPRGSKDIKKNKNVTNRSKGTAEKLKPEDITQIQPQQLVLRLRSGEPQTFTLKFKRAEDYPIDLYYLMDLSYSMKDDLENVKSLGTDLMNEMRRITSDFRIGFGSFVEKTVMPYISTTPAKLRNPCTSEQNCTSPFSYKNVLSLTNKGEVFNELVGKQRISGNLDSPEGGFDAIMQVAVCGSLIGWRNVTRLLVFSTDAGFHFAGDGKLGGIVLPNDGQCHLENNMYTMSHYYDYPSIAHLVQKLSENNIQTIFAVTEEFQPVYKELKNLIPKSAVGTLSANSSNVIQLIIDAYNSLSSEVILENGKLSEGVTISYKSYCKNGVNGTGENGRKCSNISIGDEVQFEISITSNKCPKKDSDSFKIRPLGFTEEVEVILQYICECECQSEGIPESPKCHEGNGTFECGACRCNEGRVGRHCECSTDEVNSEDMDAYCRKENSSEICSNNGECVCGQCVCRKRDNTNEIYSGKFCECDNFNCDRSNGLICGGNGVCKCRVCECNPNYTGSACDCSLDTSTCEASNGQICNGRGICECGVCKCTDPKFQGQTCEMCQTCLGVCAEHKECVQCRAFNKGEKKDTCTQECSYFNITKVESRDKLPQPVQPDPVSHCKEKDVDDCWFYFTYSVNGNNEVMVHVVENPECPTGPDIIPIVAGVVAGIVLIGLALLLIWKLLMIIHDRREFAKFEKEKMNAKWDTGENPIYKSAVTTVVNPKYEGK
PTMs - P05556 As Substrate
| Site | PTM Type | Enzyme | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| K71 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K100 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K105 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K107 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T130 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K134 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K134 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y141 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y147 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K163 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S186 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K190 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S197 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K202 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| N212 | N-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| K220 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S224 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| T226 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K228 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K238 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S263 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| N269 | N-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| T271 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K289 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K346 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K349 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T394 | O-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| K402 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| N406 | N-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| N481 | N-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| K540 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S549 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K551 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K575 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| N669 | N-Glycosylation | Uniprot | |
| K672 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K678 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K692 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K765 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K768 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| K774 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| T777 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| Y783 | Phosphorylation | P42684 (ABL2) | Uniprot |
| K784 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| S785 | Phosphorylation | P17252 (PRKCA) | Uniprot |
| T788 | Phosphorylation | Q02156 (PRKCE) , Q9UQM7 (CAMK2A) | Uniprot |
| T789 | Phosphorylation | Q9UQM7 (CAMK2A) , Q02156 (PRKCE) | Uniprot |
| K794 | Acetylation | Uniprot | |
| K794 | Sumoylation | Uniprot | |
| K794 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot | |
| Y795 | Phosphorylation | Uniprot | |
| K798 | Ubiquitination | Uniprot |
Research Backgrounds
Integrins alpha-1/beta-1, alpha-2/beta-1, alpha-10/beta-1 and alpha-11/beta-1 are receptors for collagen. Integrins alpha-1/beta-1 and alpha-2/beta-2 recognize the proline-hydroxylated sequence G-F-P-G-E-R in collagen. Integrins alpha-2/beta-1, alpha-3/beta-1, alpha-4/beta-1, alpha-5/beta-1, alpha-8/beta-1, alpha-10/beta-1, alpha-11/beta-1 and alpha-V/beta-1 are receptors for fibronectin. Alpha-4/beta-1 recognizes one or more domains within the alternatively spliced CS-1 and CS-5 regions of fibronectin. Integrin alpha-5/beta-1 is a receptor for fibrinogen. Integrin alpha-1/beta-1, alpha-2/beta-1, alpha-6/beta-1 and alpha-7/beta-1 are receptors for lamimin. Integrin alpha-6/beta-1 (ITGA6:ITGB1) is present in oocytes and is involved in sperm-egg fusion (By similarity). Integrin alpha-4/beta-1 is a receptor for VCAM1. It recognizes the sequence Q-I-D-S in VCAM1. Integrin alpha-9/beta-1 is a receptor for VCAM1, cytotactin and osteopontin. It recognizes the sequence A-E-I-D-G-I-E-L in cytotactin. Integrin alpha-3/beta-1 is a receptor for epiligrin, thrombospondin and CSPG4. Alpha-3/beta-1 may mediate with LGALS3 the stimulation by CSPG4 of endothelial cells migration. Integrin alpha-V/beta-1 is a receptor for vitronectin. Beta-1 integrins recognize the sequence R-G-D in a wide array of ligands. Isoform 2 interferes with isoform 1 resulting in a dominant negative effect on cell adhesion and migration (in vitro). When associated with alpha-7/beta-1 integrin, regulates cell adhesion and laminin matrix deposition. Involved in promoting endothelial cell motility and angiogenesis. Involved in osteoblast compaction through the fibronectin fibrillogenesis cell-mediated matrix assembly process and the formation of mineralized bone nodules. May be involved in up-regulation of the activity of kinases such as PKC via binding to KRT1. Together with KRT1 and RACK1, serves as a platform for SRC activation or inactivation. Plays a mechanistic adhesive role during telophase, required for the successful completion of cytokinesis. Integrin alpha-3/beta-1 provides a docking site for FAP (seprase) at invadopodia plasma membranes in a collagen-dependent manner and hence may participate in the adhesion, formation of invadopodia and matrix degradation processes, promoting cell invasion. ITGA4:ITGB1 binds to fractalkine (CX3CL1) and may act as its coreceptor in CX3CR1-dependent fractalkine signaling. ITGA4:ITGB1 and ITGA5:ITGB1 bind to PLA2G2A via a site (site 2) which is distinct from the classical ligand-binding site (site 1) and this induces integrin conformational changes and enhanced ligand binding to site 1. ITGA5:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and mediates R-G-D-dependent cell adhesion to FBN1. ITGA5:ITGB1 is a receptor for IL1B and binding is essential for IL1B signaling. ITGA5:ITGB3 is a receptor for soluble CD40LG and is required for CD40/CD40LG signaling.
Isoform 5 displaces isoform 1 in striated muscles.
(Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA2:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human echoviruses 1 and 8.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Cytomegalovirus/HHV-5.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Epstein-Barr virus/HHV-4.
(Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA5:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human parvovirus B19.
(Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA2:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human rotavirus.
(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Mammalian reovirus.
(Microbial infection) In case of HIV-1 infection, integrin ITGA5:ITGB1 binding to extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions.
The cysteine residues are involved in intrachain disulfide bonds.
Cell membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection>Invadopodium membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection>Ruffle membrane>Single-pass type I membrane protein. Recycling endosome. Melanosome. Cleavage furrow. Cell projection>Lamellipodium. Cell projection>Ruffle. Cell junction>Focal adhesion. Cell surface.
Note: Isoform 2 does not localize to focal adhesions. Highly enriched in stage I melanosomes. Located on plasma membrane of neuroblastoma NMB7 cells. In a lung cancer cell line, in prometaphase and metaphase, localizes diffusely at the membrane and in a few intracellular vesicles. In early telophase, detected mainly on the matrix-facing side of the cells. By mid-telophase, concentrated to the ingressing cleavage furrow, mainly to the basal side of the furrow. In late telophase, concentrated to the extending protrusions formed at the opposite ends of the spreading daughter cells, in vesicles at the base of the lamellipodia formed by the separating daughter cells. Colocalizes with ITGB1BP1 and metastatic suppressor protein NME2 at the edge or peripheral ruffles and lamellipodia during the early stages of cell spreading on fibronectin or collagen. Translocates from peripheral focal adhesions sites to fibrillar adhesions in a ITGB1BP1-dependent manner. Enriched preferentially at invadopodia, cell membrane protrusions that correspond to sites of cell invasion, in a collagen-dependent manner. Localized at plasma and ruffle membranes in a collagen-independent manner.
Cell membrane>Sarcolemma. Cell junction.
Note: In cardiac muscle, isoform 5 is found in costameres and intercalated disks.
Isoform 1 is widely expressed, other isoforms are generally coexpressed with a more restricted distribution. Isoform 2 is expressed in skin, liver, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, placenta, umbilical vein endothelial cells, neuroblastoma cells, lymphoma cells, hepatoma cells and astrocytoma cells. Isoform 3 and isoform 4 are expressed in muscle, kidney, liver, placenta, cervical epithelium, umbilical vein endothelial cells, fibroblast cells, embryonal kidney cells, platelets and several blood cell lines. Isoform 4, rather than isoform 3, is selectively expressed in peripheral T-cells. Isoform 3 is expressed in non-proliferating and differentiated prostate gland epithelial cells and in platelets, on the surface of erythroleukemia cells and in various hematopoietic cell lines. Isoform 5 is expressed specifically in striated muscle (skeletal and cardiac muscle).
Heterodimer of an alpha and a beta subunit. Beta-1 associates with either alpha-1, alpha-2, alpha-3, alpha-4, alpha-5, alpha-6, alpha-7, alpha-8, alpha-9, alpha-10, alpha-11 or alpha-V. ITGA6:ITGB1 is found in a complex with CD9; interaction takes place in oocytes and is involved in sperm-egg fusion (By similarity). Interacts with seprase FAP (seprase); the interaction occurs at the cell surface of invadopodia membrane in a collagen-dependent manner. Binds LGALS3BP and NMRK2, when associated with alpha-7, but not with alpha-5. Interacts with FGR and HCK. Interacts (via the cytoplasmic region) with RAB25 (via the hypervariable C-terminal region). Interacts with RAB21. Interacts with KRT1 in the presence of RACK1 and SRC. Interacts with JAML; integrin alpha-4/beta-1 may regulate leukocyte to endothelial cells adhesion by controlling JAML homodimerization. Interacts with FLNA, FLNB and RANBP9. Isoform 5 interacts with ACE2. Isoform 1 interacts with the C-terminal region of FLNC. Interacts with MYO10. Interacts with DAB2. Interacts with FERMT2; the interaction is inhibited in presence of ITGB1BP1. Interacts with ITGB1BP1 (via C-terminal region); the interaction is a prerequisite for focal adhesion disassembly. Interacts with TLN1; the interaction is prevented by competitive binding of ITGB1BP1. Interacts with ACAP1; required for ITGB1 recycling. Interacts with ASAP3. Isoform 5 interacts with alpha-7A and alpha-7B in adult skeletal muscle. Isoform 5 interacts with alpha-7B in cardiomyocytes of adult heart. Interacts with EMP2; the interaction may be direct or indirect and ITGB1 has a heterodimer form (By similarity). ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with CCN3. ITGA4:ITGB1 is found in a ternary complex with CX3CR1 and CX3CL1. ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with FBN1. ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with IL1B. Interacts with MDK. ITGA4:ITGB1 interacts with MDK; this interaction mediates MDK-induced osteoblast cells migration through PXN phosphorylation. ITGA6:ITGB1 interacts with MDK; this interaction mediates MDK-induced neurite-outgrowth.
(Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA2:ITGB1 interacts with human echoviruses 1 and 8 capsid proteins.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with human cytomegalovirus/HHV-5 envelope glycoprotein B/gB.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with Epstein-Barr virus/HHV-4 gB protein.
(Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with human parvovirus B19 capsid protein.
(Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA2:ITGB1 interacts with human rotavirus VP4 protein.
(Microbial infection) Interacts with mammalian reovirus capsid proteins.
(Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with HIV-1 Tat.
Belongs to the integrin beta chain family.
Research Fields
· Cellular Processes > Transport and catabolism > Phagosome. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Focal adhesion. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cellular community - eukaryotes > Tight junction. (View pathway)
· Cellular Processes > Cell motility > Regulation of actin cytoskeleton. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > Rap1 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > ECM-receptor interaction. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signaling molecules and interaction > Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Shigellosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pertussis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Toxoplasmosis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Human papillomavirus infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Proteoglycans in cancer.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Small cell lung cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC).
· Human Diseases > Cardiovascular diseases > Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).
· Organismal Systems > Development > Axon guidance. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Platelet activation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Leukocyte transendothelial migration. (View pathway)
References
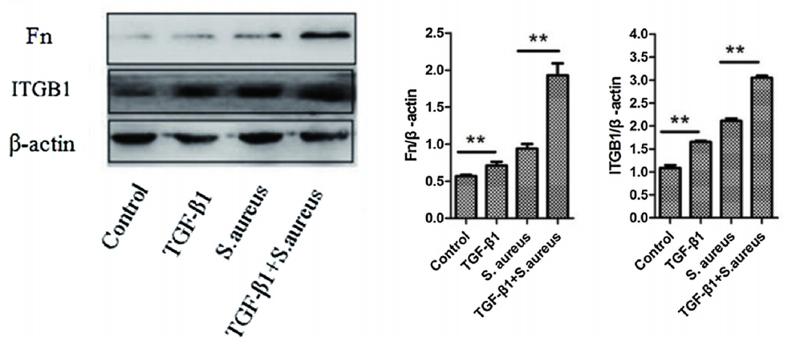
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: BMECs
Application: IF/ICC Species: mouse Sample: BMECs
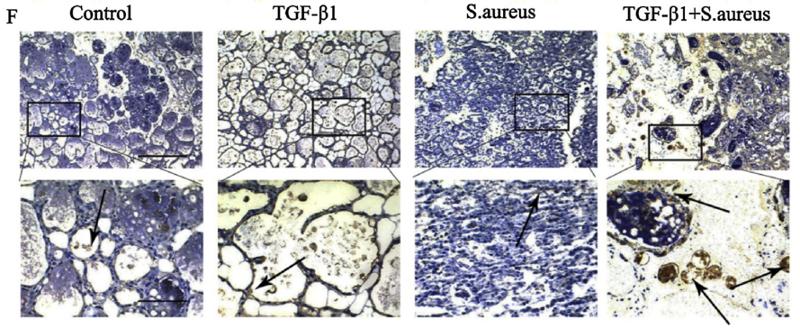
Application: IHC Species: mouse Sample: acini and the surrounding connective tissue
Restrictive clause
Affinity Biosciences tests all products strictly. Citations are provided as a resource for additional applications that have not been validated by Affinity Biosciences. Please choose the appropriate format for each application and consult Materials and Methods sections for additional details about the use of any product in these publications.
For Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Not for resale. Not for distribution without written consent. Affinity Biosciences will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences Logo and all other trademarks are the property of Affinity Biosciences LTD.